33
Korean Circulation J 2007;37:33-38 ⓒ 2007, The Korean Society of Circulation
돼지 관상동맥 재협착 모형에서 약물 용출 스텐트 중첩 시술 후 내피세포 재생 및 염증반응
제주대학교 의과대학 내과학교실,1 전남대학 의과대학 전남대학교병원 심장센터, 의과학연구소2
임상엽1·정명호2·김정하2·이상록2·문재연2·홍영준2·김주한2 안영근2·조정관2·박종춘2·김기석1·주승재1·강정채2
Re-endothelization and Inflammatory Reaction at Site of Overlapping Drug-Eluting Stents in a Porcine Coronary In-Stent Restenosis Model
Sang Yup Lim, MD
1, Myung Ho Jeong, MD
2, Jeong Ha Kim, BS
2, Sang Rok Lee, MD
2, Jae Youn Moon, MD
2, Young Joon Hong, MD
2, Ju Han Kim, MD
2,
Youngkeun Ahn, MD
2, Jeong Gwan Cho, MD
2, Jong Chun Park, MD
2, Ki-Seok Kim, MD
1, Seung-Jae Joo, MD
1and Jung Chaee Kang, MD
21Department of Internal Medicine, Cheju National University, Jeju, 2The Heart Center of Chonnam National University Hospital, Chonnam National University Research Institute of Medical Sciences, Gwangju, Korea
ABSTRACT
Background and Objectives:This study was conducted to evaluate the inflammatory reaction at sites of over- lapping stents in a porcine in-stent restenosis (ISR) model. Materials and Methods:Twenty bare metal stents ( BMS, Group I; n=10), 20 sirolimus-eluting stents (SES, Group II; n=10), 20 paclitaxel-eluting stents (PES, Group III; n=10), 10 PESs and 10 SESs (Group IV; n=10) were deployed and overlapped in the left anterior descending coronary arteries of 40 pigs. Follow-up coronary angiograms and histopathologic analysis were per- formed at 4 weeks after stenting. Results:The minimal luminal diameter of the overlapped segment at 4 weeks was smaller in group I than that in the other groups (1.78±0.13 mm vs. 2.79±0.09 mm vs. 2.90±0.04 mm vs.
2.80±0.07 mm, respectively, p<0.001). The neointimal area (5.51±0.58 mm
2vs. 2.38±0.53 mm
2vs. 2.07±
0.37 mm
2vs. 2.39±0.58 mm
2, respectively, p<0.001) and the area stenosis (68.74±4.02% vs. 27.79±4.73% vs.
23.66±3.24% vs. 27.63±4.07%, respectively, p<0.001) of the overlapped segment were significantly higher in Group I than that in the other groups. The inflammatory score of the overlapped segment was significantly higher in Group III than that in the other groups (1.80±0.42 vs. 2.10±0.32 vs. 2.90±0.31 vs. 2.50±0.52, res- pectively, p<0.001). The endothelization score of the overlapped segment was significantly lower in Group III than that in the other groups (2.80±0.42 vs. 2.30±0.67 vs. 1.30±0.48 vs. 2.10±0.74, respectively, p<0.001).
Conclusion:Compared with the BMS, the DES inhibits neointimal hyperplasia, but inflammation and poor endothelization are observed at the sites of overlapped stents. (Korean Circulation J 2007;37:33-38)
KEY WORDS:
Coronary disease;Restenosis;Stents.
서 론
스텐트를 중첩하여 시술해야하는 미만성의 긴 관상동맥 질
환은 경피적 관상동맥 중재술(PCI; percutaneous coronary intervention)의 발전에도 불구하고, 높은 재협착율과 좋지 않은 임상결과를 보이고 있으며,1-3) 특히 스텐트 혈전증이 논문접수일:2006년 11월 14일
심사완료일:2007년 01월 17일
교신저자:정명호, 501-757 광주광역시 동구 학동 8번지 전남대학 의과대학 전남대학교병원 심장센터 전화:(062) 220-6243·전송:(062) 228-7174·E-mail:myungho@chollian.net
발생하는 경우 사망 등의 치명적인 결과를 초래하므로,4)5) 아직도 PCI 영역에서 완전히 해결되지 않은 부분이다.
최근 미만성의 긴 병변에 일반 금속 스텐트(bare metal stent: BMS)보다는 약물 용출성 스텐트(drug-eluting stent:
DES)를 겹쳐서 시술하는 경우가 많아지고 있으나, DES 중첩 부위에서 과도한 염증반응으로 인해 내피의 치유(healing) 가 늦게 일어날 것이라는 우려가 있다.6) 그러나 DES의 중 첩시술 후 조직반응에 대한 연구는 많지 않으며, 특히 siro- limus-eluting stent(SES) 혹은 paclitaxel-eluting stent (PES)처럼 각기 다른 DES를 중첩한 후 조직반응에 대한 연구는 거의 시행되지 않았다.
본 연구에서는 돼지의 관상동맥 재협착 모형에서 BMS와 DES를 각각 중첩하였을 경우 조직반응과 신생내막 증식에 의한 재협착에 미치는 영향을 알아보았다.
재료 및 방법
실험동물은 체중이 25~35 kg의 암퇘지를 사용하였으며, 전남대학교 의과대학 의과학연구소 윤리위원회의 허가를 받아 동물실험을 실시하였다.
실험당일 ketamine 12 mg/kg을 근주하여 전처치 후 xyla-
zine 8 mg/kg을 근주하여 전신마취를 유도하였으며, 실험 중 30분마다 ketamine 12 mg/kg을 추가로 근주하여 마취 상태를 유지하였다. 무균 상태에서 2% 리도케인으로 목 중 앙부에 국소마취를 실시한 후 돼지의 좌측 경동맥을 절개하 여 7 French 동맥 유도초를 삽입한 후, 헤파린 300 U/kg을 동맥 내로 단일 주사요법으로 투여하고 7 French의 관상동맥 유도도자를 C-arm(Philips사 BV-25 Gold)의 투시 하에 관상동맥 개구부에 위치시켰다. 실험 중에는 안면 산소마스 크를 이용하여 지속적으로 산소를 공급하였고, 귀의 정맥을 통하여 식염수를 공급하였다.
스텐트 시술은 좌전하행지의 근위부에 스텐트를 위치시 키고 8~12기압의 압력으로 참고혈관 크기보다 1.1~1.3배 로 혈관이 약간 과확장 되도록 30초간 풍선을 확장시켜 삽입하였다. 하나의 스텐트를 삽입한 후 다른 스텐트를 중 첩시켜 중첩부위가 5~10 mm 되도록 삽입하였으며, 중첩부 위에 12~14기압의 압력으로 30초간 풍선을 확장시켰다.
1군(n=10)은 10개의 3.0×18 mm의 BMS(S7®, Medtronic AVE Co, USA)를 동일한 10개의 BMS에 중첩시켰으며, 2군(n=10)은 10개의 3.0×18 mm SES(Cypher®, Cordis Corp, Johnson & Johnson Co, USA) 를 동일한 10개의 SES에, 3군(n=10)은 10개의 3.0×16 mm의 PES(TaxusTM, Boston Scientific Co, USA)를 동일한 10개의 PES에, 4군 (n=10)은 10개의 3.0×18 mm SES를 다른 10개의 3.0×
16 mm PES에 각각 중첩시켰다.
스텐트 시술 전후로 관상동맥 조영술을 실시하여 CD에 녹화 기록하고, 저장된 영상을 Philips H5000 DCI program
을 이용하여 정량분석을 하였다. 시술 후 경동맥을 결찰한 후 목의 피부를 봉합하고, 돼지를 사육사로 옮겨 4주 동안 관찰 하였으며, 이 기간 동안 계속 aspirin과 clopidogrel을 투여 하였다. 스텐트 시술 4주 후에 추적 관상동맥 조영술을 시행 한 후, 유도도관을 통하여 과량의 KCl(potassium chloride)을 주사하여 안락사를 유도하였다. 측부 흉곽을 절개하여 실험 동물의 심장을 적출한 뒤 상행 대동맥과 폐동맥을 통하여 4%
formalin을 이용하여 70 mmHg의 관류압으로 24시간 이상 관류-고정(perfusion-fixation)을 시행하였다.
조직형태 검사(Histomorphometry)
조직 절편으로 파라핀 블록을 제작한 후 Tungsten blade가 부착된 microtome을 이용하여 절단하여 미세한 절편(5 μm) 을 만들었다. 조직형태 검사는 현미경에 부착된 video시설 과 computerized visual image analysis system인 VISUS 2000프로그램을 이용하여 스텐트 시술에 참여하지 않은 연 구원에 의하여 분석하였다. 조직의 형태가 양호한 절편을 대 상으로 관상동맥 근위부, 중심부, 원위부의 3부위 이상을 스텐트 시술 혈관의 외탄력층(external elastic lamina; EEL) 면적, 내탄력층(internal elastic lamina; IEL) 면적, 내강 (lumen) 면적, 신생내막 면적 등을 측정하였다. 스텐트 혈관 의 면적 협착(area stenosis)은 100×(1-lumen area/IEL area)의 공식을 이용하여 기존의 방식에 따라서 계산하였다.7)
스텐트에 의한 혈관벽의 손상 지수, 염증 세포의 침윤 지수 (inflammation score) 및 내피화(endothelization)지수는 Schwartz의 방법에 의하여 평가하였다.8) 혈관벽의 손상지 수는 내탄력층이 손상되지 않고 내피세포만 손상된 경우를 0점, 내탄력층이 손상된 경우 1점, 중막이 손상된 경우를 2 점, 외탄력층이 손상된 경우를 3점으로 하였다. 염증 세포 의 침윤 지수는 strut 주위로 염증 세포가 침윤되지 않았으 면 0점, 약간 침윤되었으나 strut주위를 둘러싸지 않으면 1점, 중증도로 침윤되었으나 strut주위를 둘러싸지 않으면 2점, 염증 세포가 strut주위를 둘러싸고 촘촘하게 침윤된 경우면 3점으로 하였다. 내피화 지수는 내피가 생성되지 않은 경우 0점, 내피가 생성되었으나 내강의 25%이하인 경우 1점, 내강의 25%이상 75%이하인 경우 2점, 내피가 완전히 생성 된 경우를 3점으로 하였다.
통계학적 분석
모든 자료는 평균±표준편차로 표시하며, 변수의 비교는 MS Window용 SPSS-PC 12.0 프로그램을 이용하여 paired t-test와 chi-square test, ANOVA test로 하였고, p값이 0.05 미만인 경우에 통계학적으로 유의하다고 판정하였다.
결 과
실험에 사용된 돼지는 4주 후 모두 생존하였다. 관상동맥
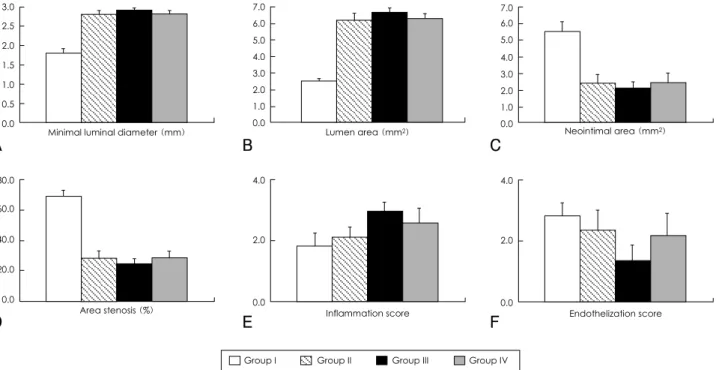
조영술 결과 중첩부위의 길이는 각 군간 유의한 차이를 보이지 않았으며, 스텐트 시술 전의 중첩부위의 혈관 내경은 양군 간에 유의한 차이를 보이지 않았으나, 스텐트 시술 4주 후에는 중첩부위의 최소 내경(minimal luminal diameter;
MLD)이 I군 1.78±0.13 mm, II군 2.79±0.09 mm, III군 2.90±0.04 mm, IV군 2.80±0.07 mm로서 I군의 MLD가 유의하게 컸다(p<0.001, Table 1, Fig. 1, 3). 조직형태학적 검사에서 중첩부위의 세포손상 지수 및 내탄력층 면적은 각 군 간에 유의한 차이가 없었으나, 중첩부위의 신생내막 면적이 I군 5.51±0.58 mm2, II군 2.38±0.53 mm2, III군 2.07±0.37 mm2, IV군 2.39±0.58 mm2로서 I군에서 유 의하게 넓었다(p<0.001). 중첩부위의 면적협착은 I군 68.74
±4.02%, II군 27.79±4.73%, III군 23.66±3.24%, IV군
27.63±4.07%로서 I군에서 면적협착이 유의하게 컸다(p<
0.001). 신생내막의 염증세포 침윤 지수는 중첩부위의 근 위부(proximal segment)와 원위부(distal segment)에서는 각 군간에 유의한 차이를 보이지 않았으나, 중첩부위에서 는Ⅰ군 1.80±0.42, II군 2.10±0.32, III군 2.90±0.31, IV군 2.50±0.52로서 III군에서 유의하게 높았다(p<0.001).
중첩부위의 내피화 지수는 Ⅰ군 2.80±0.42, II군 2.30±
0.67, III군 1.30±0.48, IV군 2.10±0.74로서 III군에서 유의하게 낮았다(p<0.001, Table 2, Fig. 2, 3).
고 찰
본 연구에서 DES의 중첩시술은 BMS보다 내막증식을
Table 1. Quantitative coronary angiographic findings of porcine coronary arteries
Group I (n=10) Group II (n=10) Group III (n=10) Group IV (n=10) p Baseline (mm)
Reference diameter 2.83±0.12 2.81±0.10 2.78±0.07 2.80±0.12 <0.674
Post-stenting diameter 3.11±0.09 3.12±0.07 3.12±0.80 3.14±0.07 <0.816
Overlapped segment 9.38±0.84 9.23±0.83 8.74±1.37 8.95±0.37 <0.508
4 weeks after stenting (mm)
Target reference diameter 3.01±0.12 2.99±0.75 3.04±0.09 3.01±0.11 <0.801
Minimal luminal diameter 1.78±0.13 2.79±0.09 2.90±0.04 2.80±0.07 <0.001
p: Group I vs. II, III, IV, Group I: overlapped bare metal stent group, Group II: overlapped sirolimus-eluting stent (SES) group, Group III:
overlapped paclitaxel-eluting stent (PES) group, Group IV: overlapped SES and PES group
Table 2. Histopathologic assessment of porcine coronary arteries at 4 weeks after stenting
Group I (n=10) Group II (n=10) Group III (n=10) Group IV (n=10) p
Injury score 01.40±0.70 01.60±0.84 01.41±0.69 01.30±0.82 <0.758
Lumen area (mm2) 02.50±0.13 06.14±0.41 06.63±0.21 06.17±0.31 <0.001*
IEL area (mm2) 08.01±0.66 08.53±0.65 08.69±0.46 08.57±0.85 <0.126
Neointima area (mm2) 05.51±0.58 02.38±0.53 02.07±0.37 02.39±0.58 <0.001*
Area stenosis (%) 0 68.74±4.02 27.79±4.73 23.66±3.24 27.63±4.07 <0.001*
Inflammatory score
Proximal segment 01.35±0.47 01.40±0.52 01.60±0.52 01.65±0.47 <0.460
Overlapped segment 01.80±0.42 02.10±0.32 02.90±0.31 02.50±0.52 <0.001†
Distal segment 01.30±0.48 01.50±0.53 01.45±0.50 01.50±0.47 <0.778
Endothelization score 02.80±0.42 02.30±0.67 01.30±0.48 02.10±0.74 <0.001† p: *group I vs. II, III, IV, †: group III vs. I, II, IV. Group I: overlapped bare metal stent group, Group II: overlapped sirolimus-eluting stent (SES) group, Group III: overlapped paclitaxel-eluting stent (PES) group, Group IV: overlapped SES and PES group
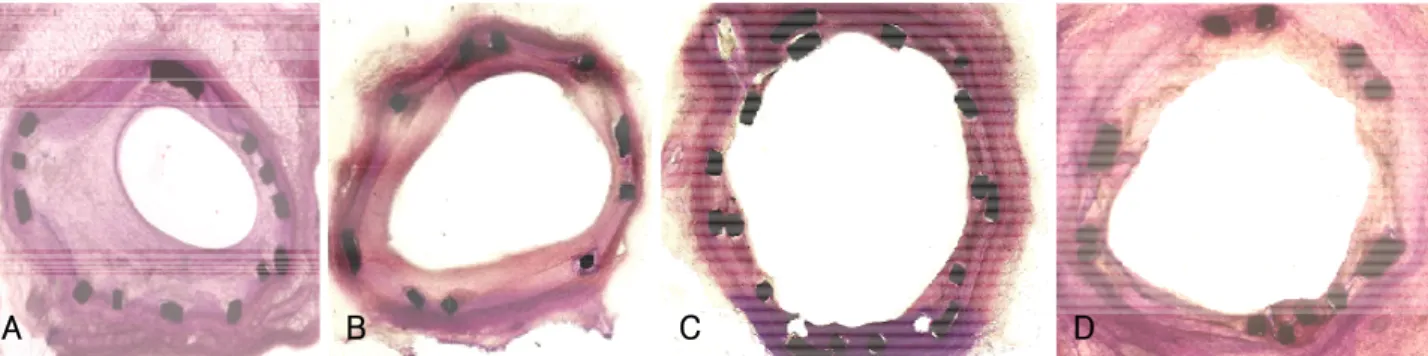
Fig. 1. Methyl methacrylate staining. A: overlapped bare stent group. B: overlapped sirolimus-eluting stent (SES) group. C: overlapped paclitaxel- eluting stent (PES) group. D: overlapped SES and PES group. Overlapped PES group showed exposed stent struts into the lumen and poor endothelization.
A B C D
효과적으로 억제하여 BMS의 중첩시술로 인한 재협착의 한 계를 극복할 수 있을 것으로 보인다. BMS를 이용한 중첩시 술은 시술 후 혈관 합병증 및 재협착율을 높이는 기존의 결 과를 다시 한번 확인할 수 있었으며, DES 시대에는 BMS의 중첩시술은 더 이상 임상에서 유용하지 않음을 알 수 있었 다.9)
DES는 스텐트의 중첩시술이 필요한 미만성의 긴 병변에 대하여도 신생내막의 증식에 의한 스텐트 재협착을 현저히 감소시킬 수 있는 혁신적인 방법으로 생각되어 왔다. 그러 나 항암제나 증식억제제를 코팅한 스텐트들은 과민반응이 나 세포독성 등이 문제가 되고 있다. 실제로 SES를 삽입 후 18개월이 경과한 환자가 급사한 후 부검에서 스텐트를 삽 입한 동맥의 aneurysmal dilatation과 T림프구와 호산구 매 개성의 심한 국소적인 과민반응이 보고된 바 있다.10)11) 이러
한 과민반응이나 세포독성들은 스텐트에 코팅된 약물 혹은 polymer에 의한 것으로 생각되며,12) DES 삽입 후 내피손상 의 회복을 지연시켜 내피화의 장애를 초래하는 것으로 알려져 있다.
미만성의 긴 병변에 대하여 DES 중첩시술에 대한 최근의 보고에 의하면 DES 중첩시술시 중첩된 분절에서 중첩되지 않은 분절에 비해 치유과정이 지연되었고, PES의 경우에 염증세포의 침착이 SES, BMS 보다 많았음을 보고하여,6) 본 연구의 결과와 유사하였다.
DES 중첩 시술이 치유과정을 지연시키는 기전에 대하여 서는 DES 중첩시 국소적인 약물 함유량을 증가시키며, 스텐트 strut와 조직사이의 직접 접촉을 증가시키고, 중첩되 는 모양에 의해서도 조직 내의 약물농도가 증가할 수 있다.13) SES의 경우 2개를 중첩할 때 혈중에 측정되는 rapamycin의
Fig. 2. High power light microscopic findings (×200) of Hematoxyline and Eosin staining. A: overlapped bare stent group. B: overlapped sirolimus-eluting stent (SES) group. C: overlapped paclitaxel-eluting stent (PES) group. D: overlapped SES and PES group. The number of Inflammatory cells in overlapped PES group was higher than that of other groups.
A B C D
Fig. 3. Histopathologic assessment of overlapped segment of porcine coronary arteries (A) minimal luminal diameter (mm). B: lumen area (mm2). C: neointimal area (mm2). D: area stenosis (%). E: inflammation score. F: endothelization score. Group I: overlapped bare stent group, Group II: overlapped sirolimus-eluting stent (SES) group, Group III: overlapped paclitaxel-eluting stent (PES) group, Group IV: overlapped SES and PES group.
Minimal luminal diameter (mm) 3.0
2.5 2.0 1.5 1.0 0.5
0.0 Lumen area (mm2)
7.0 6.0 5.0 4.0 3.0 2.0 1.0
0.0 Neointimal area (mm2)
7.0 6.0 5.0 4.0 3.0 2.0 1.0 0.0
Area stenosis (%) 80.0
60.0
40.0
20.0
0.0
Inflammation score 4.0
2.0
0.0
Endothelization score 4.0
2.0
0.0
Group I Group II Group III Group IV
A B C
D E F
혈중농도는 1.1 ug/mL로 혈소판 응집을 촉진시킬 수 있으 며,14) 이러한 결과는 약물농도의 장기간의 증가에 의한 내피 생성의 지연과 함께 스텐트 혈전증의 우려를 나타내고 있다.
BMS의 경우에 급성 또는 아급성 혈전증의 빈도는 0.5~
1.9% 정도인데 DES도 이와 비슷한 것으로 알려져 있으며, 실제 임상에서도 비슷한 결과가 보고되었다.15-17) 하지만 스텐트 혈전증에 대한 우려가 남아 있어서 DES 삽입 후 항혈 소판제를 6개월 내지 1년 이상 사용하는 것이 권유되고 있다.
보통 DES를 시술받은 많은 환자들은 6개월~1년 이상 clopidogrel을 사용하는데, 항혈소판제를 언제까지 사용할 것인가에 대한 문제는 여전히 해결되지 않았다. 스텐트 혈전증 은 환자의 약 20~48%가 사망하고 60~70%에서 주요한 급성 심근경색증이 발생할 정도로 심각한 결과를 초래하므로,18-20) aspirin과 clopidogrel의 병합요법을 중단하는 것은 매우 신중하게 고려해야 한다. 최근 clopidogrel을 중단한 이후에 발생한 후기 스텐트 혈전증의 보고21)22)가 있어 더욱 많은 연구가 필요한 부분이다.
실제 임상에서는 보다 복잡한 병소를 치료하고, 대단위 무 작위 연구 대상에서 제외되었던 병소 및 환자들이 치료 대 상에 포함되는 경우가 많기 때문에 DES의 안정성에 대한 결론을 내리기까지는 많은 연구와 더욱 장기간의 연구결과 가 필요할 것으로 사료된다.
항혈소판제의 사용에 대한 연구와 더불어, 기존의 rapamy- cin, paclitaxel 등 항증식성 약물을 방출하여 혈관재생을 지연 시키는 DES보다 carvedilol, abciximab, alpha-lipoic acid 등 혈관재생에 장기적인 지장을 초래하지 않는 약물을 코팅 한 DES의 중첩에 대한 지속적인 연구가 이루어져야 할 것 이다.23-30)
본 연구의 주요한 제한점은 실험동물로 비교적 큰 동물 인 돼지를 사용하는 어려움으로 인해 대상 수가 적은 편이 었다. 또한 서로 다른 DES를 중첩하였을 때보다 PES를 중 첩하였을 때 내피손상이 더욱 심하여지는 경향을 보였는데, 상대적으로 적은 대상 수에 의한 것인지 실제 임상에서도 그러한지 확인되지 않은 점 등이며, 이는 대규모의 전향적 임상연구 등을 통하여 해결할 수 있을 것으로 보인다.
결론적으로 DES를 중첩시술 하였을 때 BMS의 중첩시술 에 비해 재협착을 효과적으로 억제할 수 있었으나, 중첩부 위의 심한 염증으로 인한 내피화의 장애를 보였으며, 이는 PES를 중첩하였을 때 더욱 심하였다. 따라서 DES의 중첩 시술을 받은 환자의 경우 그렇지 않은 환자보다 항혈소판 제를 더욱 오래 사용하여야 할 것으로 생각되었다.
요 약
배경 및 목적:
돼지의 관상동맥 재협착 모형에서 일반 금속 스텐트(bare metal stent, BMS)와 약물 용출 스텐트(drug-eluting stent,
DES)를 각각 중첩하였을 경우 조직반응과 신생내막 증식에 미치는 영향을 알고자 하였다.
방 법:
돼지의 좌전하행지 근위부에 스텐트를 삽입한 후 다른 스 텐트를 중첩시켜 삽입하였으며, 중첩부위에 추가적으로 풍 선을 확장시켰다. 1군(n=10)은 10개의 BMS를 동일한 10개 의 BMS에 중첩시켰으며, 2군(n=10)은 10개의 sirolimus- eluting stent(SES)를 동일한 10개의 SES에, 3군(n=10)은 10개의 paclitaxel-eluting stent(PES)를 동일한 10개의 PES 에, 4군(n=10)은 10개의 SES를 다른 10개의 PES에 각각 중첩시켰다. 4주 후에 추적 관상동맥 조영술을 시행한 후, 돼지를 희생시켜, 스텐트를 함유하고 있는 관상동맥을 분리, 관류고정한 후 조직병리 관찰 및 측정을 시행하였다.
결 과:
스텐트 시술 4주 후 중첩부위의 최소 내경면적은 I군 1.78
±0.13 mm, II군 2.79±0.09 mm, III군 2.90±0.04 mm, IV군 2.80±0.07 mm로서 I군에서 유의하게 컸다(p<0.001).
조직형태학적 검사에서 중첩부위의 신생내막 면적은 I군 5.51
±0.58 mm2, II군 2.38±0.53 mm2, III군 2.07±0.37 mm2, IV군 2.39±0.58 mm2로서 I군에서 유의하게 넓었으며(p<
0.001), 면적협착은 I군 68.74±4.02%, II군 27.79±4.73%, III군 23.66±3.24%, IV군 27.63±4.07%로서 I군에서 면 적협착이 유의하게 컸다(p<0.001). 중첩부위의 신생내막의 염증세포 침윤지수는 Ⅰ군 1.80±0.42, II군 2.10±0.32, III 군 2.90±0.31, IV군 2.50±0.52로서 III군에서 유의하게 높았으며(p<0.001), 내피화지수는 Ⅰ군 2.80±0.42, II군 2.30±0.67, III군 1.30±0.48, IV군 2.10±0.74으로서 III 군에서 유의하게 낮았다(p<0.001).
결 론:
DES를 중첩시술 하였을 때 BMS의 중첩시술에 비해 재 협착을 효과적으로 억제할 수 있었으나, 중첩부위의 심한 염 증으로 인한 내피화의 장애를 보였고 PES를 중첩하였을 때 더욱 심하였다.
중심 단어:관상동맥 질환;재협착;스텐트.
이 논문은 2006년도 전남대학교 학술연구비 지원에 의하여 연구되 었음.
REFERENCES
1) Serruys PW, Foley DP, Suttorp MJ, et al. A randomized com- parison of the value of additional stenting after optimal balloon angioplasty for long coronary lesions: final results of the addi- tional value of NIR stents for treatment of long coronary lesions (ADVANCE) study. J Am Coll Cardiol 2002;39:393-9.
2) Kornowski R, Bhargava B, Fuchs S, et al. Procedural results and late clinical outcomes after percutaneous interventions using long (≥25 mm) versus short (<20 mm) stents. J Am Coll Cardiol 2000;35:612-8.
3) Kornowski R, Mehran R, Satler LF, et al. Procedural results and
late clinical outcomes following multivessel coronary stenting. J Am Coll Cardiol 1999;33:420-6.
4) Iakovou I, Schmidt T, Bonizzoni E, et al. Incidence, predictors, and outcome of thrombosis after successful implantation of drug- eluting stents. JAMA 2005;293:2126-30.
5) Kuchulakanti PK, Chu WW, Torguson R, et al. Correlates and long-term outcomes of angiographically proven stent thrombosis with sirolimus- and paclitaxel-eluting stents. Circulation 2006;
113:1108-13.
6) Finn AV, Kolodgie FD, Harnek J, et al. Differential response of delayed healing and persistent inflammation at sites of overlapp- ing sirolimus- or paclitaxel-eluting stents. Circulation 2005;112:
270-8.
7) Ahn YK, Jeong MH, Kim JW, et al. Preventive effects of heparin coated stent on restenosis in the porcine model. Catheter Car- diovasc Interv 1999;48:324-30.
8) Schwartz RS, Huber KC, Murphy JG, et al. Restenosis and the proportional neointimal response to coronary artery injury:
results in a porcine model. J Am Coll Cardiol 1992;19:267-74.
9) Schalij MJ, Udayachalerm W, Oemrawsingh P, Jukema JW, Reiber JH, Bruschke AV. Stenting of long coronary artery lesions: initial angiographic results and 6-month clinical outcome of the micro stent II-XL. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv 1999;48:105-12.
10) Nebeker JR, Virmani R, Bennett CL, et al. Hypersensitivity cases associated with drug-eluting coronary stents: a review of avai- lable cases from the Research on Adverse Drug Events and Re- ports (RADAR) project. J Am Coll Cardiol 2006;47:175-81.
11) Virmani R, Farb A, Guagliumi G, Kolodgie FD. Drug-eluting stents: caution and concerns for long-term outcome. Coron Artery Dis 2004;15:313-8.
12) Azarbal B, Currier JW. Allergic reactions after the implantation of drug-eluting stents: is it the pill or the polymer? J Am Coll Cardiol 2006;47:182-3.
13) Balakrishnan B, Tzafriri AR, Seifert P, Groothuis A, Rogers C, Edelman ER. Strut position, blood flow, and drug deposition:
implications for single and overlapping drug-eluting stents. Cir- culation 2005;111:2958-65.
14) Babinska A, Markell MS, Salifu MO, Akoad M, Ehrlich YH, Kornecki E. Enhancement of human platelet aggregation and secretion induced by rapamycin. Nephrol Dial Transplant 1998;
13:3153-9.
15) Stone GW, Ellis SG, Cox DA, et al. One-year clinical results with the slow-release, polymer-based, paclitaxel-eluting TAXUS stent. Circulation 2004;109:1942-7.
16) Sousa JE, Costa MA, Sousa AG, et al. Two-year angiographic and intravascular ultrasound follow-up after implantation of sirolimus- eluting stents in human coronary arteries. Circulation 2003;107:381-3.
17) Lemos PA, Serruys PW, van Domburg RT, et al. Unrestricted
utilization of sirolimus-eluting stents compared with conventional bare stent implantation in the “real world”. Circulation 2004;
109:190-5.
18) Karrillon GJ, Morice MC, Benveniste E, et al. Intracoronary stent implantation without ultrasound guidance and with repla- cement of conventional anticoagulation by antiplatelet therapy:
30-day clinical outcome of the French Multicenter Registry. Cir- culation 1996;94:1519-27.
19) Moussa I, di Mario C, Reimers B, Akiyama T, Tobis J, Colombo A. Subacute stent thrombosis in the era of intravascular ultra- sound-guided coronary stenting without anticoagulation: fre- quency, predictors and clinical outcome. J Am Coll Cardiol 1997;29:6-12.
20) Cutlip DE, Baim DS, Ho KK, et al. Stent thrombosis in the modern era: a pooled analysis of multicenter coronary stent clinical trials. Circulation 2001;103:1967-71.
21) Ong AT, McFadden EP, Regar E, de Jaegere PP, van Domburg RT, Serruys PW. Late angiographic stent thrombosis (LAST) events with drug-eluting stents. J Am Coll Cardiol 2005;45:
2088-92.
22) McFadden EP, Stabile E, Regar E, et al. Late thrombosis in drug- eluting coronary stents after discontinuation of antiplatelet therapy.
Lancet 2004;364:1519-21.
23) Park HW, Jeong MH, Park OY, et al. The long-term clinical effects of heparin-coated coronary stent. Korean Circ J 2002;32:773-80.
24) Kim W, Jeong MH, Cha KS, et al. The effect of anti-oxidants (carvedilol and probucol) loaded stents in a porcine coronary restenosis model. Circ J 2005;69:101-6.
25) Kim W, Jeong MH, Hong YJ, et al. The long-term clinical results of a platelet glycoprotein IIb/IIIa receptor blocker (Abciximab:
ReoPro®) coated stent in patients with acute myocardial infarc- tion. Korean Circ J 2004;34:1063-9.
26) Hong YJ, Jeong MH, Kim W, et al. Effect of abciximab-coated stent on in-stent intimal hyperplasia in human coronary arteries.
Am J Cardiol 2004;94:1050-4.
27) Park OY, Jeong MH, Kim JH, et al. The inhibitory effects of platelet glycoprotein IIb/IIIa receptor blocker-coated stent on neointima formation and inflammatory response in porcine co- ronary stent restenosis. Korean Circ J 2003;33:439-45.
28) Lim SY, Jeong MH. Is heparin-coated stent effective in patients with acute myocardial infarction? Korean Circ J 2004;34:537-9.
29) Kang WC, Han SH, Ahn TH, Son MS, Son JW, Shin EK. The long term clinical outcomes of primary PTCA with heparin coated stent in acute myocardial infarction. Korean Circ J 2004;34:
540-7.
30) Lim SY, Bae EH, Jeong MH, et al. The effect of oral administra- tion of alpha lipoic acid and alpha lipoic acid coated stent in porcine in-stent restenosis model. Korean Circ J 2006;36:495- 502.