Histomorphometric Analysis on Bone Formation Effect of Beta-tricalciumphosphate around Dental Implants in Rabbit Mandibular Body: Pilot Study
전체 글
수치
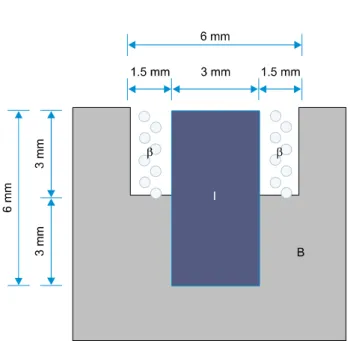
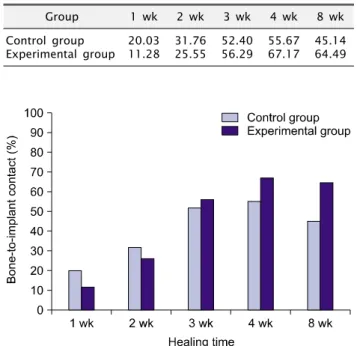
관련 문서
12 As such, using finite element modeling, the effect of stress distribution around the internal non-submerged type implants on marginal bone resorption
The study carried out small group cooperative learning as an experimental group and lecture-type learning as a control group for 12 weeks and compared
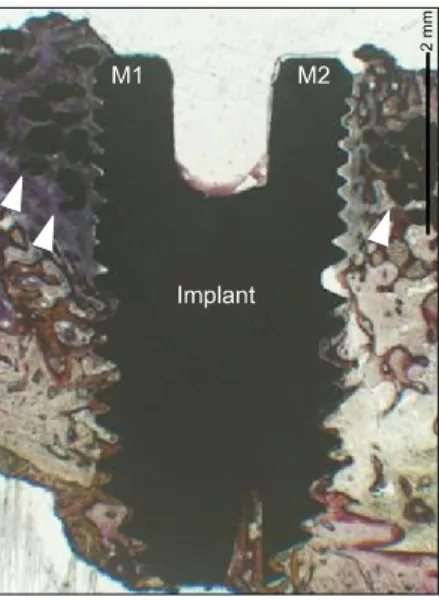
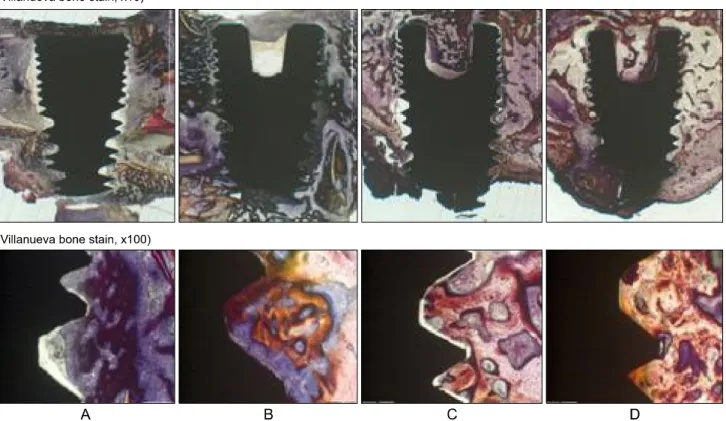
:Continuous new-bone formation (asterisk) is identified around the defect margin (arrows).(H-E stain, × 40) Higher magnification demonstrates some new-bone formation (asterisks)
Methods to overcome insufficient bone due to poor bone quality, the pneumatization of a maxillary sinus and other anatomical limitations of implant placement
Histopathologic findings of control group at 4 weeks show little bone- implant contact (BIC) around the implant (asterisks) and new-bone formation in the defect
From the results of this study, we concluded that two different sized graft materials have positive effects on new bone formation.. Additionally, smaller
The aim of this study was to compare the effect on bone regeneration relative to maintenance period of PTFE membrane in rabbit calcarial defects.. Eight adult
Effects of pulse frequency of low-level laser thrapy (LLLT)on bone nodule formation in rat calvarial cells.. Low-level laser therapy stimulats