1203
미치는 영향
Effect of Posterior Urethral Reconstruction (PUR) in Early Recovery of Urinary Continence after
Robotic-Assisted Radical Prostatectomy
Soo Dong Kim, Tae Hyo Kim, Jae Wook Cho, Youn Chul You, Gyung Tak Sung
From the Department of Urology, College of Medicine, Dong-A University, Busan, Korea
Purpose: Prolonged urinary incontinence is one of the greatest concerns for patients undergoing radical prostatectomy. One of the possible causes for this urinary incontinence is a postoperative deficiency of the external striated urethral sphincter (EUS) complex and continence nerves. We evaluated the effect of posterior urethral reconstruction (PUR) in the early recovery of urinary continence after robotic-assisted radical prostatectomy.
Materials and Methods: Between January 2008 and March 2009 we per- formed robotic-assisted radical prostatectomy with PUR in 30 patients (PUR group) and without PUR in 30 patients (non-PUR group). We compared perioperative parameters and postoperative continence rates between the two groups. Continence was defined as no pads or one diaper per 24 hours and was assessed 1 month, 3 months, and 6 months after the procedure.
Results: Patients in the PUR group achieved better continence rates at 1 month (43% vs. 35%) and 3 months of follow-up (89% vs. 64%). At 6 months of follow-up, the continence rate was similar between the two groups (96% vs. 90%). No major complications were observed in the PUR group. However, 2 cases of anastomotic site leakage and 1 case of delayed bleeding were observed in the non-PUR group.
Conclusions: Posterior urethral reconstruction appears to be an easy and reproducible technique in robotic-assisted radical prostatectomy. Our early experience demonstrates that PUR in robotic-assisted radical prostatec- tomy appears to confer early continence recovery and reduce intraopera- tive complications. (Korean J Urol 2009;50:1203-1207)
Key Words: Robotics, Prostatectomy, Urinary incontinence
Korean Journal of Urology Vol. 50 No. 12: 1203-1207, December 2009
DOI: 10.4111/kju.2009.50.12.1203
동아대학교 의과대학 비뇨기과학교실 김수동ㆍ김태효ㆍ조재욱
유윤철ㆍ성경탁
Received:November 27, 2009 Accepted:December 4, 2009 Correspondence to: Gyung Tak Sung
Department of Urology, College of Medicine, Dong-A University, 3 ga-1, Dongdaesin-dong, Seo-gu, Busan 602-715, Korea
TEL: 051-240-2896 FAX: 051-253-0591 E-mail: sunggt@dau.ac.kr This study was supported by research funds from Dong-A University.
Ⓒ The Korean Urological Association, 2009
서 론
최근 전립선암의 치료에 있어 수술적 치료가 강조되고 있으며, 그 중에서도 2001년 도입된 Da Vinci robot system을 이용한 비침습적 수술방법에 대한 많은 발전이 있었다. 다 양한 술기의 개발로 기존의 개복 수술방법이나 복강경 수 술방법과 비교하여 종양학적 및 기능적 면에서 비슷하거나 우수한 결과를 보이고 있다. 하지만, 술 후에 발생하는 일시
적인 요실금은 아직까지 전립선암의 수술적 치료에 있어 한계 중 하나로 여겨지고 있다. 물론 장기적인 결과에서 보 면 술 후 1년째에 85-97%의 요자제 기능을 회복함으로써 만족할 만한 결과를 보이나, 회복하는데 걸리는 시간이 평 균 4.5개월 정도 소요되며, 완전한 요자제의 회복되기까지 는 더 많은 시간이 필요하다 [1-5]. 술 후 발생하는 요실금은 육체적, 정신적 그리고 사회생활의 삶의 질에 많은 영향을 미치며, 이 일시적인 요실금을 해결하고자 여러 가지 기술 적 방법들이 연구 개발되고 있다. 본 연구에서는 방광과 요
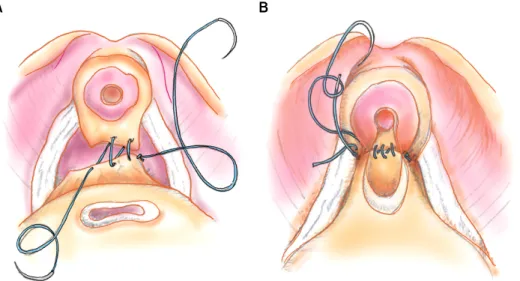
Fig. 1. Schematic diagram of pos- terior urethral reconstruction during robot-assisted radical prostatectomy.
(A) Denonvillier’s fascia is appro- ximated to the posterior aspect of the rhabdosphincter and the poste- rior median raphe by using one arm of the continuous suture. (B) The running suture takes three “bites” of each, the urethra and the bladder neck are approximated, and the suture is tied.
도를 문합하기 이전에 Denonvillier 근막과 요도 후벽을 문 합한 후 다시 방광 경부와 요도를 고정시켜주는 요도후벽 재건술 (posterior urethral reconstruction; PUR)을 통한 빠른 요자제의 향상성을 알아보고자 하였다.
대상 및 방법
2008년 1월부터 2009년 3월까지 본원에서 단일 술자에 의해 전립선암 환자를 대상으로 로봇 복강경 근치적 전립 선절제술 (robot-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy;
RALP)을 시행한 환자 중 요도후벽재건술을 하지 않은 최근 30례 (non-PUR group)와 요도후벽재건술을 시행한 30례 (PUR group)의 전립선암 환자에서 의무기록을 후향적으로 조사하여 무작위적으로 두 군으로 나눈 뒤 수술 전후의 임 상경과와 술 후 요자제능에 대한 결과를 분석하였다.
모든 환자에서 수술 전 직장수지검사, 전립선 조직검사, 전립선 자기공명 영상검사, 골주사검사를 시행하였으며 수 술 시간은 첫 피부 절개부터 마지막 피부 봉합까지의 시간 으로 정의하였다. 출혈량은 마취의에 의해 측정된 출혈량 을 술 중 출혈량으로 정의하였고, 술 후 요자제능은 도뇨관 제거 직후와 술 후 1, 3, 6개월에 외래에서 문진을 통하여 평가하였다. 요자제능의 평가 기준으로는 요실금이 전혀 없거나 양이 적어 예방적 패드를 1일 1개 이하로 착용하는 정도까지를 요자제능이 있다고 판단하였다.
요도후벽재건술을 시행한 환자군과 시행하지 않은 환자 군간의 술 전, 술 중 및 술 후 변수들을 Student’s t-test와 chi-square test, Fisher’s exact test를 이용하여 비교 분석하였 으며, p값이 0.05 미만인 경우를 통계적으로 유의한 것으로 하였다. 통계프로그램은 SPSS 12 (SPSS Inc, Chicago, USA)
를 이용하였다.
1. 수술 방법
요도후벽재건술을 시행하지 않는 환자들에서는 전립선 절제 후 곧바로 modified Van Velthoven 방법을 이용하여 방 광과 요도의 연속 봉합을 시행하여 방광요도문합을 완성하 였고, 요도후벽재건술을 시행한 환자들에 있어서는 전립선 을 절제한 후 방광요도문합 전에 요도후벽재건술을 시행하 였다 [6]. 요도후벽재건술은 Rocco 등에 의하여 시행된 방 법인 요도 뒷면의 횡문조임근과 Denovillier's 근막의 문합 및 방광 후벽과 횡문조임근의 문합을 원칙으로 하였다 [7].
하지만, 전통적인 Rocco 술식의 경우 Denovillier's 근막과 방광 후벽을 동시에 요도 후벽의 횡문조임근에 문합하는 도중 조직의 손상이 있을 수 있으며 술기상의 어려움으로 본 연구에서는 변형된 Patel 술식을 이용하였다 [8,9]. 변형 된 Patel 술식은 첫 번째 단계로 요도 뒷면의 횡문조임근과 Denovillier's 근막을 문합하고, 두 번째 단계로 요도 후면과 방광경부를 문합하여 고정하는 방법이다.
봉합사는 2-0 monocryl 봉합사 두 개를 각각 12 cm 길이 로 자른 다음 양쪽끝을 묶어 사용하였다. 요도후벽재건은 전립선절제술 이후에 직장의 앞쪽, 방광의 뒷쪽에서 Deno- villier's 근막의 남아있는 부분을 확인하고, 이를 요도 후면 의 횡문 조임근에 접근시켜 왼쪽 실을 이용하여 5시에서 8시 방향으로 연속봉합한 후 매듭을 지었다 (Fig. 1A). 다음 단계로, 남아있는 우측 실을 이용하여 방광경부와 요도를 접근 시켜 3회 연속 봉합을 시행한 후 그 끝을 처음 완성하 였던 매듭과 다시 매듭을 지어 고정하였다 (Fig. 1B). 이러 한 방법으로 요도후벽재건을 완료한 후 modified Van Vel- thoven 방법을 이용하여 방광과 요도의 연속 봉합을 시행하
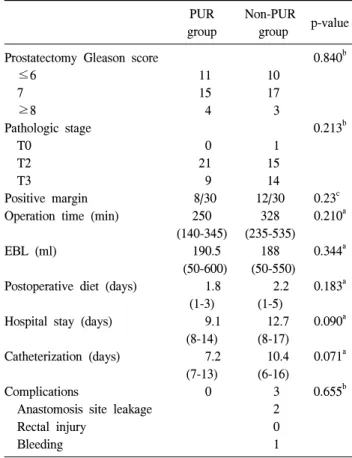
Table 2. Intraoperative and perioperative parameters based on operation methods
PUR group
Non-PUR
group p-value Prostatectomy Gleason score
≤6 7 ≥8
Pathologic stage T0
T2 T3
Positive margin Operation time (min) EBL (ml)
Postoperative diet (days) Hospital stay (days) Catheterization (days) Complications
Anastomosis site leakage Rectal injury
Bleeding
11 15 4 0 21 9 8/30
250 (140-345)
190.5 (50-600)
1.8 (1-3) 9.1
(8-14) 7.2
(7-13) 0
10 17 3 1 15 14 12/30
328 (235-535)
188 (50-550)
2.2 (1-5) 12.7 (8-17) 10.4 (6-16) 3 2 0 1
0.840b
0.213b
0.23c 0.210a 0.344a 0.183a 0.090a 0.071a 0.655b
PUR: posterior urethral reconstruction, EBL: essential blood loss,
a: Student's t-test, b: Fisher's exact test, c: chi-square test
Table 3. Return of continence based on the operative methods PUR
group
Non-PUR
group p-value Postoperative 1 month (%)
Postoperative 3 months (%) Postoperative 6 months (%)
49 89 96
35 64 90
0.369a 0.031a 0.294a PUR: posterior urethral reconstruction, a: chi-square test Table 1. Preoperative patient characteristics
PUR group
Non-PUR
group p-value
No. of patieints Age (years) BMI (kg/m2) PSA (ng/ml) Clinical staging T2
T3a T3b
30 65.2 (54-80) 25.25 (20.08-31.98)
9.52 (1.84-36)
26 1 3
30 65.9 (50-80) 24.33 (19.9-30.6)
9.36 (2.91-19.79)
25 2 3
0.775a 0.409a 0.855a 0.193b
PUR: posterior urethral reconstruction, BMI: body mass index, PSA: prostate-specific antigen, a: Student's t-test, b: Fisher's exact test
였으며, 이때 요도후벽재건을 시행한 부분도 포함하여 방 광요도문합을 완성하였다 [10].
결 과
총 60명의 환자 중 30명에서 요도후벽재건을 시행하였고 30명에서 요도후벽재건을 시행하지 않았다. 두 군의 술 전 임상소견은 Table 1과 같이 평균 연령, 체질량지수 (body mass index; BMI), 술 전 전립선특이항원 (prostate- specific antigen; PSA)검사 및 술 전 임상적 병기에서 유의한 차이가 없었다.
술 중 및 술 후 결과에서 요도후벽재건술을 시행한 군과 시행하지않은 군의 수술 시간, 술 중 실혈량, 술 후 식이진 행, Gleason 점수 및 술 후 병리학적 병기에서 또한 유의한 차이는 없었다.
하지만, 요도후벽재건술을 시행한 군에서 도뇨관 유치 기간이 7.2일로 10.4일에 비해 짧았고, 이로 인하여 입원기 간 또한 9.1일로 12.7일에 비하여 조기에 퇴원할 수 있었으 나 통계학적 유의성은 없었다.
술 중 및 술 후 합병증은 요도후벽재건술을 시행한 군에 서는 없었으나 요도후벽재건술을 시행하지 않은 군에서 3 례 발생하였다. 술 후 2례에서 방광 요도 문합부위의 요누 출이 있었으나 이들 모두 방광조영술 추적 검사에서 요누 출이 더 이상 발견되지 않을 때까지 도뇨관을 유치함 (14일, 16일)으로써 해결되었고, 1례의 수술 후 지연출혈이 있었 던 경우에서는 수혈 및 보존적 치료로 해결할 수 있었다 (Table 2).
요자제 기능의 회복은 요도후벽재건술을 시행한 군에서
술 후 1개월째에 49%의 요자제기능의 회복을 보였으며, 요 도후벽재건술을 시행하지 않은 군에서 나타난 35%의 요자 제기능의 회복보다 통계적인 유의한 차이는 없었으나, 빠 른 요자제회복을 보였다. 술 후 3개월에서는 89%와 64%로 유의한 차이를 보였다. 술 후 6개월에서는 양 군에서 모두 96%와 90%의 요자제능의 회복을 보였으며, 통계적으로 유 의한 차이는 보이지 않았다 (Table 3).
고 찰
로봇을 이용한 전립선절제술은 현재 전립선암의 치료에
있어 안전하고 유용한 술기로 인정받고 있다. 또한 술기의 발전 및 비침습적 술기의 사용으로 근치적 전립선절제술에 따른 사망률 및 합병증의 유병률이 감소하고 있다. 하지만 개복수술이나 복강경 전립선절제술과 함께 로봇을 이용한 전립선절제술에 있어 술 후 일시적으로 나타나는 요실금은 환자의 삶의 질을 저해시키는 요인으로 지적되고 있다 [8,11]. 현재까지 요실금에 대한 장기적인 결과는 만족할만 한 성적을 보이고 있으며 Rassweiler의 연구보고에 의하면 복강경하 전립선절제술을 시행받은 환자의 1년 후 요자제 능은 50-91.7%로 다양하게 보고되고 있고, 이들은 술자의 술기의 능력에 따라 요자제능은 많이 좌우된다고 하였다 [12]. 또한, Trabulsi와 Guilloneau는 83-100% 요자제기능의 회복을 보고하고 있다 [13].
하지만, 최근 술기의 발달로 수술이 더욱 정교해지고 환 자의 기대치 또한 상승함으로 인하여 보다 빠른 요자제기 능의 회복을 기대하고 있으며 이에 대한 많은 연구가 이루 어지고 있다. Stolzenburg 등은 치골전립선인대를 보존함으 로써 요자제능의 빠른 회복을 가져올 수 있다고 보고하였 고, 자신의 논문에서 술 후 2주후에 치골전립선인대를 보존 한 군과 본존하지 않은 군을 비교하여 보았을 때 24%와 12%로 나타났으며, 술 후 3개월째에 그 비율은 76%와 48%
로 요자제능의 향상을 보였다고 하였다 [14].
Montorsi 등은 전립선 첨부를 박리할 때 정교한 박리를 통하여 횡문조임근을 보존함으로써 44%에서 조기 요자제 능의 회복을 얻을수 있다고 보고하였고 [15], 또한, Graefen 등과 Burkhard 등은 신경보존술을 통하여 의미 있는 요자제 능의 향상을 얻었다고 보고하였다 [16,17]. 본 연구에서도 적응증이 되는 환자에 있어 신경보존술과 요도후벽재건술 을 동시에 시행한 경우도 있었지만, 아직까지 요자제능과 신경보존술과의 상관관계에 있어서는 논란이 많은 부분이 기에 본 연구에서는 제외시켰다 [18,19].
Rocco 술식은 해부학적-기능적 가설에 기초한 것으로 횡 문조임근의 후방기시부를 재건함으로써 요자제능의 회복 을 기대하는 것이다. Rocco 등은 전립선 후벽에 위치하고 있는 Denonvillier 근막과 횡문조임근의 후방에 연결되는 정 중 봉선은 골반내에서 중요한 근육-근막판을 형성하여 횡 문조임근의 근육들이 고정될 수 있는 지지구조를 형성한다 고 하였고, 이 때문에 요도후벽의 재건은 요자제능의 향상 에 큰 도움을 준다고 하였다 [11,20]. 이들은 실제로 이 방법 을 이용하여 시행한 개복 전립선절제술에서 도뇨관 제거 후 3일째에 74%에서 요자제증이 회복되었고 요도후벽재건 을 시행하지 않은 군에서는 30%의 요자제능의 회복을 보였 다고 보고하였다. 물론 이들의 연구자체가 무작위 연구가 아니고, 환자 선택에 있어 오류가 있어 비교하기는 어렵지
만, 72%라는 객관적인 결과만을 볼 때 충분한 의의를 가진 다고 하겠다 [7].
본 연구에서도 술 후 요자제능을 요도후벽재건술을 시행 한 군과 시행하지 않은 군을 비교해 볼 때 통계학적으로 유의하지는 않았지만, 술 후 1개월째에 49%와 35%의 상대 적으로 빠른 요자제능의 회복을 보였으며, 술 후 3개월째에 는 89%와 64%로 통계학적으로 의미 있는 차이를 보이는 빠른 회복을 보였다. 술 후 6개월에는 양 군 모두에서 90%
이상의 요자제능의 회복을 보였다. 전체적으로 보았을 때 술 후 1개월째의 결과는 다른 연구보고에 비하여 약간의 차이가 있었으나 술 후 3개월 및 6개월에서는 유사한 결과 를 얻을 수 있었다. 본 연구의 대상이된 환자들의 전체적인 병기가 높고, 대상 환자군이 적어 다른 연구에 비하여 약간 의 차이가 있었던 것으로 생각하며, 향후 환자군이 늘어날 경우 더욱 좋은 결과를 얻을 수 있을 것으로 기대한다.
술 후 발생하는 합병증 중 요도방광문합부위의 요누출의 발생률을 양 군에서 비교해볼 때 요도후벽제건술을 시행한 군에서는 요누출이 발생하지 않았고, 요도후벽재건술을 시 행하지 않은 군에서만 2례에서 발생하였다. 각각의 증례에 서 14일과 16일 동안 도뇨관을 연장 유치함으로써 해결 할 수 있었다. 이와 같은 결과는 요도후벽재건술로 인하여 요 도와 방광 문합 시에 요도와 방광사이의 장력을 줄여줄 수 있어 더욱 안정적인 문합이 가능하게되어 술 후 문합부위 에서 요누출의 발생률이 낮아지는 것으로 생각한다. 변형 된 Patel 술식을 이용한 요도후벽재건술은 요자제의 빠른 회복에 영향을 미치는 것으로 생각되나, 아직 장기적인 결 과가 없고, 적은 환자 수로 인한 한계점을 극복하지 못하였 기에 향후 지속적인 연구를 통한 술기의 개발 및 보완이 이루어진다면 더욱 좋은 요자제능의 회복을 기대할 수 있 을 것이다.
결 론
횡문조임근과 Denonvillier 근막의 문합 및 방광경부의 고 정을 통한 요도후벽재건술은 간단하면서도 효과적인 술기 로 로봇을 이용한 전립선절제술에서 요도후벽재건술을 시 행하지 않은 군에 비하여 요자제능의 빠른 회복 및 합병증 의 감소를 보였다.
REFERENCES
1. Rassweiler J, Sentker L, Seemann O, Hatzinger M, Rumpelt HJ. Laparoscopic radical prostatectomy with the Heilbronn technique: an analysis of the first 180 cases. J Urol 2001;
166:2101-8.
2. Eden CG, Cahill D, Vass JA, Adams TH, Dauleh MI.
Laparoscopic radical prostatectomy: the initial UK series. BJU Int 2002;90:876-82.
3. Guillonneau B, el-Fettouh H, Baumert H, Cathelineau X, Doublet JD, Fromont G, et al. Laparoscopic radical pro- statectomy: oncological evaluation after 1,000 cases a Mont- souris Institute. J Urol 2003;169:1261-6.
4. Salomon L, Anastasiadis AG, Katz R, De La Taille A, Saint F, Vordos D, et al. Urinary continence and erectile function:
a prospective evaluation of functional results after radical laparoscopic prostatectomy. Eur Urol 2002;42:338-43.
5. Peyromaure M, Ravery V, Boccon-Gibod L. The management of stress urinary incontinence after radical prostatectomy. BJU Int 2002;90:155-61.
6. Kong GS, Seong YK, Sung GT. Robotic-assisted radical prostatectomy using da vinciTM surgical robotic system: initial Korean experience. Korean J Urol 2005;46:353-9.
7. Rocco F, Carmignani L, Acquati P, Gadda F, Dell'Orto P, Rocco B, et al. Early continence recovery after open radical prostatectomy with restoration of the posterior aspect of the rhabdosphincter. Eur Urol 2007;52:376-83.
8. Rocco B, Gregori A, Stener S, Santoro L, Bozzola A, Galli S, et al. Posterior reconstruction of the rhabdosphincter allows a rapid recovery of continence after transperitoneal videola- paroscopic radical prostatectomy. Eur Urol 2007;51:996-1003.
9. Coughlin G, Dangle PP, Patil NN, Palmer KJ, Woolard J, Jensen C, et al. Surgery illustrated-focus on details. Modified posterior reconstruction of the rhabdosphincter: application to robotic-assisted laparoscopic prostatectomy. BJU Int 2008;102:
1482-5.
10. Van Velthoven RF, Ahlering TE, Peltier A, Skarecky DW, Clayman RV. Technique for laparoscopic running urethrove- sical anastomosis: the single knot method. Urology 2003;61:
699-702.
11. Rocco F, Carmignani L, Acquati P, Gadda F, Dell'Orto P, Rocco B, et al. Restoration of posterior aspect of rhabdo- sphincter shortens continence time after radical retropubic prostatectomy. J Urol 2006;175:2201-6.
12. Rassweiler J, Hruza M, Teber D, Su LM. Laparoscopic and robotic assisted radical prostatectomy--critical analysis of the results. Eur Urol 2006;49:612-24.
13. Trabulsi EJ, Guillonneau B. Laparoscopic radical prostatec- tomy. J Urol 2005;173:1072-9.
14. Stolzenburg JU, Liatsikos EN, Rabenalt R, Do M, Sake- laropoulos G, Horn LC, et al. Nerve sparing endoscopic extraperitoneal radical prostatectomy--effect of puboprostatic ligament preservation on early continence and positive margins. Eur Urol 2006;49:103-11.
15. Montorsi F, Salonia A, Suardi N, Gallina A, Zanni G, Briganti A, et al. Improving the preservation of the urethral sphincter and neurovascular bundles during open radical retropubic prostatectomy. Eur Urol 2005;48:938-45.
16. Graefen M, Walz J, Huland H. Open retropubic nerve-sparing radical prostatectomy. Eur Urol 2006;49:38-48.
17. Burkhard FC, Kessler TM, Fleischmann A, Thalmann GN, Schumacher M, Studer UE. Nerve sparing open radical retropubic prostatectomy--Does it have an impact on urinary continence? J Urol 2006;176:189-95.
18. Catalona WJ, Carvalhal GF, Mager DE, Smith DS. Potency, continence and complication rates in 1,870 consecutive radical retropubic prostatectomies. J Urol 1999;162:433-8.
19. Lepor H, Kaci L. The impact of open radical retropubic prostatectomy on continence and lower urinary tract symp- toms: a prospective assessment using validated self-admini- stered outcome instruments. J Urol 2004;171:1216-9.
20. Burnett AL, Mostwin JL. In situ anatomical study of the male urethral sphincteric complex: relevance to continence preserva- tion following major pelvic surgery. J Urol 1998;160:1301-6.