서
론
프로바이오틱스(probiotics)는 숙주의 장내 균총의 능력 을 개선시킴으로 숙주의 건강에 유익한 효과를 주는 살 아 있는 미생물 (젖산균과 다른 박테리아, 또는 건조된 상태 또는 발효제품 내의 효모)이다(Klaenhammer 2000). 최근 사용되어지는 프로바이오틱스 미생물은 Lactobacillus, Bifidobacterium, Lactococcus와 같은 젖산균이 많이 사용 되어지고 있으며 Leuconostoc, Pediococcus, Bacillus, Propionibacterium 그리고 효모 등은 대부분 동물에 사용 되어 진다 (Isolauri et al. 2004). 이러한 젖산균 (lactic acid bacteria)은 gram-positive bacteria로 건강한 사람의 장내 미생물 생태계의 일부로 존재하며, 장내 상피세포에 정Journal of Radiation Industry 5 (2) : 175~178 (2011)
─ ─ 175 ──
시판 유제품 중에서 분리된 젖산균의 감마선 조사에 의한
생존 효과
이지혜
1,2∙김재경
1∙조으리
1∙성낙윤
1∙최종일
1∙김재훈
1송범석
1∙박종흠
1∙육홍선
2∙이주운
1,*
1한국원자력연구원 정읍방사선과학연구소, 2충남대학교 식품영양학과The Effect of Gamma Irradiation on the Survival of
Lactic Acid Isolated from Commercial Daily Product
Ji-hye Lee
1,2, Jae-Kyung Kim
1, Eu-Ri Jo
1, Nak-Yun Sung
1, Jong-Il Choi
1, Jae-Hun Kim
1,
Beom-Seok Song
1, Jong-Heum Park
1, Hong-Sun Yook
2and Ju-Woon Lee
1,*
1Advanced Radiation Technology Institute, Korea Atomic Energy Reserch Institute,Jeongeup 580-185, Korea
2Department of Food Science & Human Nutrition, Chungnam National University, Daejeon 305-764, Korea
Abstract-- This study was conducted with effect of lactic acid bacteria by gamma irradiation.
Lactic acid bacteria were exposed to irradiation with a single absorbed dose of 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, and 10 kGy. Possible lactic acid bacteria, including Lactobacillus paracasei KCTC 13169, Lactobacillus casei KCTC 3109, Lactobacillus acidophilus KCTC 3140, Lactobacillus plantarum subsp plantarum KCTC 3103, Lactobacillus debruekii subsp bulgaricus KCTC 3635, Streptococcus thermophilus KCTC 3658 were selected. The radiation sesitivities of lactic acid bacteria were expressed as D10
values. The D10values of Lactobacillus paracasei, Lactobacillus casei, Streptococcus thermophilus,
Lactobacillus acidophilus, Lactobacillus plantarum, and Lactobacillus debruekii were calculated as 0.42, 0.51, 0.47, 0.90, 0.44, and 0.61 kGy, respectively. Results suggest that L. acidiphilus has the highly resistant to gamma irradiation.
Key words : Gamma irradiation, Lactic acid bacteria, D10value
* Corresponding author: Ju-Woon Lee, Tel. +82-63-570-3204, Fax. +82-63-570-3207, E-mail. sjwlee@kaeri.re.kr
착하여 정상적인 장관 내 미생물 균총 유지, 유당 불내 증의 완화, 혈중 콜레스테롤의 감소, 항암작용, 면역 조절 작용, 식품의 영양학적 가치의 증진 등의 유익한 효과를 나타내는 것으로 알려져 있다 (Kim 2009). 현재 방사선 식품 조사는 병원성 미생물을 제어하거 나 음식물의 부패 미생물을 감소시키기 위하여 널리 사 용되고 있다 (Fielding 1996). 식품의 방사선 적용 기술은 현재 어떤 위생화 처리방법보다 효과적이고 영양학적, 독성학적, 유전학적 및 미생물학적으로 안전성있는 기술 로 평가되고 있으므로 국제적으로 식품에 대한 방사선 조사 기술은 산업적으로 가속화 될 전망이다 (Maltila-Standholm and Skytta 1991; Son and Chyun 2001; Kim et
al. 2005; Rahman and Kang 2009). 이러한 이온화 방사선 이 미생물에 치명적인 영향을 미친다는 것이 알려졌지 만, 미생물은 방사선에 매우 다양하게 저항한다고 밝혀 졌다 (Minck 1896). 가장 일반적으로 음식물의 부패균 (e.g., pseudomonas sp.)을 포함하는 gram-negative bacteria 는 gram-positive bacteria (e.g., lactic acid bacteria and
micrococci)보다 더 방사선 조사에 민감하다고 보고되고 있다(Ingram 1975). 현재 젖산균에 방사선 조사를 적용한 연구로 시판 플레인 요구르트에 감마선 조사 (1~5 kGy) 하여 감마선 조사 기술의 요거트의 품질 변화를 최소화 하면서 미생물학적 안전성을 확보하고, 발효유 제품을 제조하는 기술로 적용하는데 효과적이라고 보고하였다 (Kim et al. 2008). 또한, 감마선 조사한 요거트를 각각 다 른 저장 온도에서 품질 평가를 한 연구에서는 온도마다 플레인 요거트의 화학적, 관능적에 유의적인 차이가 없 었다고 보고하고 있다 (Ham et al. 2009). 따라서 본 연구는 현재 시판되고 있는 유제품에 사용 되는 젖산균을 이용하여 방사선에 저항성이 우수한 젖산 균을 선별하기 위한 기초자료를 얻기 위하여 방사선 감 수성을 평가하였다.
재료 및 방법
1. Lactobacillus분리 및 동정
시중에 유통되고 있는 발효유 제품의 유산균에서 Lactobacillus 균주를 한국생물공학연구원 생물자원센터 에서 구입하여 실시하였다. 2.사용 균주 및 시약
본 실험에 사용한 Lactobacillus paracasei KCTC 13169, Lactobacillus casei KCTC 3109, LactobacillusacidophilusKCTC 3140, Lactobacillus plantarum subsp plantarum KCTC 3103, Lactobacillus debruekii subsp bulgaricus KCTC 3635, Streptococcus thermophilus KCTC 3658은 한 국생물공학연구원 생물자원센터(KCTC Korean Collection for Type Cultures, Daejeon, Korea)에서 분양 받아 실험을 실시하였다. 본 실험에 사용된 배지는 MRS (Lactobacilli, Difco, Detroit, MI, USA) broth, Streptococcus thermophilus 는 Corynebacterium Agar (Yeast extract 5.0 g, Glucose 5.0 g, NaCl 5.0 g, Agar 15.0 g, Distilled water 1,000 ml, Casein peptone, trypric digest 10 g)에 젖산균을 접종하여 37�C, 72 hr 배양하여 9 logCFU g-1까지 자라게 한 후 본 실험
에 사용하였다.
3.
감마선 조사
감마선 조사는 한국원자력연구원 방사선과학연구소 (Jeongeup, Korea)내 선원 11.1 PBq, Co-60 감마선 조사시 설 (point source AECL, IR-79, MDS Nordion International Co., Ltd., Canada)을 이용하여 선량률은 각각 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8 및 10 kGy의 흡수선량을 얻도록 하였다. 흡수선 량의 확인은 alanine dosimeter (5 mm, Bruker Instruments, germant)를 사용하였으며, 흡수선량의 오차는 ±5% 이내 였다. 시료는 실험 시작 전까지 4�C에 보관하여 사용하 였다. 4.
젖산균 배양 및 균수 측정
감마선 조사한 5종의 젖산균의 미생물 평가를 측정하 기 위해 시료 9 logCFU g-1(±1)자란 균 배양액 0.1 ml에 멸균된 식염수 (0.85%, NaCl) 0.9 ml를 첨가한 다음 혼합 하여 10진 희석법으로 희석한 희석액을 MRS agar (Difico, Laboratories, USA)에 plating 하였다. 미생물 증식은 표준 한천배양방법으로 각각 37�C, 72 hr incubator에 배양하였다. 젖산균수 측정은 MRS agar에서 plate count 방법으로 검사하여 30~300개의 집락을 형성한 배지만 계수하여 시료 logCFU g-1로 나타낸 후 회귀분석을 이용하였다. 또 이를 90%의 미생물 사멸 선량인 방사선량 D10값은 아래의 log 생균수 값의 회귀식에 의하여 산출하였다. 5.통계처리
동일 실험을 3회 반복하여 얻어진 결과는 Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS, 10.0)를 이용하여 One Way ANOVA test로 분석하였으며, 시료간의 유의성은 Duncan’s multiple range test법으로 p⁄0.05 수준에서 평 가하였다.이지혜∙김재경∙조으리∙성낙윤∙최종일∙김재훈∙송범석∙박종흠∙육홍선∙이주운 176
결과 및 논의
1.
감마선 조사에 의한 젖산균의 생존 평가
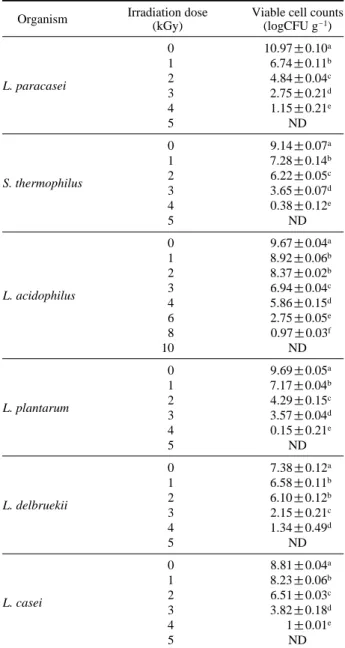
감마선 조사 (0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8 및 10 kGy)에 의한 젖 산균의 생존결과를 Table 1에 나타내었다. 먼저 72시간 배양한 비조사군의 유산균의 동정 결과 L. paracasei는 10.97 logCFU g-1, L. casei는 8.81 logCFU g-1, S. thermo-philus는 9.14 logCFU g-1, L. acidophilus는 9.67 logCFU g-1, L. plantarum는 9.69 logCFU g-1 및 L. debruekii는
7.38 logCFU g-1이 검출되었다. 6종의 젖산균 모두 조사 선량이 증가함에 따라 생존율이 유의적으로 감소한 것 을 확인할 수 있었다. L. acidophilus를 제외한 유산균들 에서 5 kGy를 조사하였을 때 모두 멸균이 되는데 반해, L. acidophilus는 10 kGy에서 조사 후 멸균되었다. 뿐만 아니라, L. acidophilus를 제외한 모든 젖산균에서 조사 선량마다 유의적인 차이로 생균수가 감소하였는데, L.
acidophilus는 1 kGy와 2 kGy 사이에서 유일하게 유의적 인 차이를 보이지 않았다. 이러한 결과는 L. acidophilus 가 방사선에 의해 쉽게 사멸되지 않는다는 보고와 일치 하였다 (Morichi 1997). 결과적으로 6종의 Lactobacillus spp. 중에서 L. acidophilus가 가장 감마선에 대한 저항이 우수한 것을 알 수 있었다. 2.
감마선 조사에 의한 젖산균의 감수성 평가
젖산균 6종의 방사선 감수성을 평가하여 계산한 D10 값을 Table 2에 제시하였다. 각 젖산균의 감마선에 의한 D10값을 측정한 결과 L. paracasei는 0.42 kGy, L. casei 는 0.51 kGy, S. thermophilus는 0.47 kGy, L. acidophilus는 0.90 kGy, L. plantarum는 0.44 kGy 및 L. delbruekii 0.61kGy로 각각 나타났다. L. acidophilus가 가장 방사선에
대한 저항성이 높은 것을 관찰하였고 그 다음으로는 L.
debruekii, L. casei, S. thermophilus, L. plantarum, L. para-casei 순으로 나타났다. Hastings (1986) 등은 조사된 meat
으로부터 Lactobacilli를 분리 한 균주들의 D10값을 얻
은 결과 L. plantarum과 L. casei 모두 0.47 kGy로 본 실험 결과와 유사한 값을 나타내었다. 반면에 Byun (2009)은 Lactobacillus spp.의 방사선 감수성이 0.23~0.38 kGy로 보고하고 있어 Lactobacillus 종마다 서로 다른 방사선감 수성에 대한 차이를 보이는 것으로 사료된다. 이것은 방 사선에 대한 미생물의 감수성은 방사선 조사 시 온도, 산소, 수분, 미생물의 성장단계 및 배지 조성 등에 영향 을 받아서 동일한 미생물이라고 할지라도 그 환경에 따 라 미생물 감수성이 변하게 되므로(Molins 2001) 이 같은 차이가 나타나는 것이라고 사료된다. 시판 유제품 중에서 분리된 젖산균의 감마선 조사에 의한 생존 효과 177
Table 1. Radiation sensitivity of lactic acid bacteria
Organism Irradiation dose Viable cell counts (kGy) (logCFU g-1) 0 10.97±0.10a 1 6.74±0.11b L. paracasei 2 4.84±0.04 c 3 2.75±0.21d 4 1.15±0.21e 5 ND 0 9.14±0.07a 1 7.28±0.14b S. thermophilus 2 6.22±0.05 c 3 3.65±0.07d 4 0.38±0.12e 5 ND 0 9.67±0.04a 1 8.92±0.06b 2 8.37±0.02b L. acidophilus 3 6.94±0.04 c 4 5.86±0.15d 6 2.75±0.05e 8 0.97±0.03f 10 ND 0 9.69±0.05a 1 7.17±0.04b L. plantarum 2 4.29±0.15 c 3 3.57±0.04d 4 0.15±0.21e 5 ND 0 7.38±0.12a 1 6.58±0.11b L. delbruekii 2 6.10±0.12 b 3 2.15±0.21c 4 1.34±0.49d 5 ND 0 8.81±0.04a 1 8.23±0.06b L. casei 2 6.51±0.03 c 3 3.82±0.18d 4 1±0.01e 5 ND
a-fMean±standard deviation within a column with different superscripts and
significantly different (p⁄0.05).
Table 2. D10value of lactic acid bacteria by gamma-irradiation
Organism D10(kGy) R2 L. paracasei 0.42 0.96 S. thermophilus 0.47 0.96 L. acidophilus 0.90 0.98 L. plantarum 0.44 0.97 L. delbruekii 0.61 0.89 L. casei 0.51 0.96
결
론
현재 시중에 판매되고 있는 유산균 음료에 사용되는 대표적인 젖산균 6종의 방사선에 대한 감수성을 평가하 고자 다양한 선량의 감마선을 조사하였다. 실험결과 6종 의 젖산균 모두 서로 다른 방사선 저항성을 보였으며 그 중 Lactobacillus acidophilus의 D10값이 0.90으로 방 사선 저항성이 가장 우수 한 것을 확인하였다. 본 연구결 과를 토대로 하여 L. acidophilus는 방사선 저항성이 우 수한 유가공 제품에 활용할 수 있을 것으로 판단된다.참 고 문 헌
Byun MW. 2009. Current status and prospect of radiation tech-nology for the safety and security of food. J. Korea Radiat.
Ind. 3(3):145-160.
Fielding LM, Cook PE and Grandison AS. 1996. The effect of electron beam irradiation, combined with acetic acid, on the survival and recovery of Escherichia coli and Lactobacillus curvatus. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 35(3):259-265.
Ham JS, Jeong SG, Lee SG, Han GS, Jang A, Yoo YM, Chae HS, Kim DH, Kim HJ, Lee WK and Jo C. 2009. Quality of irradiated plain yogurt during storage at different tempera-tures. Asian-Australasian J. of Anim. Sci. 22(2):289-295. Hastings JW, Holzapfel WH and Niemand JG. 1986. Radiation
resistance of lactobacilli isolated from radurized meat rela-tive to growth and environment. Appl. Environ. Microb. 52(4):898-901.
Ingram M. 1975. Microbiology of foods pasteurized by ionising radiation. Technical Report Series. Report IFIP-R33. Inter-national Project in the Field of Food Irradiation. Institut Fur strahlentechnologie, Karlstuke, Fed. Republic of Germany. Isolauri E, Salminen S and Ouwehand AC. 2004.
Microbial-gut-interactions in health and disease probiotics. Best Pract.
Res. Clin Gastroenterol. 18(2):299-313.
Kim CH. 2009. Immunomodulatory effects of Lactic acid bac-teria and bioactive peptides derived from milk. Korean J.
Dairy Sci. Technol. 27(1):37-43.
Kim HJ, Song HP, Ham JS, Lee JW, Kim KH and Jo CH. 2008. Effect of gamma irradiation on the overall quality of a com-mercial plain-type yogurt products. Korean J. Food Sci.
Ani. Resour. 28(5):574-579.
Kim JH, Lim SY, Song HP, Kim BK, Chung JW, Yoon HJ, Byun MW and Kim DH. 2005. Microbiological contamina-tion level and radiacontamina-tion sterilizacontamina-tion in disposable kitchen utensil. Korean J. Food Preserv. 12(4):317-322.
Klaenhammer TR. 2000. Probiotic bacteria: today and tomorrow.
J. Nutr. 130(2):415-416.
Matila-Standholm T and Skytta E. 1991. The effect of spoilage flora on the growth of food pathogens in minced meat stored at chilled temperature. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 24(1):116-120.
Minck F. 1896. Zur Frage der Wirksamkeit der Rontgen-strah-lung auf Bakterien, Sowie die Moglichkeit ihrer eventuellen.
Anwendung. Muench. Med. Wochenschr. 5:101.
Molins RA. 2001. Food irradiation: principles and applications. pp. 131-191. John Wiley & Sons Inc., New York. Morichi T. 1997. Characteristic and utilization of lactic acid
bacteria; progress in recent researches. Milk Sci. 46(3):1-20. Rahman A and Kang SC. 2009. In vitro control of foodborne and food spoilage bacteria by essential oil and ethanol extracts of Lonicera japonica Thunb. Food Chem. 116(3): 670-675.
Son JH and Chyun JH. 2001. Comparative analysis of satisfac-tion level on hospital foods in elderly and middle aged patients. Korean J. Dietary Culture 16(5):442-450.
Manuscript Received: May 16, 2011 Revision Accepted: May 27, 2011
이지혜∙김재경∙조으리∙성낙윤∙최종일∙김재훈∙송범석∙박종흠∙육홍선∙이주운