홍삼추출물(KGC05P0)이 고인슐린혈증 제2형 당뇨병 마우스에서 인슐린 민감성, 인슐린 분비량 및 혈당 조절에 미치는 영향
권한올․구기방․이윤지․김종한․이미향․인 교 (주)KGC인삼공사
Effect of Korean Red Ginseng Extract (KGC05P0) on Regulating Insulin Sensitivity, Insulin and Blood Glucose Level in Hyperinsulinemia
Type 2 Diabetic Mice
Hanol Kwon, Gi-Bang Koo, Yun Ji Lee, Jonghan Kim, Mi-Hyang Lee, and Gyo In Korea Ginseng Corporation Research Institute, Korea Ginseng Corporation
ABSTRACT Korean red ginseng extracts (KGC05P0) showed anti-diabetic activity, especially regarding fasting blood glucose and insulin sensitivity in vivo, in this study. To confirm their effectiveness in animals, C57BL/6J ob/ob (hyperinsulinemia/diabetic model) mice were orally administrated with or without KGC05P0 for 12 weeks. The ex- perimental group was divided as follows: NC (C57BL/6J mice), C (C57BL/6J ob/ob mice), Met 200 (metformin, 200 mg/kg b.w.), P0 100(KGC05P0, 100 mg/kg b.w.), P0 200(KGC05P0, 200 mg/kg b.w.), and P0 400(KGC05P0, 400 mg/kg b.w.). We found that KGC05P0 significantly reduced fasting glucose and insulin levels in serum and increased the serum adiponectin level. KGC05P0 improved insulin sensitivity modulators such as IR, IRS-1, PI3K, Akt, AMPK, and GLUT2/4 and inhibited liver function indicators in the liver. This suggests that KGC05P0 has great potential as a health food for improving blood glucose.
Key words: Korean red ginseng, non-saponin fraction, insulin sensitivity, fasting blood glucose, hyperinsulinemia
Received 9 April 2020; Accepted 18 May 2020
Corresponding author: Gyo In, Laboratory of Efficacy Research, Korea Ginseng Corporation, Daejeon 34128, Korea
E-mail: 20109042@kgc.co.kr, Phone: +82-42-870-3051
서 론
당뇨병(diabetes mellitus, DM)은 여러 만성질환 중 전 세계에서 발병률이 3번째로 높은 매우 흔한 질환으로 신장 병증, 망막병증과 같은 다양한 합병증을 유발하는 것으로 알려져 있다(Oh 등, 2017). 이 질환은 2가지의 형태로 나뉘 며, 제1형 당뇨병은 인슐린 의존성 당뇨병, 제2형 당뇨병은 인슐린 비의존성 당뇨병으로 인슐린 저항성에 의해 발생하 는 것으로 알려져 있고, 당뇨 환자의 대부분이 제2형 당뇨병 에 속해 있다(Kwon 등, 2016). 당뇨병 발생의 특성은 다양 하며 그중 하나는 간의 대사과정 변화인데 간은 영양소의 대사작용을 통해 인체의 에너지로 활용할 수 있는 시스템을 조절하는 중요한 기관이다(Cordero-Herrera 등, 2013).
간에서 해당 과정과 당신생합성을 통해 혈당을 조절하는 작 용은 공복혈당 조절에 중요하다. 특히 당신생합성은 포도당 생성 후 혈중으로 방출시켜 공복 시 혈당을 조절하는 기능을 하며, 이 과정은 당뇨병 전단계 및 환자에서 공복혈당을 조 절하는 매우 중요한 작용이다(Whiteman 등, 2002). 또한
공복혈당과 식후혈당은 다른 기전에 의해 혈당이 조절된다 는 연구 결과가 있는데 인체실험 결과에서 공복혈당 장애를 가진 그룹은 인슐린 저항성과 연관성이 크고, 식후혈당 장애 를 가진 그룹은 인슐린 분비 감소와의 연관성이 더 크다는 것으로 보고되었다(Rhee 등, 2010; Aoyama-Sasabe 등, 2016; Meyer 등, 2006; Faerch 등, 2009b). 그러나 만성적 으로 혈당조절 기능에 문제가 지속되면 인슐린 보상작용을 통한 고인슐린혈증이 발생하고 인슐린 저항성을 통해 당뇨 병으로 이어지며 합병증이 발생하므로 예방이 매우 중요하 다.
췌장은 인슐린, 글루카곤 및 다양한 호르몬을 분비하여 세포 내에서 에너지 생성과 저장을 조절한다. 이러한 호르몬 의 분비와 작용의 이상은 영양소의 항상성에 대한 중대한 영향을 미치게 된다. 그중 인슐린은 당질 및 지방의 동화작용 을 촉진하며 혈당을 조절하는 중요한 인자로 췌장의 β-cell 에서 분비되는 호르몬이다(Kahn, 2003; Cryer 등, 2003).
인슐린 활성도를 뜻하는 인슐린 민감성은 다양한 인자들에 의해 조절되는데, 특히 간, 근육, 신장 및 지방조직에서 PI3K pathway를 통한 Akt 및 AMPK 활성화 등을 통해 IRs, IRS- 1, GLUT2/4들이 재활성되고 인슐린의 민감성이 향상되며, 혈당을 조절하는 데 매우 중요한 작용을 하게 된다(DeFronzo, 1988; Taniguchi 등, 2006). 이러한 조절인자들이 외부 환
Table 1. Experimental design of animal (n=10)
Group1) Experiment Mouse species
NC C Met 200
P0 100 P0 200 P0 400
AIN93G AIN93G
AIN93G+orally administrated metformin 200 mg/kg b.w AIN93G+orally administrated KGC05P0 100 mg/kg b.w AIN93G+orally administrated KGC05P0 200 mg/kg b.w AIN93G+orally administrated KGC05P0 400 mg/kg b.w
C57BL/6J C57BL/6J ob/ob
1)
경요인에 의해 활성도가 감소하면 체내 표적 장기에 대한 인슐린의 반응이 감소하고 인슐린 저항성이 증가하게 된다 (Choi, 2009). 인슐린 저항성이 진행되면 제2형 당뇨, 고지 혈증, 심장질환 등을 포함한 여러 대사질환과의 합병증을 유발하기 때문에 건강 위험인자로 간주되므로 인슐린 저항 성 개선에 많은 노력이 필요하다(Eckel 등, 2005; Kopel- man, 2000).
홍삼(Korean red ginseng, Panax ginseng C. A.Meyer) 은 인삼의 증숙과 건조를 통해 만들어지며 아시아의 여러 나라에서 오래전부터 전통 약재로 사용되어 왔다. 또한 증숙 과 건조 과정을 통해 인삼의 ginsenoside의 화학적 구조가 변화되고 생리활성 성분이 증가하는 것으로 알려져 있다 (Kim, 2001). 이러한 성분변화와 생리활성 성분의 증가로 홍삼은 항암, 항염 등의 약리학적 연구가 많이 진행되어 왔 고 그중 혈당에 영향을 준다는 연구도 많이 보고되고 있다 (Attele 등, 2002; Yun 등, 2004; Kim 등, 2005; Vuksan 등, 2000; Sotaniemi 등, 1995). 또한 Park 등(2020)의 비 사포닌 분획(KGC05P0) 추출물의 선행연구에서 C57BL/6J db/db 마우스를 활용하여 혈당개선 효능은 확인하였으나, Katsuda 등(2013)의 당뇨병 동물모델 논문에서 C57BL/6J db/db 마우스는 인슐린의 자연 감소로 인해 인슐린 민감성 실험을 진행하기 어렵다고 보고된 특징과 Lim과 Jang(2008) 의 연구 결과에서 비만의 지표로 알려진 아디포넥틴이 당뇨 병과 관련되어 인슐린 민감성을 향상시킨다는 결과를 바탕 으로, 본 연구에서 홍삼추출물을 활용하여 인슐린 민감성과 아디포넥틴의 변화 및 인슐린 분비량과 그에 따른 혈당 변화 에 대한 조절작용을 밝히고자 Cheon 등(2015)의 연구 방법 을 응용하여 고인슐린혈증 당뇨병 모델인 C57BL/6J ob/ob 마우스를 활용하여 연구를 진행하였다.
재료 및 방법
실험 재료
본 연구에서 사용된 홍삼추출물(KGC05P0)은 홍삼농축 액(2.0 kg)을 증류수에 용해하여 Diaion HP-20(Mitsubishi Chemical, Tokyo, Japan)에 흡착시키고 물, 30% 에탄올을 순차적으로 용출시켰다. 물과 30% 에탄올에 의해 용출되어 나온 비사포닌 분획을 농축 후 분무 건조(1.1 kg, 수율 55%) 하였다. Discovery C18 column(4.6 mm×250 mm, 5 μm,
Supelco, Bellefonte, PA, USA)을 이용하여 High per- formance liquid chromatography(Waters, Milford, MA, USA) 분석을 통해 홍삼 다당체의 구성 당 3종(galacturonic acid, galactose, arabinose)의 함량이 53.64 mg/g으로 지 표 성분이 설정된 KGC05P0을 -20°C에 보관하여 실험 시 사용하였다.
실험동물
동물실험은 한국인삼공사 동물실험 윤리위원회의 심의 및 승인을 거처 수행되었다(승인번호: KGC-2019-011).
(주)새론바이오(Uiwang, Korea)로부터 공급받은 고인슐린 혈증/당뇨병 모델로 알려진 5주령의 수컷 C57BL/6J ob/ob 마우스 50마리와 수컷 C57BL/6J 마우스 10마리를 입수하 여 2주간 동물사육실 환경에 적응시켰다. 체중 및 공복혈당 수치를 바탕으로 군당 10마리씩 군 분리 후 실험에 사용하 였다. 동물사육실 온도는 22±2°C, 상대습도 50±10%, 환기 횟수 10~15회/시간, 조명 시간 12시간(오전 8시~오후 8시), 조도 250~300 Lux로 유지하였다. 실험 기간에 KGC05P0 및 양성대조군으로 사용한 metformin은 1일 1회 일정한 시 간에 경구 투여하였고 식이와 음용수는 자유롭게 섭취하도 록 하였으며, 1주일에 한 번씩 일정한 시간에 체중을 측정하 였다. 실험군의 정보는 Table 1에 나타내었다.
혈청 및 조직 처리
실험동물은 isoflurane(Piramal Critical Care Inc., Be- thlehem, PA, USA)으로 마취한 상태에서 심장채혈을 통해 혈액을 채취하였으며, 채취한 혈액은 3,000 rpm에서 20분 간 원심분리 후 혈청을 분리하였다. 혈액 채취 후 복부를 절개하여 간, 신장을 적출하여 무게를 측정하였고, 실험에 사용될 간 조직은 무게 측정 후 -80°C deep freezer에 보관 후 실험에 사용하였다. 근육조직은 장딴지근을 적출하여 무 게를 측정하였다.
혈중 인슐린 및 아디포넥틴 농도 측정
분리한 혈청의 인슐린 농도는 Rat/Mouse Insulin 96-well plate Assay kit(EMD Millipore, St. Louis, MO, USA)을 이용하여 실험 protocol에 따라 분석하였고, 아디포넥틴 농 도는 Adiponectin Mouse ELISA kit(Abcam, Cambridge, UK)을 이용하여 실험 protocol에 따라 분석하였다.
Table 2. Weight, liver, kidney, and muscle weight of experimental groups at weeks 12 (n=10) Group1) Initial BW (g) Final BW (g) Liver (g) Kidney (g) Muscle (g)
NC C Met 200
P0 100 P0 200 P0 400
20.90±0.52***
32.11±4.81 33.48±5.62 33.48±6.49 32.14±7.53 34.96±7.69
30.78±2.12***
48.82±10.37 47.08±13.42 47.08±15.46 44.84±16.12 41.12±15.64
4.41±0.05***
7.64±0.39 7.53±1.19 7.73±0.91 6.33±0.44* 6.50±0.33*
1.16±0.02 1.53±0.25 1.11±0.11 1.21±0.19 1.50±0.21 1.63±0.19
0.56±0.01***
0.22±0.02 0.17±0.01 0.20±0.02 0.20±0.02 0.23±0.02
1)NC: normal control, C: control, Met: metformin, P0: KGC05P0.
Data were expressed as mean±standard deviation. A significant difference was determined by Student’s t-test at P<0.05.
*P<0.05, ***P<0.001; compared with the control (C group).
공복혈당, lipid profile, 간기능 및 신장기능 지표 측정 혈청을 HITACHI-7180 생화학 자동분석기(HITACHI, Tokyo, Japan)를 이용하여 공복혈당, 혈중의 지질 지표인 TC(total cholesterol), TG(triglycerides), HDL-C(high density lipoprotein-cholesterol)와 LDL-C(low density lipoprotein-cholesterol), 간기능 지표인 ALT(alanine am- inotransferase)와 AST(aspartate aminotransferase) 및 신장기능 지표인 BUN(blood urea nitrogen)과 CREA (creatinine)를 측정하였다.
간조직 인슐린 민감성 단백질 분석
단백질의 발현량을 조사하기 위하여 간조직을 균질기로 균질화하고, RIPA buffer를 처리하여 원심분리 후 상등액인 단백질 추출물을 획득하였다. Bio-Rad protein assay dye (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA)를 이용하여 단백질을 정량 한 후 SDS-PAGE(sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacryl- amide gel electrophoresis)를 통해 단백질을 분자량 크기 별로 분리하였다. 분리된 단백질은 polyvinylidene fluoride membranes로 transfer 시킨 후 5% skim milk를 이용하여 1시간 동안 상온에서 blocking 하였다. 그리고 IRs, IRS-1, Akt, PI3K, AMPK, PPAR-γ(Cell Signaling, Danvers, MA, USA) 항체들을 1:1,000으로 희석하여 4°C에서 overnight 시켰다. TBST로 세척 후 2차 항체를 상온에서 1시간 반응시 키고 chemiluminescent substrate(ECL, GE Healthcare, Chalfont St. Giles, UK)를 이용하여 밴드를 확인하였다.
단백질은 Image J software java 1.8.0 program(NIH, Bethesda, MD, USA)을 이용하여 정량하였다.
통계처리
모든 실험에서 얻어진 결과는 SAS Program version 9.3 (SAS Institute, Cary, NC, USA)을 이용하여 분석하였고, 모든 측정 항목의 결과는 각 실험군의 평균(mean)±표준편 자(standard deviation, SD)로 표시하였다. 실험군 간의 유 의적 차이는 Student’s t-test를 실시하여 유의성 P<0.05 수준에서 검정하였다.
결과 및 고찰
실험동물의 체중 및 장기 무게 변화
KGC05P0 투여에 의한 실험동물의 체중 및 주요 장기에 미치는 영향을 확인하기 위해 실험동물에 12주간 투여한 후의 체중 변화, 간, 신장 및 근육의 무게를 측정하고 Table 2에 나타내었다. 실험 기간의 체중 변화는 정상 마우스인 NC군을 제외한 실험군인 C57BL/6J ob/ob 그룹들에서 초 기 체중과 12주 투여 완료 후 희생 전 무게가 그룹 간에 유의 적 차이를 보이지 않았다. 그러나 간의 무게는 정상 마우스 인 NC군에 비하여 대조군인 C군에서 고인슐린혈증 당뇨병 모델이 유의적으로 증가하는 것을 확인하였고, 대조적으로 P0 200군과 P0 400군에서 간의 무게가 유의적으로 감소하 였다. 이는 Harris(2005)의 연구에서 간의 비대화가 당뇨병 환자에서 나타난다는 결과를 통해 당뇨병으로 인한 간의 비 대화가 진행되었다는 것을 예상할 수 있었으며, KGC05P0 의 섭취로 간의 비대화가 억제된 것으로 시사된다. 또한 당 뇨병 유발 시간의 상대적인 무게가 유의적으로 증가한다는 Choi 등(2004)의 연구 결과와 비슷한 경향을 본 연구에서 확인하였다. 신장 및 근육의 무게는 유의적인 차이를 보이지 않았다.
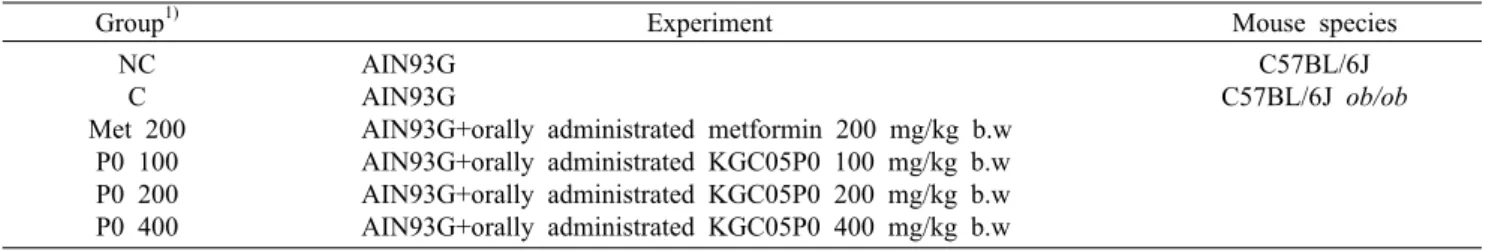
공복혈당 변화
당뇨병을 확인하는 대표적인 지표 중 하나인 공복혈당은 식후혈당과의 작용기전이 다르다고 보고되어 있다. 간의 인 슐린 민감성 감소, 췌장 β-cell의 기능 결핍과 지속적인 무 게 감소, GLP(glucagon-like peptide)-1 분비 변화, 글루 카곤 분비조절 기능 저하 등이 공복혈당 수치를 증가시킨다 고 알려져 있고, 말초 인슐린 민감성 감소, 췌장 β-cell의 점진적 기능 저하, GIP(glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide) 분비 감소 등이 식후혈당 수치를 증가시킨다 고 알려져 있다(Faerch 등, 2009a). 본 실험에서 KGC05P0 투여에 의한 실험동물의 공복혈당 수치에 미치는 영향을 확 인하기 위해 실험동물에 12주간 투여 후 공복혈당 결과를 Fig. 1에 나타내었다. NC군에 비하여 C군의 공복혈당이 유 의적으로 증가하는 것을 확인하였고, 대조적으로 P0 200군 과 P0 400군에서 C군에 비하여 공복혈당이 유의적으로 감 소하였다. 이는 당뇨병의 특징 중에서 인슐린 저항성 증가에
0 100 200 300 400 500 600
NC C Met 200 P0 100 P0 200 P0 400
Serum glucose level (mg/dL) . *** ***
*
Fig. 1. Effects of KGC05P0 on fasting glucose level in C57BL/
6J and C57BL/6J ob/ob mice. NC, C57BL/6J mice; C, C57BL/
6J ob/ob mice; Met 200, C57BL/6J ob/ob mice supplemented with metformin 200 mg/kg b.w.; P0 100, C57BL/6J ob/ob mice supplemented with KGC05P0 100 mg/kg b.w.; P0 200, C57BL/
6J ob/ob mice supplemented with KGC05P0 200 mg/kg b.w.;
P0 400, C57BL/6J ob/ob mice supplemented with KGC05P0 400 mg/kg b.w.. Data were expressed as mean±standard deviation.
A significant difference was determined by Student’s t-test at P<
0.05. *P<0.05, ***P<0.001; compared with the control (C group).
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18
NC C Met 200 P0 100 P0 200 P0 400
Serum insulin level (ng/mL) . ***
* * * *
Fig. 2. Effects of KGC05P0 on serum insulin level in C57BL/6J and C57BL/6J ob/ob mice. NC, C57BL/6J mice; C, C57BL/6J ob/ob mice; Met 200, C57BL/6J ob/ob mice supplemented with metformin 200 mg/kg b.w.; P0 100, C57BL/6J ob/ob mice sup- plemented with KGC05P0 100 mg/kg b.w.; P0 200, C57BL/6J ob/ob mice supplemented with KGC05P0 200 mg/kg b.w.; P0 400, C57BL/6J ob/ob mice supplemented with KGC05P0 400 mg/kg b.w.. Data were expressed as mean±standard deviation.
A significant difference was determined by Student’s t-test at P<
0.05. *P<0.05, ***P<0.001; compared with the control (C group).
따라 인슐린 민감성 감소로 인해 혈당의 조절이 어려워져서 공복혈당이 증가한 것을 뜻하며 지속 시 공복혈당장애가 유 도되는데, 상승한 공복혈당이 KGC05P0의 섭취로 인해 감 소하여 혈당조절에 도움을 주는 것을 확인하였다.
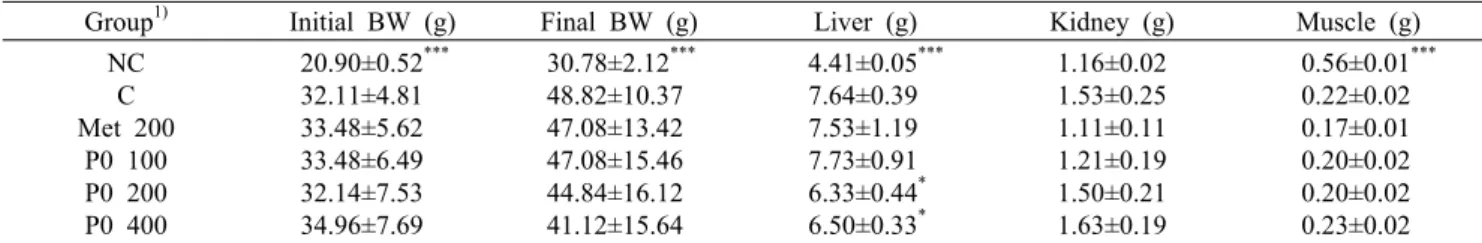
혈중 인슐린 농도 변화
제2형 당뇨병의 특징을 보면 정상혈당 상태에서 생활 습 관 등의 외부요인에 의해 체내조직의 인슐린 저항성 증가로 공복혈당장애 및 내당능장애가 발생하면 혈중 포도당의 농 도를 낮추기 위한 보상작용으로 혈중 인슐린 농도는 증가하 게 된다. 당뇨병 전 단계에서 공복혈당장애나 내당능장애가 개선되지 않고 지속되면 인슐린 저항성으로 인해 혈중 인슐 린 농도가 증가하여도 혈중 포도당 수치는 감소하지 않고 지속해서 증가하게 되고 체내에서는 혈중 포도당 농도를 낮 추기 위해 인슐린을 과량 분비하게 되는데, 이때 고인슐린혈 증이 발생하게 된다. 이러한 상태가 지속되면 인슐린을 분비 하는 췌장의 β-cell의 기능장애가 시작되고 당뇨로 발전하 면서 혈중 인슐린 농도가 감소하게 된다(DeFronzo, 1988).
본 실험에서 KGC05P0 투여가 실험동물의 인슐린 농도에 미치는 영향을 확인하기 위해 실험동물에 12주간 투여 후 혈중 인슐린 농도를 측정한 결과를 Fig. 2에 나타내었다.
정상 마우스인 NC군에 비하여 C군에서 증가한 혈당을 낮추 기 위한 보상작용으로 인슐린의 농도가 유의적으로 증가하 는 것을 확인하였고 대조적으로 P0 200군과 P0 400군에서 인슐린 농도가 유의적으로 감소하는 것을 확인하였다. 특히 양성대조군인 Met 200군과 KGC05P0을 섭취시킨 군에서 유사한 수준으로 인슐린이 개선되었으며, 이는 홍삼과 met- formin을 투여한 마우스에서 간의 유전자 발현양상이 비슷
한 Yuan 등(2008)의 연구와 유사한 경향을 보였다. 또한 Park 등(2020)의 선행연구에서는 C57BL/6J db/db 마우스 에 KGC05P0을 섭취시켰을 때 감소한 인슐린의 농도가 증 가됨을 확인하였는데, 대조적으로 C57BL/6J ob/ob 마우스 를 활용한 본 연구에서는 증가한 인슐린의 농도가 감소하였 다. 따라서 KGC05P0 섭취 시 인슐린 저항성으로 인한 인슐 린 수치의 불균형을 정상으로 조절하는 adaptogen의 역할 을 하는 것으로 예상할 수 있다. 그러나 인슐린 분비조절과 관련하여 인슐린을 생성하는 췌장조직을 활용하여 추가적 인 기전 연구가 진행되어야 할 것으로 사료된다.
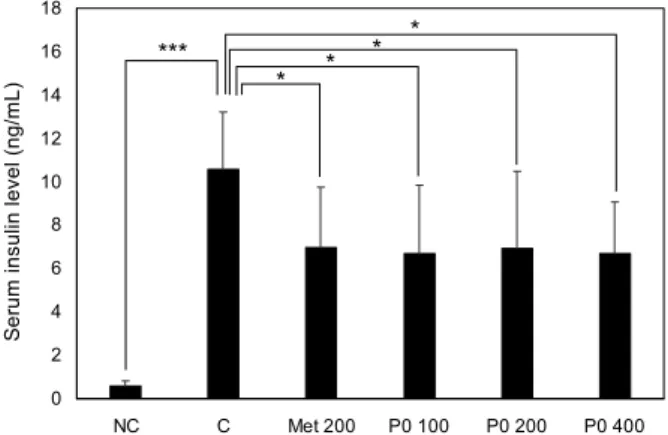
혈중 아디포넥틴 농도 변화
아디포넥틴은 비만과 매우 밀접한 연관성을 가지고 있으 며 중요한 역할을 하는 지표 중 하나로 알려져 있다. 그러나 여러 연구 결과를 통해 비만 외 다양한 질병과의 상관관계가 있다는 것이 알려져 있고, 특히 그중 하나가 당뇨병과 관련 되어 있다는 논문이 보고되었다(Lim과 Jang, 2008). 선행 연구 결과들에서 혈중 아디포넥틴은 복부지방, 공복 시 혈 당, 식후혈당, 공복 시 인슐린 농도를 낮추는 중요한 인자로 확인되었고(Snehalatha 등, 2003; Stefan 등, 2002) 또한 인슐린 민감성을 증가시킨다고 알려져 있는데, 근육과 간에 서 공통으로 AMPK를 활성화시켜 인슐린 민감성 증가 및 혈당 수치를 감소시키며(Yamauchi 등, 2002; Tomas 등, 2002) 간에서 인슐린 민감성 증가 시 포도당 신생합성이 억제되어 혈당 상승을 억제한다고 보고되었다(Combs 등, 2001). 본 실험에서 KGC05P0 투여가 실험동물의 아디포 넥틴 수치에 미치는 영향을 확인하기 위해 실험동물에 12주 간 투여 후 혈중 아디포넥틴 농도를 측정한 결과를 Fig. 3에
0 10 20 30 40 50 60
NC C Met200 P0 100 P0 200 P0 400
Serum adiponectin level (ng/mL) .
***
*
*
*
Fig. 3. Effects of KGC05P0 on serum adiponectin level in C57BL/
6J and C57BL/6J ob/ob mice. NC, C57BL/6J mice; C, C57BL/
6J ob/ob mice; Met 200, C57BL/6J ob/ob mice supplemented with metformin 200 mg/kg b.w.; P0 100, C57BL/6J ob/ob mice supplemented with KGC05P0 100 mg/kg b.w.; P0 200, C57BL/
6J ob/ob mice supplemented with KGC05P0 200 mg/kg b.w.;
P0 400, C57BL/6J ob/ob mice supplemented with KGC05P0 400 mg/kg b.w.. Data were expressed as mean±standard deviation.
A significant difference was determined by Student’s t-test at P<
0.05. *P<0.05, ***P<0.001; compared with the control (C group).
Table 3. Effects of KGC05P0 on serum lipid profile in C57BL/6J and C57BL/6J ob/ob (n=10)
Group1) TC2) TG3) HDL-C4) LDL-C5)
NC C Met 200
P0 100 P0 200 P0 400
113.0±29.1 141.1±23.3 179.0±27.6 205.3±24.5 185.4±26.8 115.5±15.5
86.6±16.2 117.2±18.9 129.0±25.9 104.8±29.2 92.0±18.5 49.4±3.2*
50.3±8.7 57.9±7.3 68.8±8.3 77.1±7.6 71.3±7.6 66.5±2.8
12.0±2.8 9.8±2.0 14.1±2.8 15.0±2.2 13.9±2.9 6.4±1.6
1)NC: normal control, C: control, Met: metformin, P0: KGC05P0.
2)TC: total cholesterol. 3)TG: triglycerides. 4)HDL-C: high density lipoprotein cholesterol. 5)LDL-C: Low density lipoprotein cholesterol.
Data were expressed as mean±standard deviation. A significant difference was determined by Student’s t-test at P<0.05.
*P<0.05; compared with the control (C group).
Table 4. Functional indicators of liver and kidney from blood in C57BL/6J and C57BL/6J ob/ob (n=10)
Group1) ALT2) AST3) BUN4) CREA5)
NC C Met 200
P0 100 P0 200 P0 400
181.9±15.6* 359.9±55.5 394.3±46.1 464.9±51.3 432.3±37.3 127.8±52.5*
123.5±10.0**
460.7±102.3 416.8±103.6 545.4±95.5 505.0±101.8 97.5±74.4*
25.2±1.4 27.0±1.5 25.2±2.0 23.0±1.2 22.1±1.3 25.5±0.6
0.32±0.01 0.33±0.01 0.31±0.01 0.34±0.02 0.34±0.01 0.33±0.01
1)NC: normal control, C: control, Met: metformin, P0: KGC05P0.
2)ALT: alanine aminotransferase. 3)AST: aspartate aminotransferase. 4)BUN: blood urea nitrogen. 5)CREA: creatinine.
Data were expressed as mean±standard deviation. A significant difference was determined by Student’s t-test at P<0.05.
*P<0.05, ***P<0.001; compared with the control (C group).
나타내었다. 정상 마우스인 NC군에 비하여 C군에서 증가한 인슐린 저항성으로 인하여 혈중 아디포넥틴이 감소하는 것 을 확인하였고, 대조적으로 P0 200군과 P0 400군에서 인슐 린 농도가 유의적으로 증가하는 것을 확인하였다. 아디포넥 틴은 비만뿐 아니라 혈당과 관련하여 인슐린 민감성을 향상 시켜 혈당 개선에 도움을 주는 지표이며, 간조직에서 인슐린
민감성과 관련된 단백질들과 세포 내 에너지대사 조절작용 을 하는 AMPK 단백질을 유의적으로 개선시킨 결과와 같은 경향임을 확인하였다.
혈중 lipid profile, 간기능 및 신장기능 지표 변화 당뇨는 비만과 그에 따른 합병증인 이상지질혈증 등과 매 우 밀접한 연관성을 가지고 있다. 그에 따라 KGC05P0의 섭취가 혈중 지질의 변화와 간기능 및 신장기능에 미치는 영향과 그에 따른 안전성의 유무를 확인하고자 실험동물에 12주간 투여 후 혈중 지질 농도를 측정한 결과를 Table 3, 간기능 및 신장기능 지표들을 측정한 결과를 Table 4에 나 타내었다. 혈중 지질 중 TG가 P0 400군에서 C군에 대비하 여 유의적으로 감소한 것을 확인하였지만 TC, LDL 및 HDL 은 유의적인 차이를 확인하지 못하였다. 간기능의 지표로는 ALT, AST가 있으며 정상 마우스인 NC군에 비하여 C군에 서 증가한 ALT, AST가 P0 400군에서 유의적으로 감소하 는 것을 확인하였다. 신장기능 지표인 BUN, CREA는 모든 군 간 유의적인 차이가 없음을 확인하였다. ALT, AST, BUN 및 CREA는 기능성 지표뿐만 아니라 독성지표로도 활 용이 되며 안전성 확인을 위해 GLP(Biotoxtech study no:
B17919~24) 시설에서 독성검사를 진행한 결과, KGC05P0 의 반복 투여 실험에서 NOAEL(no observed adverse ef- fect level)은 2 g/kg/d이며 복귀돌연변이시험, 염색체이상 시험 및 소핵시험에서 독성이 없음을 확인하였다. 또한, 당 뇨병환자에서 간기능의 지표인 ALT, AST가 증가하여 간기 능 저하 및 간독성이 나타났다는 Harris(2005)의 연구 결과
A B C
D E
F G H I
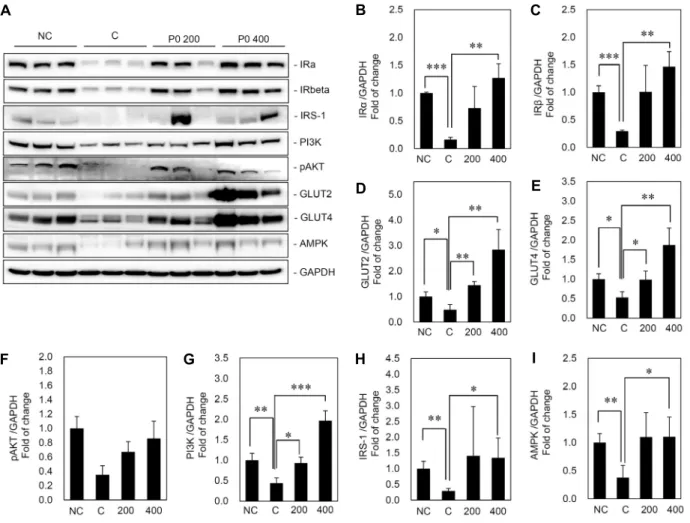
Fig. 4. Effects of KGC05P0 on protein expression in liver of C57BL/6J and C57BL/6J ob/ob mice. (A) Protein expressions, (B) the ratio of IRα/GAPDH protein expression, (C) the ratio of IRβ/GAPDH protein expression, (D) the ratio of GLUT2/GAPDH protein expression, (E) the ratio of GLUT4/GAPDH protein expression, (F) the ratio of pAKT/GAPDH protein expression, (G) the ratio of PI3K/GAPDH protein expression, (H) the ratio of IRS-1/GAPDH protein expression, (I) the ratio of AMPK/GAPDH protein expression. NC, C57BL/6J mice; C, C57BL/6J ob/ob mice; P0 200 and 200, C57BL/6J ob/ob mice supplemented with KGC05P0 200 mg/kg b.w.; P0 400 and 400, C57BL/6J ob/ob mice supplemented with KGC05P0 400 mg/kg b.w.. Data were expressed as mean±standard deviation. A significant difference was determined by Student’s t-test at P<0.05. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001;
를 바탕으로 본 실험의 결과에서는 KGC05P0 섭취 시 독성 이 없으며 간에서 ALT, AST의 양을 감소시켜 간기능을 향 상시킨다는 것을 확인하였다. 따라서 본 연구의 간기능 향상 과 함께 인슐린 민감성 증가를 통해 공복혈당이 감소하는 기전과 부합하는 결과임을 확인하였다.
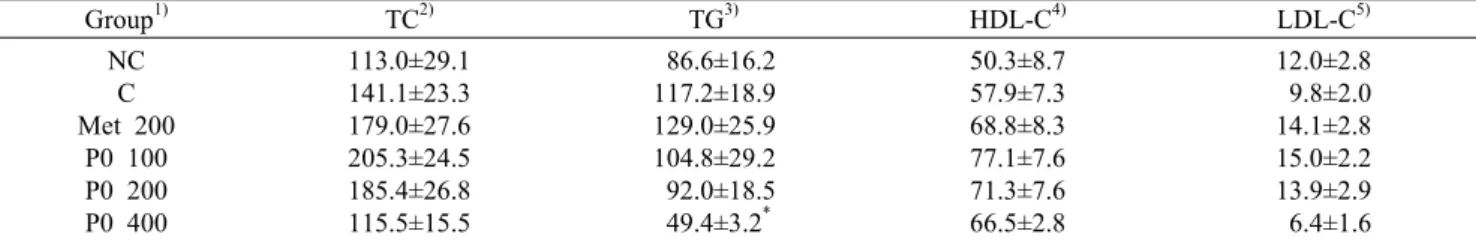
간조직의 인슐린 민감성 단백질 변화
식후 혈중 포도당을 낮추는 여러 작용 중 하나는 근육에서 발생되는데 골격근이 혈중 포도당을 흡수하는 것을 통해 혈 당 수치를 낮추는 것이다. 이 작용에는 말초 인슐린 민감도 가 매우 중요한 역할을 하며 근육으로 흡수된 포도당은 대부 분 글리코겐으로 저장된다(O’Rahilly 등, 1994). 따라서 근 육의 인슐린 민감성이 감소하면 혈당이 상승하게 되며, 이는 식후혈당의 급격한 상승과 연관이 있는 것으로 알려져 있다 (Faerch 등, 2009a; Abdul-Ghani 등, 2006; Nóvoa 등, 2005). 그러나 공복 혈중 포도당을 낮추는 작용은 간에서
주로 발생하며, 간은 체내 에너지 공급과 수요에 관련된 대 사와 해독작용을 담당하는 기관으로 특히 포도당 대사를 통 해 혈당을 일정하게 유지시켜주는 매우 중요한 역할을 한다 (DeFronzo 등, 1987). 공복 시 체내 필요한 포도당은 포도 당신생합성에 의해서 공급되는데, 특히 간에서는 글리세롤 로부터 포도당을 합성하고 이를 혈중으로 방출하여 혈당을 조절하게 된다(Megyesi 등, 1967). 이때 외부 요인으로 인 하여 간에서 인슐린 저항성이 증가하면 혈당조절이 어려워 지고, 이는 공복혈당장애 및 내당능장애로 발전되는 것으로 알려져 있다(Cornier 등, 2008). 본 실험에서는 KGC05P0 을 섭취한 고인슐린/당뇨 동물모델에서 적출한 간조직을 활 용하여 인슐린 저항성과 관련 있는 단백질을 분석하였으며 그 결과는 Fig. 4에 나타내었다. 정상 마우스인 NC군에 비 하여 C군에서 간조직의 IRs, IRS-1, Akt, AMPK, PI3K, GLUT2/4 단백질이 현저히 감소함을 확인할 수 있는데, 인 슐린 저항성으로 인해 감소한 단백질이 KGC05P0를 섭취한
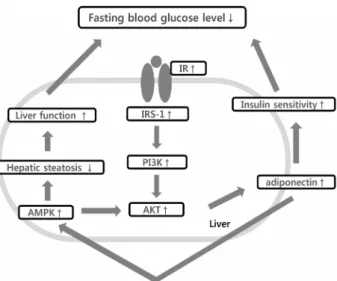
Fig. 5. Expected mechanism of fasting blood glucose control by KGC05P0. IR, insulin receptor; IRS-1, insulin receptor sub- strate-1; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase; AKT, protein kin- ase B; AMPK, activated protein kinase.
군에서 유의적으로 증가하였고, 특히 P0 200군보다 P0 400 군에서 더 많은 단백질이 유의적으로 증가하는 것을 확인하 였다. 인슐린 저항성의 증가는 인슐린 민감성의 감소를 뜻하 는데 이는 혈당이 높아지게 되면 생리적으로 인슐린의 분비 가 증가되고, IR에 binding 함으로 시작된다. 그리고 PI3K pathway가 활성화되어 혈당 조절기전이 진행되는데, 이때 PI3K 단백질이 AMPK, Akt, PI3K, GLUT2/4의 작용에 영 향을 주고 인슐린 민감성이 증가되어 높아진 혈당을 빠르게 낮추어 정상혈당으로 돌아오게 된다. KGC05P0을 섭취함 으로써 인슐린 민감성에 영향을 주는 단백질의 활성화가 유 도되고 혈당을 조절하게 되는 것이다.
요 약
본 연구에서는 홍삼 비사포닌 분획 추출물(KGC05P0)이 인 슐린 민감성 향상과 아디포넥틴의 연관성 및 그에 따른 혈당 변화에 미치는 영향을 확인하기 위하여 고인슐린혈증 및 제 2형 당뇨 동물모델에서 간조직의 인슐린 민감도 활성 단백 질, 혈중 포도당 수치, 혈중 인슐린 수치, 혈중 아디포넥틴 수치의 변화를 살펴보았다. 그 결과 인슐린 민감성을 향상시 키는 단백질 발현 증가와 혈중 아디포넥틴 수치 증가 및 공 복혈당, 인슐린 농도를 감소시켜 고인슐린혈증 억제 및 항당 뇨 효과를 나타내는 것을 확인하였다. 특히 KGC05P0은 양 성대조군인 metformin과 유사한 수준으로 지표들을 개선하 여 metformin이 나타낼 수 있는 lactic acidosis와 같은 부 작용이 없고 건강한 혈당 유지에 도움을 주는 소재로 사용 가능성을 시사하였다. 따라서 KGC05P0는 고인슐린혈증의 제2형 당뇨병 모델에서 간기능의 향상과 함께 인슐린 민감 성과 관련된 지표들의 활성화를 통해 혈당 조절에 효능이 있음을 확인하였다.
REFERENCES
Abdul-Ghani MA, Sabbah M, Kher J, Minuchin O, Vardi P, Raz I. Different contributions of insulin resistance and beta- cell dysfunction in overweight Israeli Arabs with IFG and IGT. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2006. 22:126-130.
Aoyama-Sasabe S, Fukushima M, Xin X, Taniguchi A, Nakai Y, Mitsui R, et al. Insulin secretory defect and insulin resist- ance in isolated impaired fasting glucose and isolated im- paired glucose tolerance. J Diabetes Res. 2016. Article ID:
1298601. https://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/1298601
Attele AS, Zhou YP, Xie JT, Wu JA, Zhang L, Dey L, et al.
Antidiabetic effects of Panax ginseng berry extract and the identification of an effective component. Diabetes. 2002. 51:
1851-1858.
Cheon JM, Kim DI, Kim KS. Insulin sensitivity improvement of fermented Korean red ginseng (Panax ginseng) mediated by insulin resistance hallmarks in old-aged ob/ob mice. J Ginseng Res. 2015. 39:331-337.
Choi CB. Potential therapeutic strategies for fat induced insulin resistance. J Korean Endocr Soc. 2009. 24:65-74
Choi SP, Choi HT, Lee HJ, Moon SY, Kim SH, Lee BG, et al. Hypoglycemic effect of the functional food manufactured by fermented soybean as main materials in streptozotosin-in- duced diabetic rats. J Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr. 2004. 33:
1126-1132.
Combs TP, Berg AH, Obici S, Scherer PE, Rossetti L. Endoge- nous glucose production is inhibited by the adipose-derived protein Acrp30. J Clin Invest. 2001. 108:1875-1881.
Cordero-Herrera I, Martin MA, Bravo L, Goya L, Ramos S.
Cocoa flavonoids improve insulin signalling and modulate glucose production via AKT and AMPK in HepG2 cells. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2013. 57:974-985.
Cornier MA, Dabelea D, Hernandez TL, Lindstrom RC, Steig AJ, Stob NR, et al. The metabolic syndrome. Endocr Rev.
2008. 29:777-822.
Cryer PE, Davis SN, Shamoon H. Hypoglycemia in diabetes.
Diabetes Care. 2003. 26:1902-1912.
DeFronzo RA, Ferrannini E. Regulation of hepatic glucose me- tabolism in humans. Diabetes Metab Rev. 1987. 3:415-459.
DeFronzo RA. The triumvirate: β-cell, muscle, liver: a collusion responsible for NIDDM. Diabetes. 1988. 37:667-687.
Eckel RH, Grundy SM, Zimmet PZ. The metabolic syndrome.
Lancet. 2005. 365:1415-1428.
Faerch K, Borch-Johnsen K, Holst JJ, Vaag A. Pathophysiology and aetiology of impaired fasting glycaemia and impaired glucose tolerance: does it matter for prevention and treatment of type 2 diabetes?. Diabetologia. 2009a. 52:1714-1723.
Faerch K, Vaag A, Holst JJ, Hansen T, Jørgensen T, Borch- Johnsen K. Natural history of insulin sensitivity and insulin secretion in the progression from normal glucose tolerance to impaired fasting glycemia and impaired glucose tolerance:
the Inter99 study. Diabetes Care. 2009b. 32:439-444.
Harris EH. Elevated liver function tests in type 2 diabetes. Clin- ical Diabetes. 2005. 23:115-119.
Kahn SE. The relative contributions of insulin resistance and be- ta-cell dysfunction to the pathophysiology of Type 2 diabetes.
Diabetologia. 2003. 46:3-19.
Katsuda Y, Ohta T, Shinohara M, Bin T, Yamada T. Diabetic mouse models. Open J Anim Sci. 2013. 3:334-342.
Kim JH, Hahm DH, Yang DC, Kim JH, Lee HJ, Shim I. Effect of crude saponin of Korean red ginseng on high-fat diet-in- duced obesity in the rat. J Pharmacol Sci. 2005. 97:124-131.
Kim ND. Pharmacologic effect of red ginseng. J Ginseng Res.
2001. 25:2-10.
Kopelman PG. Obesity as a medical problem. Nature. 2000. 404:
635-643.
Kwon HO, Lee MH, Kim YJ, Kim E, Kim OK. Beneficial effects of Acanthopanax senticocus extract in type Ⅱ diabetes ani- mal model via down-regulation of advanced glycated hemo- globin and glycosylation end products. J Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr. 2016. 45:929-937.
Lim S, Jang HC. Clinical implication of adiponectin. Korean Diabetes J. 2008. 32:85-97.
Megyesi C, Samols E, Marks V. Glucose tolerance and diabetes in chronic liver disease. Lancet. 1967. 2:1051-1056.
Meyer C, Pimenta W, Woerler HJ, Haeften TV, Szoke E, Mitra- kou A, et al. Different mechanisms for impaired fasting glu- cose and impaired postprandial glucose tolerance in humans.
Diabetes Care. 2006. 29:1909-1914.
Nόvoa FJ, Boronat M, Saavedra P, Diaz-Cremades JM, Varillas VF, Roche FL, et al. Differences in cardiovascular risk factors, insulin resistance, and insulin secretion in individuals with normal glucose tolerance and in subjects with impaired glu- cose regulation: The Telde Study. Diabetes Care. 2005. 28:
2388-2393.
O’Rahilly S, Hattersley A, Vaag A, Gray H. Insulin resistance as the major cause of impaired glucose tolerance: a self-ful- filling prophesy?. Lancet. 1994. 344:585-589.
Oh MJ, Kim HJ, Park EY, Ha NH, Song MG, Choi SH, et al.
The effect of Korean Red Ginseng extract on rosiglitazone-in- duced improvement of glucose regulation in diet-induced obese mice. J Ginseng Res. 2017. 41:52-59.
Park SJ, Lee DS, Kim DK, Lee MH, In G, Han ST, et al. The non-saponin fraction of Korean red ginseng (KGC05P0) de- creases glucose uptake and transport in vitro and modulates glucose production via down-regulation of the PI3K/AKT pathway in vivo. J Ginseng Res. 2020. 44:362-372.
Rhee SY, Woo TJ, Chon S, Hwang YC, Oh S, Ahn KJ, et al.
Characteristics of insulin resistance and insulin secretory ca- pacity in Korean subjects with IFG and IGT. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2010. 89:250-255.
Snehalatha C, Mukesh B, Simon M, Viswanathan V, Haffner SM, Ramachandran A. Plasma adiponectin is an independent predictor of type 2 diabetes in Asian indians. Diabetes Care.
2003. 26:3226-3229.
Sotaniemi EA, Haapakoski E, Rautio A. Ginseng therapy in non-insulin-dependent diabetic patients. Diabetes Care. 1995.
18:1373-1375.
Stefan N, Vozarova B, Funahashi T, Matsuzawa Y, Weyer C, Lindsay RS, et al. Plasma adiponectin concentration is asso- ciated with skeletal muscle insulin receptor tyrosine phos- phorylation, and low plasma concentration precedes a de- crease in whole-body insulin sensitivity in humans. Diabetes.
2002. 51:1884-1888.
Taniguchi CM, Emanuelli B, Kahn CR. Critical nodes in signal- ing pathways: insights into insulin action. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2006. 7:85-96.
Tomas E, Tsao TS, Saha AK, Murrey HE, Zhang CC, Itani SI, et al. Enhanced muscle fat oxidation and glucose transport by ACRP30 globular domain: acetyl-CoA carboxylase in- hibition and AMP-activated protein kinase activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002. 99:16309-16313.
Vuksan V, Sievenpiper JL, Koo VYY, Francis T, Beljan-Zdrav- kovic U, Xu Z, et al. American ginseng (Panax quinquefolius L) reduces postprandial glycemia in nondiabetic subjects and subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Arch Intern Med. 2000.
160:1009-1013.
Whiteman EL, Cho H, Birmbaum MJ. Role of Akt/protein kinase B in metabolism. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2002. 13:444-451.
Yamauchi T, Kamon J, Minokoshi Y, Ito Y, Waki H, Uchida S, et al. Adiponectin stimulates glucose utilization and fat- ty-acid oxidation by activating AMP-activated protein kinase.
Nat Med. 2002. 8:1288-1295.
Yuan HD, Shin EJ, Chung SH. Anti-diabetic mechanism study of Korean red ginseng by transcriptomics. Yakhak Hoeji.
2008. 52:345-354.
Yun SN, Moon SJ, Ko SK, Im BO, Chung SH. Wild ginseng prevents the onset of high-fat diet induced hyperglycemia and obesity in ICR mice. Arch Pharm Res. 2004. 27:790-796.