Received: June 29, 2015 Revised: July 6, 2015 Accepted: September 16, 2015
Corresponding Author: Kyu Yeol Lee, Department of Orthopedic surgery, College of Medicine, Dong-A University, 1, Dongdaesin-dong 3-ga, Seo-gu, Busan 602-715, Korea
Tel: +82-51-240-5450, Fax: +82-51-243-9764, E-mail: gylee@dau.ac.kr
골다공증성 흉요추부 골절에 대한 추체 성형술과 풍선 척추 성형술의 비교
동아대학교 의과대학 정형외과학교실 김민우․이규열․정성윤
Comparisons of Vertebroplasty and Kyphoplasty for Thoracolumbar Osteoporotic Vertebral Fractures
Min-Woo Kim, Kyu Yeol Lee, Sung Yoon Jung
Department of Orthopedic Surgery, College of Medicine, Dong-A University, Busan, Korea
Objectives: To examine and compare the effects of vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty on change in the vertebral height and kyphotic angle and presence of new vertebral fracture of adjacent level.
Materials and Methods: A total of 60 patients with vertebral compression fractures or stable burst fractures underwent vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty from Jan, 2007 to April, 2014 were included in the study.
Preoperative, postoperative and last follow-up radiographs were analyzed to quantify presence of new vertebral fractures and preoperative and postoperative vertebral height and kyphotic angle at fracture levels were also measured. Changes in the vertebral body height and kyphotic angle at fracture levels were compared for vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty to determine if there was a significant differences.
Results: Measurements revealed that vertebroplasty increased vertebral body height at fracture level by an average 5.5mm or or by 33% of preoperative height and reduced local kyphotic angle by an average 3.5 degrees and kyphoplasty increased vertebral body height at fracture level by an average 5.8mm or by 36% of preoperative height and reduced local kyphotic angel by an average 3.6 degrees. New vertebral fractures occurred in 8 patients (24%) after vertebroplasty and 4 patients (14%) after kyphoplasty.
Conclusions: There was no significant statistically greater improvement of changes in the vertebral body height at fracture level and kyphotic angle found with vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty. But the vertebroplasty has statistically greater risk of new fracture than kyphoplasty.
Key Words: Vertebroplasty, Kyphoplasty, Compression fracture, Burst fracture
척추 추체의 압박 골절 및 안정성 방출성 골절은 노년층에서 골밀도의 감소와 함께 흔히 나타나는 골 절로 평균 수명의 증가와 함께 비율이 날로 증가하 고 있는 추세이며 해마다 140만개의 새로운 골절이 발생하고 있다.1,2 이와 같은 흉요추부 골절은 통증과
활동성의 장애를 초래하게 되어 심한 경우 사망에 이르게 할 수까지 있다.3,4 이전에는 대부분의 흉요추 부 골절 시 통증 조절, 보조기, 단기간의 침상 안정 등의 보존적 치료만을 시행하였으나 최근에는 통증 이 조절되지 않고 보행이 불가능한 경우 장기간의
Table 1. Demographic data
Mean age 74.9 (59 to 97)
M / F 25 / 35
Operation type Vertebroplasty 33
Kyphoplasty 27
F/U period 2.7 years (1.5 to 5.4 years)
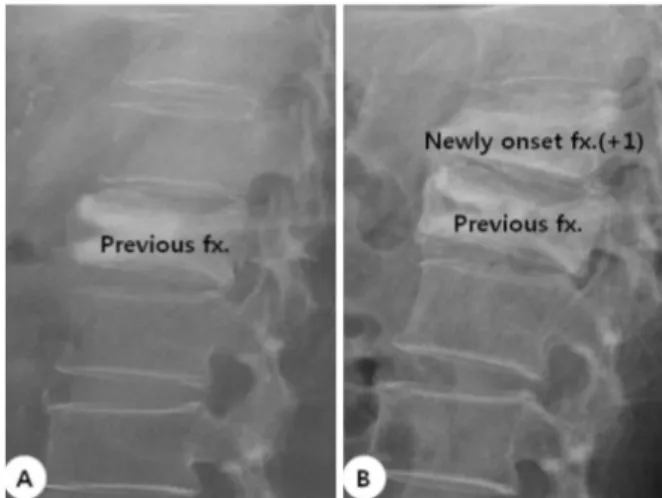
Fig. 1. (A) Previous fracture site (B) Newly onset fractures within 3 levels from fracture site.
입원치료와 높은 비용을 이유로 수술적 치료의 비중 이 높아지고 있다.5,6
추체 성형술 또는 풍선 척추 성형술은 통증 감소에 우수한 효과가 있다고 보고되고 있으며 이로 인해 기 존의 저자들은 추체 성형술 및 풍선 척추 성형술의 장점 및 단점에 대해 보고해왔다.7-10 추체 성형술은 한 측면의 주입구를 통해 적은 양의 시멘트를 추체 내부에 삽입하는 시술이며, 풍선 척추 성형술은 양측 성 접근을 시행하며 추체 내부로 풍선을 삽입한 뒤 시멘트를 주입하는 시술로써, 환자의 통증 및 척추 변 형을 방지하는 효과가 추체 성형술에 비해 높다고 보 고되고 있다.11,12 풍선 척추 성형술이 추체 성형술에 비해 Bruce 등은 인접 분절의 새롭게 발생하는 골절 비율이 높다고 하고 있으나,13 Jason 등은 추체 성형술 이 풍선 척추 성형술에 비해 통증을 경감시켜 주는 정도는 높으나, 시멘트 누출 및 인접 분절에 새로 발 생하는 골절의 비율이 더 높다고 보고하였다.14 기존의 저자들은 위와 같이 추체 성형술과 풍선 척추 성형술의 장단점에 대해 보고하였으나 현재까 지의 연구에 있어서 추체 성형술과 풍선 척추 성형 술 간의 술 후의 추체 높이의 변화 및 후만각 변화 및 인접 분절에 새롭게 발생하는 추체 골절에 대한 비교 연구에 대한 보고는 제한적이다. 우리는 이러 한 점을 고려하여 본원에서 척추 흉요추부의 압박 골절 및 안정성 방출성 골절 환자들 중 추체 성형술 및 풍선 척추 성형술을 시행한 환자들에서의 술 후 의 추체 높이 변화 및 후만각 변화 및 인접 분절에 새롭게 발생하는 추체 골절 비율에 대해 비교 분석 하고자 하였다.
연구 대상 및 방법
2007년 1월부터 2013년 4월까지 본원에서 추체 성
형술 또는 풍선 척추 성형술을 시행한 추체 압박 골 절 및 안정성 방출성 골절 환자들을 대상으로 하였 다. 이들 중 처음으로 발생한 추체 압박 골절 및 안 정성 방출성 골절 환자들에 대해서만 포함시켰으며 종양의 전이에 의한 병적 골절이나 다발성 골다공증 성 척추체 골절에 대해서는 배제하였다. 이 중 남자 는 25명, 여자는 35명 포함되었으며, 평균 연령은 74.3세(59~97세)였으며, 평균 추시 관찰 기간은 2.7년 이었다(Table 1). 술 전 및 술 후 방사선학적 사진을 통하여 기존 골절에서 3분절 이내에서 새롭게 발생 한 추체 압박 골절이나 안정성 방출성 골절이 있는 지 확인하였으며(Fig. 1), 술 전 및 술 후의 추체 높 이 및 후만각 또한 측정되었으며(Fig. 2, 3). 추체 성 형술 및 풍선 척추 성형술 간의 차이가 통계적 유의 성이 있는지에 대해서도 분석되었다.
결 과
총 60례 중 남자는 25례, 여자는 35례였으며, 평균 연령은 74.3세였다. Picture Archiving and Communi- cation System (PACS)을 이용하여 술 전 및 술 후에 촬영한 방사선 사진을 비교하였으며 술 전과 술 후 의 추체 높이의 증가 정도 및 기존의 추체 높이를 기준으로 한 비율 및 술 전과 술 후의 후만각의 변 화 정도 및 기존 골절 부위에서 3분절 내에 새롭게
Table 2. Comparsion of radiologic results (body height change, kyphotic angle change, newly onset fracture) between vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty
Vertebroplasty Kyphoplasty P-value
Body height change +5.5 mm (33%) +5.8 mm (36%) 0.216
Kyphotic angle change -3.5 degree -3.6 degree 0.074
Newly onset fracture 8 patients (24%) 4 patients (14%) 0.013
Fig. 2. (A) Preoperative vertebral body height (B) Post- operative vertebral body height.
Fig. 3. Kyphotic angle measured by angle between two lines (adjacent vertebral end plates to fractured vertebral body). (A) Preoperative kyphotic angle (B) Postopertative kyphotic angle.
발생한 골절에 대해서 각각 발생하는 비율에 대해 확인하였다. 술 전 및 술 후의 추체 높이의 변화는 추체 성형술 및 풍선 척추 성형술에서 각각 5.5 mm, 5.8 mm 만큼 증가하였으며 이는 기존의 술 전 추체 높이의 33%, 36%에 해당한다. 또한 술 전 및 술 후 의 후만각의 변화는 추체 성형술 및 풍선 척추 성형 술에서 각각 3.5도, 3.6도 감소하였다. 그러나 추체 높이의 변화 및 후만각의 변화 정도에 대해서는 추 체 성형술 및 풍선 척추 성형술간에 통계적으로 유 의한 차이는 관찰되지 않았다(P=0.216, 0.074) 추체 성형술에서 새로운 인접 추체의 골절은 8례 보고되 었으며, 이는 총 추체 성형술을 시행한 사례 중 24%
에 해당하며, 풍선 척추 성형술에서는 4례가 보고되 었으며 이는 풍선 척추 성형술을 시행한 사례 중 총 14%에 해당하며 두 군 간에 통계적 유의성이 관찰 되었다(P=0.013) (Table 2).
고 찰
흉요추부 척추 압박골절은 골밀도가 감소되어 골 다공증의 유병률이 점차 증가하는 노년층에서 가장 흔히 발생하는 골절 중의 하나이다. 흉요추부 골절 의 급성 통증으로 인한 장기간 침상 안정은 골밀도 감소를 가중시키고 만성적인 흉요추부 후방변형은 폐 기능과 소화기 기능의 장애를 초래하게 되며 이 로 인한 사망률은 23~34%까지 보고되고 있다.5,16,17 골다공증성 척추 압박골절이 발생한 고령의 환자에 대한 치료로 환자의 상태에 따라 보존적 치료 또는 수술적 치료가 시행되고 있다. 최근 수술적 치료방 법 및 술기의 발달로 수술적 치료의 비율이 높아지 고 있으며, 추체 성형술과 풍선 척추 성형술은 최소 침습적인 시술의 용이성과 환자의 급격한 통증 소실 및 환자의 삶의 질 향상을 가져오는 획기적인 치료 법으로 알려져 있다. 그러나 추체 성형술은 골시멘 트 누출로 인한 부작용과 교정되지 못한 추체 만곡 의 문제점을 여전히 가지고 있다.18 이를 보완하기
위해 풍선 척추 성형술이 시도되었으나 해면골과 상 호결합을 이루지 못한 골시멘트 덩어리 첨면을 통해 추체 상하 종판에 응력의 집중으로 인한 인접 척추 압박골절의 가능성이 제시되고 있으며, 국소 추체 만곡의 교정에도 불구하고 척추 시상면 정렬에 대해 장기 추시상 교정력이 크지 않은 점에 대한 문제점 등이 여전히 제기되고 있다.19,20
Andrew 등은 풍선 척추 성형술은 추체 성형술에 비해 재원 기간을 단축시키며 폐렴이나 폐색전증과 같은 폐합병증 및 체위성 욕창을 줄여주며 후만각을 유지시키는 효과가 우수하며 3년 이내의 사망률을 20% 이상 감소하는 효과가 있다고 보고하였다.21-24 또한, 풍선 척추 성형술은 추체 성형술에 비해 통증 경감의 효과가 우수하며,25 시멘트 누출이 적고 추체 높이 및 시상면 정렬 상태의 유지에 있어 더 우수하 다고 보고되고 있으며 또한 후만각 감소에 있어서도 우수한 효과가 있으나,26 비용적인 측면에 있어서 추 체 성형술에 비해 1.5배 이상인 것으로 보고되고 있 다.27 기존의 연구에서는 각각 20명을 대상으로 추체 성형술 및 풍선 척추 성형술을 시행한 뒤 3개월 간 추시 관찰한 결과 각각 5례, 0례에서 인접 분절에 새 롭게 골절이 발생하였다고 하였다.27 그러나 본 연구 에서는 추체 성형술과 풍선 척추 성형술에 있어 술 전, 술후의 방사선학적 비교에서 추체 높이의 변화 나 후만각의 변화는 풍선 척추 성형술에서 더 나은 결과를 보였으나 통계학적으로 의미있는 차이가 관 찰되지 않았다.
추체 성형술과 풍선 척추 성형술 후 인접 척추의 압박골절의 발생은 여러 인자들에 의해 복합적으로 작용한다. 불량한 척추 시상면 정렬 시 상체의 무게, 추간판내 누출된 골시멘트, 추체내 골시멘트의 분포 양상 및 주입량 등은 외부에서 인접 척추로의 응력 을 증가시키는 외재적 요인이며 인접 척추의 골밀도 는 이에 저항하는 내재적 요인이 되며 이들의 균형 이 상실되면 인접 척추 압박골절이 발생하게 된다.
많은 양의 골시멘트 주입 시 골다공증성 추체 종판 의 내부 돌출을 외부로 편평하게 하여 인접 추간판 내의 압력을 증가시키고 그 증가된 압력으로 인해 인접 추체로 응력전달이 증가되는 기둥 효과(pilar effect)가 인접 척추 압박골절의 위험 요소로 제시되
기도 한다.28 본 연구에서는 평균 2.7년간의 추시 관 찰 결과 인접 척추에 새롭게 발생하는 골절은 추체 성형술이 풍선 척추 성형술에 비해 많은 것으로 보 고되었으며 통계학적으로도 유의한 차이를 보였다 (P-value: 0.013).
풍선 척추 성형술 시 골시멘트 누출은 11.3~33.9%
로 비교적 빈번히 발생하는 것으로 보고된다.29-31 저 자들의 경우도 추체성형술에서 2예(5.4%), 풍선 척 추 성형술에서 1예(4.3%) 발생하였으나 누출의 양은 극히 적었고 신경학적 증상을 일으킨 예는 없었다.
풍선 척추 성형술시는 추체 성형술 시와 달리 점도 가 상당히 굳어진 상태에서 골시멘트를 주입하므로 주입시 밀려가는 골시멘트 주행 거리가 멀지 않고 출구 주위에 덩어리를 형성하는 양상을 보인다.31 따 라서 영상 투시기로 골시멘트의 분포 양상을 면밀히 관찰하여 누출이 예상되는 순간 주입을 중단하면 골 시멘트가 골절 부위를 통하여 과도하게 누출되는 것 을 예방할 수 있다.
기존의 발표에 따르면 풍선 척추 성형술은 비용적 인 측면에서 추체 성형술에 비해서 1.5배 가량 높은 것으로 되어 있으며27 본원을 기준으로 했을 때는 4 배 가량 높다. 척추 추체의 압박 골절이나 안정성 방 출성 골절 환자에 있어서 보존적 치료가 아닌 추체 성형술이나 풍선 척추 성형술과 같은 수술적 치료를 시행할 때 환자의 의학적 상태뿐만 아니라 사회경제 적인 부분 또한 반드시 고려되어야 하는 항목이다.
이 때 풍선 척추 성형술이 추체 성형술에 비해 비용 이 높은 점 또한 고려하여 환자의 사회경제적 상태 에 대해 고려한 뒤 알맞은 치료법을 선택해야 할 것 으로 사료된다.
결 론
척추의 압박 골절이나 안정성 불안정 골절 환자에 서 풍선 척추 성형술은 추체 성형술에 비해서 추체 의 높이 변화나 후만각 교정 정도에 있어서 다소 우 수한 효과를 보였으나 통계적 유의성이 관찰되지 않 았다. 그러나 인접 분절에 새롭게 발생하는 골절의 방지에 대해서는 추체 성형술에 비해 풍선 척추 성 형술이 우수한 효과를 보였으며 이는 통계적 유의성
을 나타내었다. 그러나 풍선 척추 성형술의 수술 비 용이 추체 성형술에 비해 4배 가량 높으므로 치료 방법 및 수술 방법의 선택시 환자의 임상적, 방사선 학적, 사회경제적 요인을 충분히 고려한 뒤 결정해 야 할 것으로 사료된다.
참 고 문 헌
1. Borgstrom F, Zethraeus N, Johnell O, Sari P, Olle S, Peter A, et al. Costs and quality of lifeassociated with osteoporosis-related fractures in Sweden.
Osteoporos Int 2006;17:637-50.
2. Johnell O, Kanis JA. An estimate of the worldwide prevalence anddisability associated with osteoporotic fractures. Osteoporos Int 2006;17:1726-33.
3. Hasserius R, Karlsson MK, Jonsson B, Redlund- Johnell L, Johnnel O. Long-term morbidityand mortality after a clinically diagnosed vertebral fracture in theelderly—a 12- and 22-year follow-up of 257 patients. Calcif Tissue Int 2005;76:235-42.
4. Hasserius R, Karlsson MK, Nilsson BE, Johnnel O.
Prevalent vertebral deformities predict increased mortality and increased fracture rate in both men and women: a 10-year population-based study of 598 individuals from the Swedish cohort in the European Vertebral Osteoporosis Study. Osteoporos Int 2003;14:61-8.
5. Papaioannou A, Watts NB, Kendler DL, Yuen CK, Adachi JD, Ferko N. Diagnosis and management of vertebral fractures in elderly adults. Am J Med 2002;113:220-8.
6. Black DM, Cummings SR, Karpf DB, Cauley JA, Thompson DE, Nevitt MC, et al. Randomised trial of effect of alendronate on risk of fracture in women with existing vertebral fractures. Fracture Intervention Trial Research Group. Lancet 1996;
348:1535-41.
7. Garfin SR, Yuan HA, Reiley MA. Kyphoplasty and Vertebroplasty for the Treatment of Painful Osteo- porotic Compression Fractures. SPINE 2001;26:
1511-15.
8. Evans AJ, Jensen ME, Kip KE, Denardo AJ, Lawler GJ, Negin GA, et al. Vertebral compression fractures : pain reduction and improvement in functional mobility after percutaneous polymethyl- methacrylate vertebroplasty retrospective report of 245 cases. Radiology 2003;226:366-72.
9. Alvarez L, Alcaraz M, Perez-Higueras A, Granizo JJ, de Miquel, Rossi RE, et al. Percutaneous verte- broplasty : functional improvement in patients with osteoporotic compression fractures. Spine 2006;31:
1113-8.
10. Diamond TH, Champion B, Clark WA. Manage- ment of acute osteoporotic vertebral fractures: a nonrandomized trial comparing percutaneous verte- broplasty with conservative therapy. Am J Med 2003;114:257-65.
11. Voggenreiter G. Balloon kyphoplasty is effective in deformity correction of osteoporotic vertebral com- pression fractures. Spine 2005;30:2806-12.
12. Wardlaw D, Cummings SR, Van Meirhaeghe J, Bastian L, Tillman JB, Ranstam J, et al. Efficacy and safety of balloon kyphoplasty compared with non-surgical care for vertebral compression fracture (FREE): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2009;
373:1016-24.
13. Frankel BM, Monroe T, Wang C. Percutaneous vertebral augmentation: an elevation in adjacent- level fracture risk in kyphoplasty as compared with vertebroplasty. Spine 2007;8:575-82.
14. Eck JC, Nachtigall D, Humphreys SC, Hodges SD.
Comparison of vertebroplasty and balloon kypho- plasty for treatment of vertebral compression fractures: a meta-analysis of the literature. Spine 2008;8:488-97.
15. Schlaich C, Minne HW, Bruckner T, Wagner G, Gebest HJ, Grunze M, et al. Reduced pulmonary function in patients with spinal osteoporotic fractures. Osteoporos Int 1998;8:261-7.
16. Leech JA, Dulberg C, Kellie S, Pattee L, Gay J.
Relationship of lung function to severity of osteo- porosis in women. Am Rev Respir Dis 1990;141:
68-71.
17. Kado DM, Browner WS, Palermo L, Nevitt MC, Genant HK, Cummings SR. Vertebral fractures and mortality in older women: a prospective study.
Study of Osteoporotic Fractures Research Group.
Arch Intern Med 1999;159:1215-20.
18. Appel NB, Gilula LA. Percutaneous vertebroplasty in patients with spinal canal compromise. Am J Roentgenol 2004;182:947-51.
19. Tanigawa N, Komemushi A, Kariya S, Kojima H, Shomura Y, Omura N, et al. Relationship between cement distribution pattern and new compression fracture after percutaneous vertebroplasty. Am J Roentgenol 2007;189:348-52.
20. Pradhan BB, Bae HW, Kropf MA, Patel VV, Delamarter RB. Kyphoplasty reduction of osteo- porotic vertebral compression fractures: correction of local kyphosis versus overall sagittal alignment.
Spine 2006;31:435-41.
21. Liu JT, Liao WJ, Tan WC, Lee JK, Liu CH, Chen YH, et al. Balloon kyphoplasty versus vertebro- plasty for treatment of osteoporotic vertebral com- pression fracture :a prospective, comparative, and randomized clinical study. Osteoporos Int 2010;21:
359-64.
22. Wardlaw D, Cummings SR, Van Meirhaeghe J, Bastian L, Tillman JB, Ranstam J, et al. Efficacy and safety of balloon kyphoplasty compared with non-surgical care for vertebral compression fracture (FREE) : a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2009;21:373(9668):1016-24.
23. McGirtMJ, Parker SL, Wolinsky JP, Witham TF, Bydon A, Gokaslan ZL. Vertebroplasty and kypho- plasty for the treatment of vertebral compression fractures: an evidenced-based review of the litera- ture. Spine 2009;501-8.
24. Schofer MD, Efe T, Timmesfeld N, Kortmann HR, Quante M. Comparison of kyphoplasty and verte- broplasty in the treatment of fresh vertebral com- pression fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 2009;
129:1391-9.
25. Josef G. Grohs. Minimal Invasive Stabilization of Osteoporotic Vertebral Fractures ; a prospective Nonrandomized Comparison of Vertebroplasty and Balloon Kyphoplasty. J Spinal Disord Tech 2011;
18(3).
26. Ben B, Hyun W, Michael A, Vikas V. Kyphoplasty reduction of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures : Correction of local kyphosis versus overall sagittal alignment. Spine 2006;31:435-41.
27. Mehio A, Lerner JM, Engelhart LH, Kozma CM, Slaton TL, Edwards NC, et al. Comparative hospital economics and patient presentation:
vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty for the treatment of vertebral compression fracture. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2011;32:1290-4.
28. Rohlmann A, Zander T, Bergmann G. Spinal loads after osteoporotic vertebral fractures treated by vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty. Eur Spine J 2006;
15:1255-64.
29. Jun DS, Shin WJ, Koh YH, Moon SH. MR Pre- dictors of bone cement leakage in percutaneous vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty for painful osteo- porotic vertebral compression fracture. J Korean Soc Spine Surg 2006;13:184-90.
30. Ledlie JT, Renfro MB. Kyphoplasty treatment of vertebral fractures: 2-year outcomes show sustained benefits. Spine 2006;31:57-64.
31. Baroud G, Crookshank M, Bohner M. High- viscosity cement significantly enhances uniformity of cement filling in vertebroplasty: an experimental model and study on cement leakage. Spine 2006;
31:2562-8.