123
서 론테크네슘 표지 피틴산(phytate)은 세망내피계(reticuloen- dothelial system)의 영상을 위해 개발된 방사성의약품이다.1) 정맥주사 후 테크네슘 표지 피틴산은 체내에서 칼슘과 결 합하여 세망내피계에 모이게 된다. 간의 쿠퍼세포(Kupffer cell)는 체내 세망내피계 세포의 80∼90%를 차지하므로 테 크네슘 표지 피틴산을 주사하고 얻은 영상으로 간을 관찰 할 수 있다.2) 정상인에서는 주사량의 대부분이 간에 섭취되 나, 간경변증 환자에서는 간에서 방사성의약품의 제거가 늦어지고, 간에서 섭취가 적고 불균일해지며, 간외 세망내
피계의 섭취가 증가하는 것으로 알려져 있다.3-5)
간 스캔의 임상적 이용은 초음파, 컴퓨터단층촬영술(CT) 및 자기공명영상(MRI) 등 다른 진단 기술의 등장으로 국소 적인 병변을 찾는 목적으로는 줄어들고 있는 추세지만, 간 에 생긴 종괴의 성질을 파악하거나 간경변증과 같은 미만 성 간 질환에서 기능적인 평가에 사용될 수 있다.5,6) 간경변 증의 진단은 생검을 통해 이루어지지만, 환자의 추적관찰 은 일반적으로 생화학적 검사를 통해 이루어진다. 저자들 은 간경변증 환자의 간 스캔 소견과 생화학적 검사 및 임상 소견과의 관계를 살펴보고 간경변증 환자의 평가에 있어서 간 스캔의 유용성을 알아보고자 하였다.
대상 및 방법
1. 대상
대상 환자는 고신대학교 복음병원에서 간경변증으로 진 단된 환자 중 간 스캔을 시행한 환자들로 일정기간의 추적 관찰이 가능했던 44명을 대상으로 하였다. 환자 중 남자는
간 스캔을 이용한 간경변증 환자의 평가
1고신대학교 의학부 장기려 기념 간 연구소, 2핵의학교실, 3외과학교실, 4내과학교실 배상균1,2․이석모2․신동훈1,3․이상욱1,4․이충한1,3
Clinical Evaluation of Liver Cirrhosis Patients Using Liver Scintigraphy
Sang Kyun Bae, M.D.
1,2, Seok-Mo Lee, M.D.2, Dong HoonShin, M.D.
1,3, Sang Uk Lee, M.D.1,4 and Choong Han Lee, M.D.1,3Departments of
2Nuclear Medicine,
3Surgery and
4Internal Medicine, Kosin University College of Medicine,
1Gospel Hospital, Chang Kee Ryo Memorial Liver Institute
Background/Aims: Liver scintigraphy is a useful tool in
evaluating the chronic liver disease, even though it is less sensitive to detect a mass lesion in the liver than ultra- sonography, computed tomography (CT), or magnetic reso- nance imaging (MRI). We evaluate the clinical usefulness of liver scintigraphy in patients with liver cirrhosis by comparing with the clinical and biochemical indices.Methods: Liver scintigraphy was taken beginning 20 minutes
after the intravenous injection of 370 MBq of Tc-99m phytate.Images were obtained in multiple views with a gamma camera (BasicamⓇ, Siemens). The size of the liver, left lobe
enlargement, inhomogeneity of radioactivity, the size of the spleen, the extrahepatic uptake were evaluated on liver scintigraphy. The compared clinical indices were serum albumin level, serum bilirubin level, INR (international nor- malized ratio) for prothrombin time, the presence of hepatic coma, and esophageal varix.
Results: Forty four patients (M:F=24:20) were included.
The extrahepatic uptake such as bone marrow and splenic uptake was positively correlated with the level of serum bilirubin and negatively correlated with the level of serum albumin. The size of the spleen, inhomogenous liver uptake, hypertrophy of left lobe was positively correlated with the degree of esophageal varix. The size of the liver was negatively correlated with that of esophageal varix.
Conclusion: We suggest that scintigraphic findings in liver
scintigraphy could be used in the evaluation of patients with liver cirrhosis not only to diagnose cirrhosis but also to know the severity of cirrhosis. (Korean J HBP Surg 2002;6:123-127)ꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏ Key Words: Tc-99m phytate, Liver scintigraphy, Liver cir-
rhosis
중심 단어: 테크네슘 표지 피틴산, 간 스캔, 간경변증
책임저자:배상균, 부산시 서구 암남동 34
ꂕ 602-702, 고신대학교 복음병원 핵의학과 Tel: 051-990-6384, Fax: 051-990-3027 E-mail: sbae@ns.kosinmed.co.kr
이 연구는 고신대학교 의학부 장기려 기념 간 연구소 연구비의 지
원을 받았음.
24명, 여자는 20명이었고 이들의 평균 연령은 50세(32∼
77세)였다. 간경변증의 원인은 알코올성 간경변증이 2명, 바이러스성 간염 후 간경변증이 28명(type B 25명, type C 3명)이었고 원인을 알 수 없었던 경우가 14명이었다.
2. 방법
1) 영상 획득: Tc-99m phytate 370 MBq을 주사하고 20분 후에 환자의 복부 전면상, 후면상, 우사면상, 우측면상, 좌 측면상을 범용 평형구멍조준기(all purpose parallel hole collimator)를 장착한 감마카메라(BasicamⓇ, Siemens)를 이용 하여 각각 70만 계수하였다.
2) 영상판독: 간 스캔 소견의 척도는 간 크기, 좌엽비대 유 무, 간실질 섭취의 균일성, 간 스캔에서 비장의 크기, 비장 섭취 정도, 골수섭취 정도로 하였으며, 모든 스캔은 두 명의 핵의학 의사에 의해 판독되었다. 간 스캔에서 간과 비장의 크기는 영상을 얻을 때 이용한 길이 표지자(10 cm)를 참고 로 하였고 후면상에서 크기를 비교하였다. 간 스캔의 척도 별 분류는 모두 반정량적으로 이루어졌다(Fig. 1, Table 1).
3) 생화학적 검사 및 임상소견: 생화학적 검사 및 임상소 견의 항목으로 혈청 알부민, 혈청 빌리루빈, INR (Inter- national Normalized Ratio) for Prothrombin time, 간성혼수의
유무와 식도정맥류의 정도를 조사하였다. 환자의 생화학적 검사치 및 임상소견은 간 스캔 시행 전후 1주일 이내의 것 으로 하였다. 간성혼수는 임상양상과 신경학적 증후로 판 단하여 발현여부를 나누었고 식도 정맥류의 확인은 간 스 캔 시행과 가장 가까운 시기에 시행한 식도위장관의 내시 경 소견을 Paquet7)의 기준에 따라 나누었다.
4) 통계: 반정량적으로 등급 지어진 영상소견의 각 척도 와 환자의 혈액 검사치 및 임상소견의 상관정도를 Pearson 의 상관계수를 이용하여 평가하였다. 통계결과는 유의수준 0.05에서 분석하였고, 통계분석에는 SPSS 10.0.7 (SPSS Inc., Chicago)을 이용하였다.
결 과
간 스캔의 척도와 임상 및 혈액화학 검사소견의 상관관계 를 Table 2에 정리하였다. 간 스캔 소견에서 골수 섭취 증가
Fig. 1. (A) Normal liver scintigraphy showing faint spleen uptake with normal configuration and distribution of radioactivity in the liver. (B) Relative hypertrophy of the left lobe with splenomegaly and increased splenic and bone marrow uptake. (C) In patient with severe liver cirrhosis showing shrinkage of the liver, especially right lobe and huge splenomegaly with increased splenic and bone marrow uptake.
Table 1. Grade of parameters on liver scan
ꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚ
Parameter Grade
ꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏ Bone marrow 0: normal
uptake 1: mild uptake (only vertebral bone marrow) 2: moderate uptake (vertebral and rib bone marrow)
3: marked uptake (vertebral and rib bone marrow≥hepatic uptake)
Splenic uptake 0: normal (not or faintly visualized spleen on anterior view)
1: mild uptake (<hepatic uptake) 2: moderate uptake (=hepatic uptake) 3: marked uptake (>hepatic uptake) Spleen size 0: normal (<12 cm)
1: mild enlargement (≥12 cm, ≤13 cm) 2: moderate enlargement (>13 cm, ≤14 cm) 3: marked enlargement (>14 cm)
Homogenity of 0: homogeneous
parenchymal 1: mild or moderate inhomogeneous uptake 2: marked inhomogeneous
Hypertrophy of 0: normal
left lobe 1: mild enlargement (<Rt. hepatic lobe) 2: moderate enlargement (=Rt. hepatic lobe) 3: marked enlargement (>Rt. hepatic lobe) Liver size -1 shrinkage
0 normal
1 moderate enlargement 2 marked enlargement
ꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏ
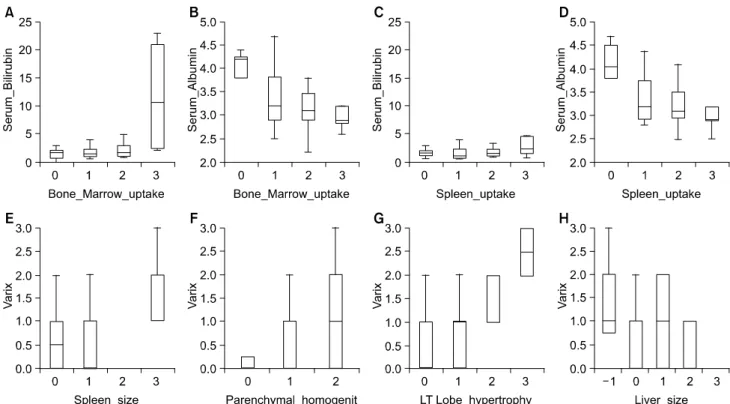
는 혈중 빌리루빈 수치와 유의한 상관관계(r=0.482, Fig. 2A) 를, 혈중 알부민 수치와는 유의한 음의 상관관계(r=-0.461, Fig. 2B)를 보였다. 비장의 섭취 정도는 혈중 빌리루빈 수치 와는 상관관계(r=0.320, Fig. 2C)를, 혈중 알부민 수치와는 음의 상관관계(r=-0.455, Fig. 2D)를 나타냈다. 비장의 크기 는 식도정맥류의 등급과 상관관계(r=0.520, Fig. 2E)를 보였 다. 간 스캔에서 간실질의 불균일 정도는 식도정맥류의 등 급과 상관관계(r=0.355, Fig. 2F)를 보였고, 간 좌엽비대 정 도도 식도정맥류의 등급과 상관관계(r=0.593, Fig. 2G)를 보 였다. 간의 크기는 식도정맥류의 등급과 음의 상관관계(r=
-0.353, Fig. 2H)를 보였다.
고 찰
방사성 교질을 이용한 간 스캔은 초음파, CT 및 MRI와 같은 경쟁적인 진단기술이 발달함에 따라 해부학적인 정보 제공의 측면에서는 그 유용성이 낮아졌지만, 급성 및 만성 간염과 간경변증과 같은 미만성 간 질환의 기능을 영상화 할 수 있으며, 장관 내 공기나 다른 장치 등의 영향을 받지 않고 간의 형태를 전체적인 영상으로 보여준다는 장점이 있다.8,9) 또한 간내 공간점유병소의 성질을 파악하는 목적
Fig 2. (A), (B) Bone marrow uptake on the liver scintigraphy shows positive correlation with serum bilirubin and negative correlation
with serum albumin. (C), (D) The spleen uptake shows positive correlation with serum bilirubin and negative correlation with serum albumin. (E) The spleen size reveals positive correlation with the grade of esophageal varix. (F), (G) The parenchymal inhomogenity and left lobe hypertrophy of the liver show positive correlation with the grade of esophageal varix. (H) The liver size has negative correlation with the grade of esophageal varix.
Table 2. Correlation between scintigraphic findings and clinical indices
ꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚ Hepatic
Serum Serum INR
encepha- Varix
bilirubin albumin for PT lopathy
ꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏ Bone marrow
0.482
†-0.461
†0.257 0.324 0.115 uptake
Splenic size 0.105 -0.264 0.152 0.520
†Spleen uptake 0.320* -0.455
†0.136 0.310 0.170 Homogenity of
parenchymal 0.094 -0.110 0.087 -0.152 0.355*
uptake Hypertrophy of
-0.014 -0.150 0.149 -0.001 0.593
†left lobe
Liver size 0.204 0.230 0.093 0.053 -0.353*
ꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏ INR for PT = international normalized ratio for prothrombin time.
* = P<0.05;
†= P<0.01
으로도 이용되고 있다.
방사성 교질은 세망내피계의 대부분을 이루는 간의 쿠퍼 세포에 의해 탐식되며, 따라서 간 영상에 쓰이고 있다. 교질 은 1∼5μm 크기의 액체상에 부유된 입자를 말하며, 체내에 서 생물학적인 분포는 입자의 크기, 표면의 전하, 항원성과 주입된 입자의 수에 의해 결정된다.10) 100 nm 이하의 교질 들은 주로 골수에 집적되고, 300∼1,000 nm의 교질들은 주 로 간에 집적되며, 1∼5μm의 교질은 주로 비장에 모인다.
본 연구에 사용된 피틴산은 체내에서 칼슘과 착화되어 교 질을 형성하며, 입자의 크기가 비교적 작아 정상인의 영상 에서는 비장의 섭취가 거의 없는 편이다.
이번 연구의 대상이 된 간경변증 환자에서의 일반적인 간 스캔 소견으로는 간경변증 초기에는 지방침착으로 섭취 의 감소 및 불균일, 간비대, 비장 및 골수의 교질 섭취 증가 가 나타난다.4) 병이 진행되면 간의 크기는 작아지고 교질 섭취의 재분포가 더욱 현저해 진다. 아울러 비장의 종대와 섭취증가가 나타날 수 있다. 간의 섭취는 더욱 감소되고 불 균일해지는데, 심한 경우 마치 종괴처럼 오인되기도 한다.
간의 섭취 감소는 간경변증이 진행됨에 따라 쿠퍼세포의 수가 감소하는 것으로 설명될 수 있는데, 이것은 괴사, 심 한 염증반응, 반흔 형성 및 재생성 결절 때문이며 간내 단락(intrahepatic shunt)에 의해서도 섭취의 감소가 일어난 다.5,11,12)
세망내피계에서 간의 쿠퍼세포가 차지하는 비중이 매우 크므로 간경변증이 진행되면 간의 섭취 감소와 더불어 비 장과 골수의 섭취가 증가하는 재분포현상이 일어난다. 이 런 재분포는 여러 가지 기전으로 설명되고 있다. Fernandez 등13은 간외섭취 증가와 쐐기 간정맥압 사이에 관련이 있다 고 보고하였다. 즉, 간 스캔에서 비장과 골수가 보이면 쐐기 간정맥압이 18 mmHg보다 크고, 비장과 골수가 보이지 않 으면, 쐐기 간정맥압이 18 mmHg보다 낮았다. Gourgoutis 등14) 의 연구에서도 비장의 섭취와 쐐기 간정맥압 사이에 관련 성을 보이고 있다. 문맥 고혈압이 재분포현상에 중요한 요 소이긴 하지만, 우회수술 후에 문맥 고혈압이 좋아지더라 도 재분포현상은 변하지 않는 경우도 있다.11) 간외 섭취의 증가는 이론적으로 간 이외에 세망내피계 세포의 증가와 활동성의 증가로도 설명될 수 있다. Horisawa 등11)의 연구 에 의하면 간정맥이나 말단에서 방사성 교질의 추출률이 정상보다 증가되지 않았고, 교질에 대한 테크네슘의 분획 제거율이 감소되었음을 증명하여 방사성 교질이 간내 시누 소이드(sinusoid)를 우회하는 간내단락에 의한 것으로 설명 되고 있다. Huet 등15)도 간외섭취가 문맥 고혈압의 정도와 는 관계가 없으며, 주로 간에서 교질을 처리하지 못하기 때 문이며, 이는 간내 미세순환의 변화와 관련있다고 보고하 였다.
본 연구에서 비장과 골수 등 간외 섭취의 증가는 혈청 빌 리루빈의 증가와 혈청 알부민의 감소와는 유의한 관련성이
있어 간경변증의 중증도와 관련이 있었으나, 문맥 고혈압 의 합병증인 식도정맥류의 정도나 간성 혼수와는 관련성이 없었다. 이 결과는 간외 섭취의 기전을 연구한 이전의 결과 중 문맥 고혈압보다는 간내단락과 같은 간내 미세순환의 변화와 더 일치하는 소견이라 생각한다. 간외 섭취의 증가 와는 달리 비장의 비대, 간섭취의 불균일성, 간의 위축 및 좌엽의 비대 소견은 식도 정맥류의 정도와 일치하여 이들 소견이 문맥 고혈압의 합병증과 관계 있는 소견이라 생각 한다.15) 하지만, 간성 혼수와는 유의한 상관관계를 보이지 않았는데 앞으로 간성 뇌증의 증상 증후를 세분화한 비교 가 필요하리라 생각한다. 간외 섭취와 간경변증 환자의 예 후와 비교한 Picard 등16)의 연구에서 간외 섭취는 Pugh 등17) 에 의해 변형된 Child 분류 및 생존율과 유의한 상관관계를
보였다.18,19) 따라서 간 스캔은 간경변증 환자에서 진단적 가
치뿐 아니라 유용한 예후 정보를 제공할 것임을 시사하고 있다.
본 연구에서는 장기간 추적관찰 자료를 포함하지 않아 간 스캔의 지표와 예후와의 상관성에 대한 결론을 내릴 수 없으나, 예후와 밀접한 생화학적 및 임상적 지표들과 유의 한 상관관계를 보였다. 본 연구에서는 평면영상만을 평가 하였으나, SPECT 영상으로 간과 비장의 섭취율을 정량화 하여 비교할 경우 간경변증의 진단과 질병의 중증도를 더 잘 알 수 있다는 보고20)도 있어, 간경변증 환자의 평가에 있어서 SPECT 영상을 추가함으로써 얻을 수 있는 장점에 대한 추가연구가 필요하리라 생각한다.
결론적으로 간경변증 환자에서 간 스캔의 여러 지표들과 생화학적 및 임상적 지표들과의 비교 결과 간 스캔에서 간 외 섭취 즉 비장 및 골수의 섭취 증가는 혈청 빌리루빈의 상승, 알부민의 감소소견과 잘 일치하여 간경변증의 중증 도를 잘 반영하였다. 또한 간 스캔에서 비장의 비대, 간섭 취의 불균일성, 간의 위축 및 좌엽의 비대 소견은 모두 식 도정맥류의 정도와 일치하였다. 이러한 간 스캔의 소견에 대한 이해는 임상의로 하여금 미만성 간 질환의 진단, 치 료 및 경과 추적에 있어서 유용한 정보를 제공할 것으로 생각한다.
요 약
목적: 간 스캔은 초음파, 컴퓨터단층촬영술(CT) 및 자기 공명영상(MRI) 등 다른 진단 기술의 등장으로 국소적인 병 변을 찾는 목적으로는 이용이 줄어들고 있는 추세지만, 간 에 생긴 종괴의 성질을 파악하거나 간경변증과 같은 미만 성 간 질환에서 기능적인 평가를 하는 데에는 유용하다. 저 자들은 간경변증 환자의 스캔 소견과 생화학적 검사 및 임 상소견과의 관계를 살펴보고 간경변증 환자에서 간 스캔의 임상적 유용성을 알아보고자 하였다.
대상 및 방법: 범용 평형구멍조준기(All purpose parallel
hole collimator)를 장착한 감마카메라(BasicamⓇ, Siemens)를 이용하여 Tc-99m phytate 370 MBq 주사 후 20분에 환자의 복부 전면상, 후면상, 우사면상, 우측면상, 좌측면상을 각각 70만 계수하였다. 간 스캔 소견의 척도는 간 크기, 좌엽비대 유무, 간실질 섭취의 균일성, 간 스캔에서 비장의 크기, 비 장섭취 정도, 골수섭취 정도로 하였으며, 모든 스캔은 두 명 의 핵의학 의사가 판독하였다. 생화학적 검사 및 임상소견 의 항목으로 혈청 알부민, 혈청 빌리루빈, INR (International Normalized Ratio) for Prothrombin time, 간성혼수의 유무와 식도정맥류의 정도를 조사하였다.
결과: 간경변증으로 진단되어 간 스캔을 시행한 환자 44 명(남:여=24:20)을 대상으로 하였다. 간 스캔에서 간외 섭취 즉 비장 및 골수의 섭취 증가는 혈청 빌리루빈의 상승, 혈청 알부민의 감소소견과 잘 일치하였다. 또한 간 스캔에 서 비장의 비대, 간 섭취의 불균일성, 간의 위축 및 좌엽의 비대 소견은 모두 식도정맥류의 정도와 일치하였다.
결론: 이러한 간 스캔의 소견에 대한 이해는 임상의로 하 여금 간경변증의 진단뿐 아니라 치료 및 경과 추적에 있어 서 간경변증의 중증도에 대한 유용한 정보를 제공할 것으 로 생각한다.
참 고 문 헌
1) Subramanian G, McAfee JG, Mehter A, Blair RJ, Thomas FD.
99m
Tc-stannous phytate: a new in vivo colloid for imaging the reticuloendothelaial system. J Nucl Med 1973;14:459.
2) Herzog H, Spohr G, Notohamiprodjo G, Feinendegen LE.
Absolute quantification of pharmacokinetic distribution of RES colloids in individuals with normal liver function. Nucl Med Commun 1987;8:157-175.
3) Waxman AD. Scintigraphic evaluation of diffuse hepatic dis- ease. Semin Nucl Med 1982;12:75-88.
4) Geslien GE, Pinsky SM, Poth RK, Johnson MC. The sen- sitivity and specificity of
99mTc-sulfur colloid liver imaging in diffuse hepatocellular disease. Radiology 1976;118:115-119.
5) Drane WE, VanNess MM. Hepatic imaging in diffuse liver disease. Clin Nucl Med 1988;13:182-185.
6) Yang SH, Park BC, Che DH, Cho JK, Park SK, Byun JH.
Prognostic value of
99mTc-phytate liver scintigraphy in patients with liver cirrhosis. Korean J Nucl Med 1991;25:76-80.
7) Piquet KJ. Prophylactic endoscopic sclerosing treatment of the esophageal wall in varices: A prospective controlled trial.
Endoscopy 1982;14:4-5.
8) McClees EC, Gedguadas-McClees RK. Screening for diffuse and focal disease: the case for hepatic scintigraphy. J Clin Ultrasound 1984;12:75-81.
9) Hoefs JC, Wang F, Kanel G, Braunstein P. The liver-spleen scan as a quantitative liver function test: correlation with liver severity at peritoneoscopy. Hepatology 1995;22:1113-1121.
10) Nishikawa J. The liver. In: Wagner HN, ed. Principles of Nu- clear Medicine. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: Saunders; 1995. p.940- 946.
11) Horisawa M, Goldstein G, Waxman AD, Reynolds T. The abnormal hepatic scan of chronic liver disease. Its relationship to hepatic haemodynamics and colloid extraction. Gastroen- terology 1976;71:210-213.
12) Lough J, Rosenthall L, Arzoumanian A, Goresky CA. Kupf- fer's cell depletion associated with capillarization of liver sinusoids in carbon tetrachloride-induced rat liver cirrhosis. J Hepatology 1987;5:190-198.
13) Fernandez JP, L'Rourke RA, Cooper JN, Ewy GA, Mullen JC.
The extrahepatic uptake of
198Au as an index of portal hy- pertension. Am J Digestive Dis 1970;15:883-893.
14) Gourgoutis GD, Das G, Lindsay N. Splenic uptake of
99mTc technetium sulphur colloid as an index of portal hypertension.
Am J Gastroenterol 1972;57:435-442.
15) Huet PM, Chartrand R, Marleau D. Extrahepatic uptake of
99m