DOI : 10.3341/jkos.2009.50.1.51
= 증례보고 =
결절맥락막혈관병증에서 유리체강내 베바시주맙 주입술의 단기 효과
이민호⋅안진환⋅이지은⋅엄부섭 부산대학교 의과대학 안과학교실
목적: 결절맥락막혈관병증(polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy, PCV) 환자에서 유리체강내 bevacizumab (AvastinⓇ)을 주입한 후 단 기간 시력과 망막 및 맥락막의 해부학적 구조에 미치는 변화를 확인하고자 하였다.
대상과 방법: 결절맥락막혈관병증으로 진단받고 유리체강내 AvastinⓇ 주입술을 시행 받은 환자 중 3개월 이상 경과 관찰이 가능했던 환자 13명 13안에 대해 의무기록을 후향적으로 검토하였다. 최대교정시력, 빛간섭단층촬영상의 망막의 두께 변화, 형광안저혈관조영술 과 인도시아닌그린혈관조영술상의 이상혈관 변화 등을 조사하였다.
결과: 최대교정시력의 변화는 주사 전 중간값 LogMAR 0.82에서 1개월 0.78, 3개월 0.73로 측정되었고, 최종 경과관찰 시 3줄 이상 상승한 경우가 2안, 3줄 미만의 시력 변화를 보인 경우가 11안이었다. 중심와 두께는 주사 전 평균 288 µm에서 주사 후 1개월 231 µm (p<0.05), 3개월 196 µm로 감소하였다. 인도시아닌그린혈관조영술에서 맥락막 결절은 4안에서 감소하였으나, 혈관이상은 모든 안에서 호전이 없었다.
결론: 결절맥락막혈관병증에서 유리체강내 AvastinⓇ 주입술은 단기간에 망막색소상피박리와 유출을 감소시켜 황반부종을 호전시키고 시력을 안정화시키는 데 효과적이나 맥락막 결절을 직접 폐쇄시키는 효과는 떨어지는 것으로 보이며, 분지하는 선형의 혈관은 변화를 일으키지 못하였다.
<대한안과학회지 2009:50(1):51-60>
■ 접 수 일: 2008년 6월 13일 ■ 심사통과일: 2008년 10월 21일
■ 통 신 저 자: 엄 부 섭
부산시 서구 아미동 1가10 부산대학교병원 안과
Tel: 051-240-7326, Fax: 051-242-7341 E-mail: bsoum@pusan,ac.krr
* 본 논문은 2008년 부산대학병원 임상연구비지원 논문임.
결절맥락막혈관병증(polypoidal choroidal vasculopthy, PCV)은 안쪽 맥락막 혈관 중 이상혈관망(inner choroidal vascular network of vessels)이 존재하고, 그 끝에 결절형 (polyp-like structures)으로 확장된 혈관류를 가지는 것 이 특징적이다.1,2 일반적으로 맥락막신생혈관에 비해 자연 예후가 좋지만,2,3 만성적, 재발성, 다발성의 출혈, 삼출성, 출혈성 망막색소상피박리 및 망막박리의 변화를 보이며 시 력저하를 보이는 경우가 많다.4,5
PCV는 삼출성 나이관련황반변성(AMD)을 보이는 환자 중 서양에서는 8~13%의 빈도를 보이는 반면,6,7 동양에서 는 상대적으로 유병율이 높아 중국과 일본에서 9.3~24.0%
의 빈도를,8,9 우리나라에서 11~16.5%의 빈도를 보고하였 다.5,10
PCV의 병인은 아직 완전히 밝혀져 있지 않으며, 일부 보 고에서는 나이관련황반변성의 다른 한 변형이라고 보고하 나,11 임상경과와 시력 예후, 치료에 대한 반응이 다른 것으 로 나이관련황반변성과는 구분된다는 주장이 더 설득력을
얻고 있다.12,13최근 PCV 환자에서 AMD 환자와 비교하여 방수의 혈관내피세포 증식인자(vascular endothelial growth factor, VEGF)가 높은 농도로 확인되었으며, 조직학적 검 사상 PCV와 VEGF의 연관성도 제시되었다.14,15
PCV를 레이저광응고치료를 하는 경우 결절만 아니라 병 변 전체를 치료하는 것이 추천되나, 중심와를 포함하는 경 우 시력저하의 위험이 있다.16 광역학치료(photodynamic therapy, PDT)의 경우 상대적으로 양호한 결과를 나타내 나,17 부작용으로 광범위한 망막하 출혈이 발생할 수 있다.
그리고 분지하는 혈관망의 폐쇄에는 효과적이지 않다는 보 고도 있다.18 이에 저자들은 PCV의 병리에서도 VEGF가 관계할 것이라는 가정하에, 나이관련황반변성과 동반된 맥락막신생혈관에 효과적이라는 보고된19,20 bevacizumab (Avastin®; Genentech, San Francisco, CA, USA)을 유리 체강 속으로 주사하고 효과를 알아보았다.
대상과 방법
2006년 6월부터 2007년 7월까지 PCV로 유리체강 내 Avastin®주입술을 시행 받은 환자 가운데 3개월 이상 경과 관찰이 가능했던 환자 13명, 13안을 대상으로 하였다. 이 중 남자 7명, 여자 6명이었으며, 연령분포는 58세에서 83 세로 평균 69세였다.
PCV의 진단은 Heidelberg Engineering Angiograph 2
Table 1. Patient characteristics and clinical date before and after intravitreal injection of bevacizumab for PCV Case
No. Age Sex Previous PDT*
Pre Tx BCVA†
Post Tx BCVA
Pre Tx fovea thickness(µm)
Post Tx fovea thickness(µm)
Polyp closure
Branching network closure
F/U mo
No of reinjection
1 81 F Yes 0.02 0.02 282 241 No No 6 2
2 72 F No 0.125 0.32 316 182 Yes No 6 3
3 70 M No 0.32 0.32 215 132 No - 5 2
4 59 M No 0.2 0.2 292 198 No No 3 0
5 58 M Yes 0.1 0.2 258 211 Yes No 8 3
6 74 M No 0.2 0.25 420 126 Yes No 4 2
7 64 F No 0.4 0.32 205 203 No No 4 1
8 64 M Yes 0.04 0.02 347 254 No No 8 1
9 70 F Yes 0.02 0.02 400 148 No No 8 3
10 83 F No 0.25 0.32 196 163 No No 4 2
11 59 M No 1.0 1.0 220 280 Yes No 4 2
12 68 M No 0.3 0.6 245 210 No No 8 2
13 73 F No 0.125 0.16 232 201 No - 8 1
*PDT=photodynamic therapy; †BCVA=best corrected visual acuity; -undetermined.
Figure 1.Change in logarithm of the minimum angle of resolution (LogMAR) best-corrected visual acuity (VA) with time (months). Improvements of three or more lines of VA were detected in 2 eyes (case 6 and 8).
(HRA2) (Heidelberg, Germany)와 Visupac FF450 plus IR fundus camera (Zeiss, Germany)를 이용하여 촬영한 형광안저혈관조영(fluorescin angiography, FA) 및 인도시 아닌그린혈관조영(indocyanine green angiography, ICGA) 소견을 바탕으로 이루어졌다. 분지하는 혈관망과 그 말단부 의 결절 병변이 보이는 특징적 소견이 있는 경우로 제한하 도록 노력하였으나, 분지하는 혈관망을 출혈이나 삼출, 위 축 병변으로 인해 파악하기 힘든 경우에는 결절 병변만 있 어도 그 모양이 특징적이면 포함시켰다. 또한 최근 1년 이 내 PDT 또는 유리체강내 스테로이드 주입술을 시행 받은 경우는 제외하였다.
주입술은 모든 환자에서 동의(informed consent)하에 시 행하였으며, 술안을 Proparacaine hydrochloride 0.5%
(Alacine®, Alcon)으로 점안 마취 후 5% 베타딘 용액으로 안검과 결막소독을 하였고, 개검기를 착용 후 결막낭에 점 안하였다. 2.5 mg (0.1 mL)의 Avastin®을 30 gauge 주사 바늘을 이용하여 수정체안에서는 윤부에서 3.5 mm, 인공 수정체안 또는 무수정체안에서는 3.0 mm 떨어진 하이측 섬모체 평면부를 통해 유리체강에 주입하였다.
주입술 후 1주, 1개월, 2개월 및 3개월째 최대교정시력, 빛간섭단층촬영(optical coherence tomography, OCT)을 이용한 황반부 두께를 측정하였고, 3개월에는 FA와 ICGA 상의 이상혈관 변화 등을 술 전과 비교하였다. Stratus OCT(Zeiss Humphrey Instruments, Dubin, CA, USA)를 황반부 두께 측정을 위해 사용하였다. 모든 조사는 의무기 록을 통하여 후향적으로 시행하였다. 시력과 황반 두께에 대한 통계 분석은 paired t test를 이용하였다.
결 과
환자들의 특징 등은 Table 1에 요약하였다. 술 후 경과 관찰 기간은 평균 27주(12주~36주)였으며, 1안에서는 추 가 주입술이 없었고, 3안에서는 1회, 6안에서는 2회, 3안에 서는 3회의 추가 주입술이 있었다. 추가 주입술은 OCT에 서 망막부종, 망막하액이나 망막색소상피박리가 지속되는 경우에 한하여 시행하였다.
최대교정시력은 경과 관찰 기간 동안 통계학적으로 유의 한 차이는 없었으나 주사 전 중간 값 LogMAR 0.82에서 1 개월째 0.78, 3개월째 0.73로 측정되어 다소 개선되었으며, 최종 경과관찰 시 3줄 이상 상승한 경우가 2안, 3줄 미만의 시력 변화를 보인 경우가 11안으로 모든 경우에서 시력이 유지 또는 상승되었다(Fig. 1).
Figure 2. Change in mean fovea thickness with time (months). A significant decrease was found at 1 month (p<0.05).
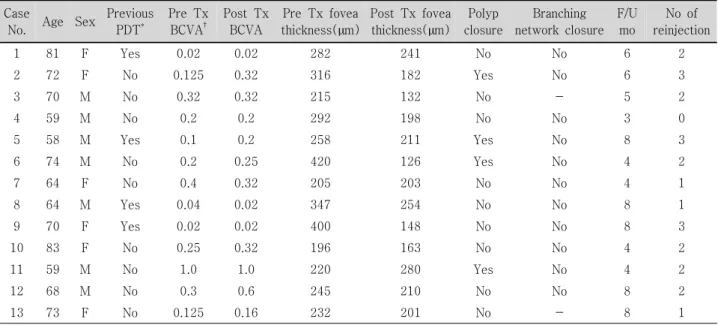
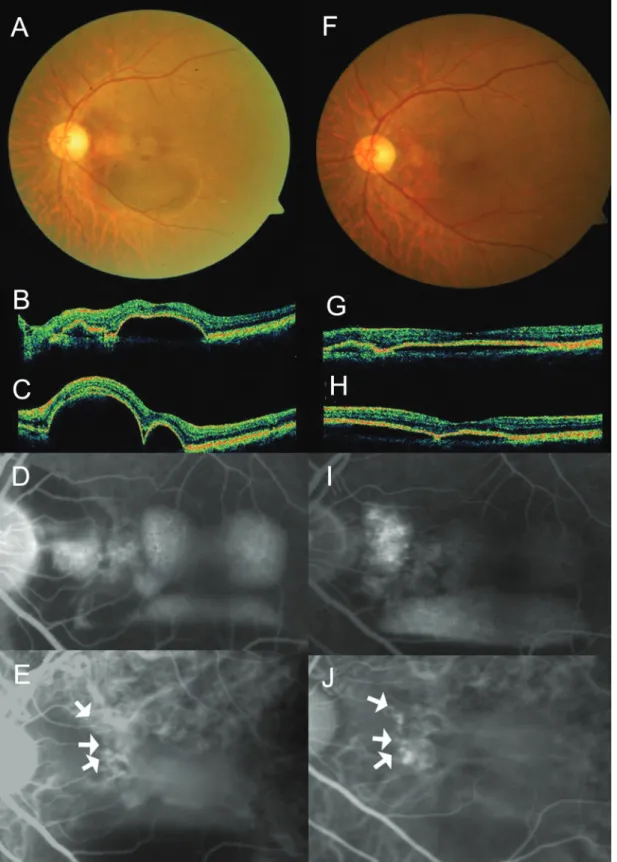
Figure 3. Case No. 3 (A) Baseline fundus photograph shows hard exudates, pigmentations around macula. (B) Baseline horizontal OCT image and (C) vertical OCT image shows protruding polyps and macular edema. (D)~(F) One month after the second injection, macular edema reduced, but subretinal hemorrhage occurred.
OCT 상 중심와 두께는 주사 전 평균 288 µm에서 주사 후 1개월에 231 µm로 통계학적으로 유의한 차이가 있었으 며(p<0.05), 3개월에 196 µm로 측정되어 지속적으로 감 소하는 양상이었다(Fig. 2).
ICGA에서 결절이 완전히 사라지거나 작은 과형광 반점 으로 크기가 감소하는 것을 결절의 폐쇄로 판단하였는데, 13안 중 4안에서만 일부의 결절이 폐쇄되었다. 그리고 분 지혈관망은 13안 중 11안에서 술 전에 명확히 관찰되었으 며, 모두에서 폐쇄를 관찰할 수 없었다.
증 례
결절의 일부 폐쇄가 있었던 증례들은 보면, 증례 3에서는 2번의 주입술 후 시력은 0.32에서 변화가 없었으며, ICGA 에서 일부 결절이 폐쇄되었으나, 분지혈관망은 출혈의 흡수 로 변화 없이 뚜렷하게 관찰되었다(Fig. 3, 4). 그리고 증례 6에서는 6주 간격으로 3번의 주입술 후 시력은 0.2에서 0.25로 약간 상승하였으며, 망막색소상피박리가 호전되고, ICGA에서 결절도 대부분 감소하였다. 하지만 일부 결절은 지속되었다(Fig. 5, 6).
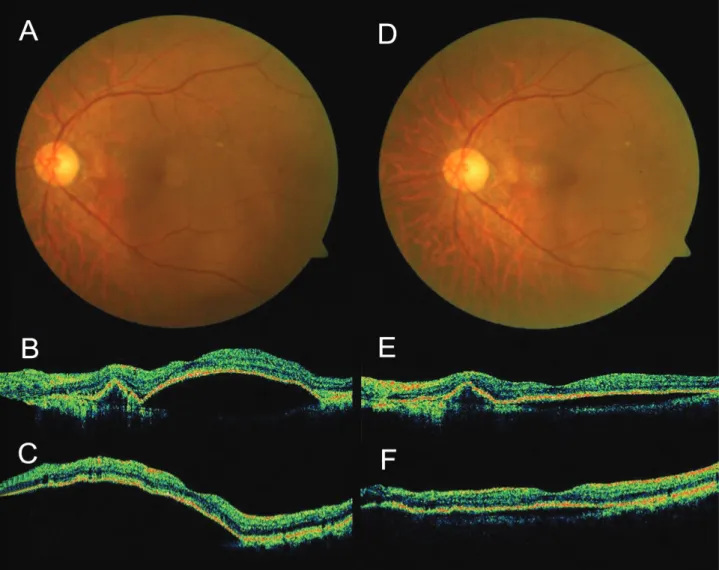
Figure 5.Case No. 6 (A) Baseline fundus photograph shows orange nodular lesion at temporal area from fovea. (B) Baseline horizontal OCT image and (C) vertical OCT image shows subretinal fluid. (D~F) One month after the third injection, subretinal fluid resolved.
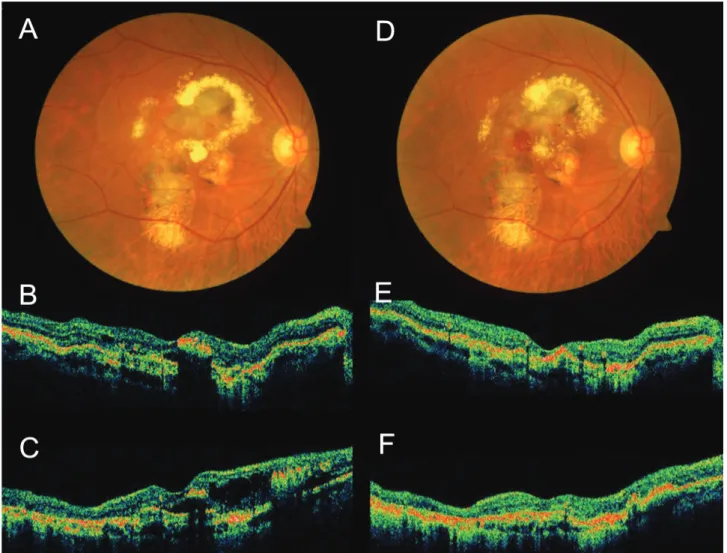
Figure 4. Case No. 3 (A) Baseline ICGA shows polypoidal dilatation of choroidal vessels and branching vascular network. (B) ICGA of one month after the second injection, the actively stained polyps resolve completely (arrows) while branching vascular network remains.
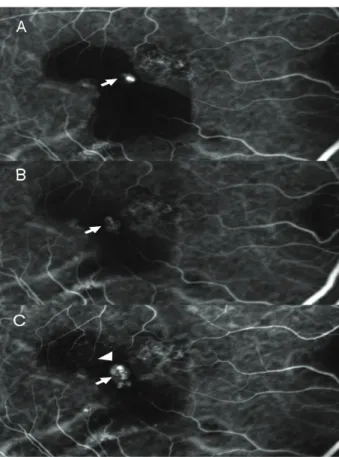
Figure 6. Case No. 6 (A) Baseline ICGA shows polypoidal dilatation of choroidal vessels and branching vascular network. (B) ICGA one month after the third injection, the polyps resolved incompletely (arrows).
반면 결절의 호전 없이 시력의 호전이 있어 추가 치료 없 이 경과 관찰하였던 증례들은 보면, 증례 12에서 술 전 빛 간섭단층촬영상 뚜렷한 망막색소상피박리가 2번의 주입술 후 감소되었고 시력도 0.3에서 1.0으로 호전되었다. 그리고 FA에서 누출이 감소하였지만, ICGA에서 결절의 변화가 없 었다(Fig. 7). 그리고 7개월 후 시력이 0.63으로 감소하며, 망막색소상피박리가 악화되어 3번째 주입술을 시행한 후, 시력은 0.8으로 호전되고 망막색소상피박리는 개선되었으 나, 결절은 감소되지 않았고 분지 혈관망은 변화가 없었다 (Fig. 8, 9). 그리고 증례 13에서도 1번 주입술 후 시력은 0.125에서 0.15로 큰 차이는 없었고 결절의 활동성은 감소 였지만, 폐쇄되지는 않았다. 그리고 6개월의 후 시력이 0.125이었고 결절의 크기 증가와 함께 활동성이 증가되었 다(Fig. 10, 11).
고 찰
PCV는 나이관련황반변성에 동반된 맥락막신생혈관과는 다른 질병으로 비교적 좋은 자연 예후를 보이는 질환으로 알려져 있다. 질병의 경과로는 재발성의 망막색소상피박리 등이 흔하다. 환자 중 거의 절반은 양호한 예후를 보이며 병변이 퇴행되는 반면, 나머지 절반은 황반 변성이 진행하 여, 시력을 잃을 수 있다.4
치료로는 결절 병변에 대해 선택적으로 레이저를 시행하 였으나,5병변 전체에 치료하는 것이 효과적이라는 보고도 있었다.16 하지만 단순 일차 치료로 선택했을 때, 그 기간 중에 심한 망막하 출혈이 발생하여 시세포 손상을 일으킬
수 있으며, 때로는 전형적인 맥락막신생혈관이 발생하여 결 국은 원반반흔을 형성할 수 있다. 그리고 중심와 부근에는 결과가 만족스럽지 못한 경우도 자주 있으며, 이에 따르는 만성 삼출성 변화는 결국 중심와의 망막색소상피위축이나 낭포형 변성을 초래할 수 있다.7,5
그리고 최근 PDT로 유의한 시력상승으로 나타내며, 형 광안저혈관조영술과 인도시아닌그린혈과조영술에서 호전 을 보인다는 보고가 있었다.21,22장점으로 망막의 시세포층 에 큰 손상 없이 이상혈관을 선택적으로 치료할 수 있어, 활동성 결절이 중심와 근처에 위치하거나 여러 개 있을 때 유용하게 사용될 수 있다. 또한 병변 전체를 치료함으로써 현재의 활동성 결절뿐 아니라 분지혈관망까지 폐쇄를 기대 할 수 있었다. 하지만 시력과 형광안저혈관조영술에서 호전 을 보이나 1년 후 재발이 흔하며, 분지혈관망을 완전히 폐 쇄시키기는 어렵다는 보고가 있다.18,23
병인으로는 전신질환인 고혈압이 PCV와 연관된다는 보 고도 있으며,5 최근 급성기 PCV의 병리조직학적 검사에서 맥락막의 동정맥 교차 부위에서 심한 동맥경화성 변화를 보이는 세동맥과 심한 혈관확장 및 사행을 보이는 세정맥, 그리고 혈관 내부와 주위의 혈액세포, 섬유소 등을 관찰하 였다.11 이에 따라 PCV는 망막분지정맥폐쇄에서처럼 맥락 막 혈관의 동정맥 교차 부위에서 경화성 변화로 세정맥의 확장과 혈류정체가 생기고, 출혈, 부종, 변성 등의 변화가 일어난 것이며, 신생혈관과는 별개의 질환으로 추측하였 다.2 그리고 망막색소상피박리도 나이관련황반변성과 중심 장액맥락망막병증에 동반된 경우, 빛간섭단층촬영에서 평 탄한 반구 모양으로 관찰되는데 비하여, PCV의 결절성 혈
Figure 7. Case No. 12 (A) Baseline fundus photograph shows orange nodular lesion at nasal area from fovea. (B) Baseline horizontal OCT image and (C) vertical OCT image shows multiple PED and polyps. (F~H) One month after the second injection, PED reduced. (D) Baseline FA shows leaking at corresponding region of the fundus, and pooling at PED region. (I) FA of one month after the second injection shows reduced leaking. (E) Baseline ICGA shows polypoidal dilatation of choroidal vessels (arrows). (J) ICGA of one month after the second injection, the vascular findings did not change.
Figure 8.Case No. 12 (A) Fundus photograph of seven month after the second injection. (B) Horizontal OCT image and (C) vertical OCT image shows increased PED. (D~ F) One month after the third injection, PED reduced.
관류에 해당하는 병변은 윗면이 다소 울퉁불퉁하고 옆면이 더 가파른 모양으로, 보다 뾰족하게 돌출된 양상을 보인다 고 보고하여,24 신생혈관과는 다른 원인이 있을 것으로 생 각하였다.하지만 최근 연구에서 나이관련황반변성과 PCV 모두에서 PEDF와 VEGF 경로 이상이 관찰되었고,15 방수 에서 VEGF의 증가도 확인되어,14VEGF가 나이관련황반변 성 뿐 아니라 PCV와도 관련되었다고 생각된다.
한편 VEGF에 대한 full-length humanized monoclonal neutralizing antibody인 bevacizumab (Avastin®)은 전이 된 직장암의 치료제로 승인되었다.25,26그리고 최근 연구에서 나이관련황반변성과 동반된 맥락막신생혈관에서 Avastin® 을 유리체강내 주입한 결과 유의한 시력상승과 빛간섭단층 촬영에서 황반부종의 감소를 보이고 형광안저혈관조영술상 호전을 나타내었다고 보고되었다.19,20
본 연구에서는 PCV 환자를 대상으로 유리체강내 Avastin® 을 주입하여 시력상승과 빛간섭단층촬영상 황반부 두께 감
소를 확인하였고, 이는 형광안저혈관조영술에서 유출감 소와 함께 확인되었다. 그러나 맥락막 결절을 폐쇄시키는 효과는 떨어지며 분지혈관망에는 영향이 없었다. 최근 Ghajarnia et al이 이전에 다른 치료로 호전이 없었던 경우 에 유리체강내 Avastin®의 주입술이 효과적이라고 보고하 였지만, 맥락막의 혈관에 대해서는 조사하지 않았고, Gomi et al은 맥락막 결절은 11안 중 1안에서만 호전되었으며 분 지 혈관망은 모든 안에서 변화가 없었다는 보고에서 본 연 구와 유사한 결과를 확인할 수 있다.27,28맥락막에 이상혈관 이 지속된다는 것은 재발로 이어질 수 있어 PDT 또는 광응 고 등의 추가 치료나 병합치료의 필요성에 근거가 될 것이다.
본 연구에서 관찰된 4안에서의 일부 결절의 폐쇄는 Avastin®의 효과일 수도 있지만, 질병의 자연경과일 수도 있다. Avastin®이 결절 및 분지혈관망에 효과적이지 않은 이유로는 full-length antibody로 상대적으로 분자량이 커 서 내경계막을 통과하지 못한다고 생각할 수 있다.19
Figure 10. Case No. 13 (A) Baseline fundus photograph shows orange nodular lesion around macula. (B) Baseline horizontal OCT image and (C) vertical OCT image shows PED, polyp and subretinal fluid (D~F) One month after the second injection, PED and subretinal fluid reduced. (G~ I) Six month after the second injection, subretinal fluid increased.
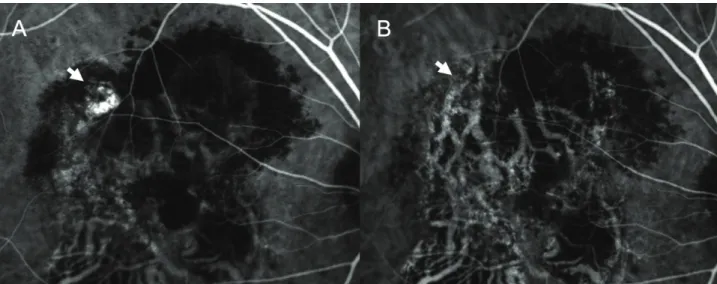
Figure 9. Case No. 12 (A) Baseline ICGA shows hidden area due to hemorrhage PED (broken arrows).
(B) ICGA of one month after the second injection, the vascular findings did not change (arrows). (C) ICGA of one month after the third injection shows increased polypoidal lesion (arrowhead).
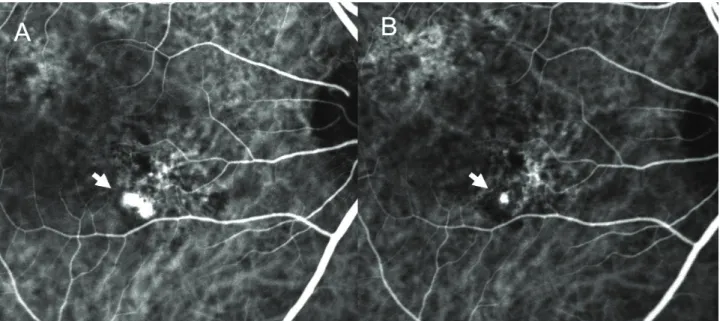
Figure 11. Case No. 13 (A) Baseline ICGA shows polypoidal dilatation of choroidal vessels hidden area due to hemorrhage PED (arrows). (B) ICGA of one month after the second injection, the polyps remain, but activity decreased. (C) ICGA of six month after the second injection shows increased polypoidal lesion (arrowhead).
하지만 최근에 전기생리학적 연구와 조직학적 연구에서 Avastin®이 망막전층을 통과할 수 있고 기능에 유해하지 않다고 주장하였다.29,30결절이나 분지혈관망의 발달 및 폐쇄 는 VEGF에 의존하지 않으며, Avastin®은 단지 비정상적인 혈관에서의 누출만 억제할 뿐이라는 가설이 더 설득력을 얻는다.
본 연구에서는 대상 안이 작아 통계분석에 한계가 있고, 경과관찰 기간이 짧아 장기간 효과를 알아보는데 문제점이 있다. 그리고 ICGA에 사용된 촬영방식이 동일하지 않아 약 간의 문제가 있을 수도 있다. 그리고 치료 효과가 어느 정 도 확인된 PDT와 병합 치료의 맥락막 결절 및 분지혈관망 에 미치는 효과에 대한 연구가 필요하다.
참고문헌
1) Yannuzzi LA, Sorenson J, Spaide RF, Lipson B. Idiopathic polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy (IPCV). Retina 1990:10:1-8.
2) Ciardella AP, Donsoff IM, Huang SJ, et al. Polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy. Surv Ophthalmol 2004:49:25-37.
3) Uyama M, Matsubara T, Fukushima I, et al. Idiopathic polypoidal vasculopathy in Japanese patients. Arch Ophthalmol 1999:117:1035-42.
4) Uyama M, Wada M, Nagai Y, et al. Polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy: Natural history. Am J Ophthalmol 2002:133:
639-48.
5) Lee WK, Kwon SI. Polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc 2000:42:2573-84.
6) Scassellati-Sforzolini B, Mariotti C, Bryan R, et al. Polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy in Italy. Retina 2001:21:121-5.
7) Lafaut BA, Leys AM, Snyers B, et al. Polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy in Caucasians. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 2000:238:752-9.
8) Wen F, Chen C, Wu D, Li H. Polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy in elderly Chinese patients. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 2004:242:625-9
9) Sho K, Takahashi K, Yamada H, et al. Polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy: incidence, demographic features, and clinical characteristics. Arch Ophthalmol 2003:121:1392-6.
10) Lee JW, Kim IT. Epidemiologic and clinical characteristics of polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy in Korean patients. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc 2006:48:63-74.
11) Rosa RH Jr. Davis JL, Eifrig CW. Clinicopathologic reports, case reports, and small case series: clinicopathologic correlation of idiopathic polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy. Arch Ophthalmol 2002:120:502-8.
12) Kuroiwa S, Tatiwa H, Hisatomi T, et al. Pathological features of surgically excised polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy membranes. Clin Experiment Ophthalmol 2004:32:297-302.
13) Yuzawa M, Mori R, Kawamura A. The origins of polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy. Br J Ophthalmol 2005:89:602-7.
14) Tong JP, Chan WM, Liu DT, et al. Aqueous humor levels of vascular endothelial growth factor and pigment epithelium-
derived factor in polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy and choroidal neovascularization. Am J Ophthalmol 2006:141: 456-62.
15) Matsuoka M, Ogata N, Otsugi T, et al. Expression of pigment epithelium derived factor and vascular endothelial growth factor in choroidal neovascular membranes and polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy. Br J Ophthalmol 2004:88:809-15.
16) Yuzawa M, Mori R, Haruyama M. A study of laser photocoagulation for polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy. Jpn J Ophthalmol 2003:47:379-84.
17) Gomi F, Ohji M, Sayanagi K, et al. 1-Year outcomes of photodynamic therapy in age-related macular degeneration and polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy in Japanese patients.
Ophthalmology 2008:115:141-6.
18) Lee PY, Kim KS, Lee WK. Photodynamic therapy with verteporfin in polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc 2004:45:216-27.
19) Rich RM, Rosenfeld PJ, Puliaflilo GA, et al. Short term safety and efficacy of intravitreal bevacizumab (Avastin) for neovascular age-related macular degeneration. Retina 2006:26:495-511.
20) Spaide RF, Laud K, Fine HF, et al. Intravitreal bevacizumab treatment of choroidal neovascularization secondary to age-related macular degeneration. Retina 2006:26:383-90.
21) Lee SC, Seong YS, Kim SS, et al. Photodynamic therapy with vertepofin for polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy of the macula. Ophthalmologica 2004:218:193-201.
22) Chan WM, Lam DC, Lai TY, et al. Photodynamic therapy with verteporfin for symptomatic polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy. Ophthalmology 2004:111:1579-84.
23) Silva RM, Figueira J, Cachulo ML, et al. Polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy and photodynamic therapy with verteporfin. Graefe Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 2005:243:973-9.
24) Iijima H, Iida T, Imai M, et al. Optical coherence tomography of orange-red subretinal lesions in eyes with idiopathic polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy. Am J Ophthalmol 2000:129:21-6.
25) Yang JC, Haworth L, Sherry RM, et al. A randomized trial of bevacizumab, an anti-vascular endothelial growth factor antibody, for metastatic renal cancer. N Engl J Med 2003:349:427-34.
26) Hurwitz H, Fehrenbacher L, Novotny W, et al. Bevacizumab plus irinotecan, fluorouracil, and leucovorin for metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med 2004:350:2335-42.
27) Ghajarnia M, Kurup S, Eller A. The therapeutic effects of intravitreal bevacizumab in a patient with recalcitrant idiopathic polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy. Semin Ophthalmol 2007:22:127-31.
28) Gomi F, Sawa M, Sakaguchi H, et al. Efficacy of intravitreal bevacizumab for polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy. Br J Ophthalmol 2008:92:70-3
29) Shahar J, Avery RL, Heilweil G, et al. Electrophysiologic and retinal penetration studies following intravitreal injection of bevacizumab (Avastin). Retina 2006:26:262-9.
30) Heiduschka P, Julien S, Hofmeister S, et al. Bevacizumab (avastin) dose not harm retinal function after intravitreal injection as shown by electroretinography in adult mice.
Retina 2008:28:46-55.
=ABSTRACT=
Short-term Efficacy of Intravitreal Bavacizumab for Polypoidal Choroidal Vasculopathy
Min Ho Lee, MD, Jin Hwan An, MD, Ji Eun Lee, MD, PhD, Boo Sub Oum, MD, PhD
Department of Ophthalmology, Pusan National University Hospital, College of Medicine, Pusan, Korea
Purpose: To evaluate the short-term effect of intravitreal bevacizumab (AvastinⓇ) in polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy.
Methods: Intravitreal AvastinⓇ was injected into 13 eyes of 13 patients with PCV in this retrospective, interventional case study.
The follow-up period lasted over 3 months after therapy. Changes in best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA), foveal height determined by optical coherence tomography, and abnormal vasculature in indocyanine green angiography (ICGA) were evaluated.
Results: The mean LogMAR BCVA was 0.82 at baseline, 0.78 at 1 month after treatment, and 0.73 at 3 months after treatment.
Visual acuity was stabilized or improved in 13 eyes (100%). The mean foveal height was 288 µm at baseline, 231 µm (p<0.05) at 1 month after treatment, and 196 µmat 3 months after treatment. The polypoidal lesions in ICGA decreased in 4 eyes (31%), although branching vasculature in ICGA was unchanged in 13 eyes (100%).
Conclusions: Intravitreal injection of AvastinⓇ may stabilize visual acuity and reduce macular edema due to decreased retinal pigment epithelial detachment and leaking. However, intravitreal injection had a minimal effect in occlusion of the symptomatic polypoidal lesions and no effect in occlusion of the branching vascular network.
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc 2009;50(1):51-60
Key Words: Bevacizumab, Polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy
Address reprint requests to Boo Sub Oum, MD, PhD
Department of Ophthalmology, Pusan National University Hospital
#1 Ga 10, Ami-dong, Seo-gu, Pusan 602-739, Korea
Tel: 82-51-240-7326, Fax: 82-51-242-7341, E-mail: bsoum@pusan.ac.kr