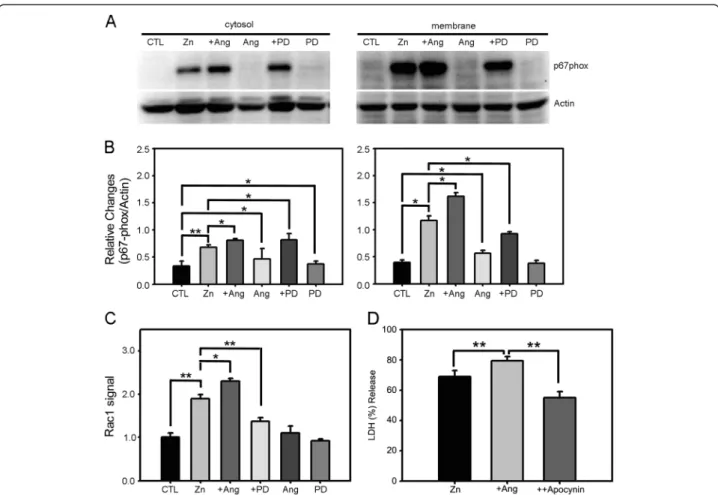
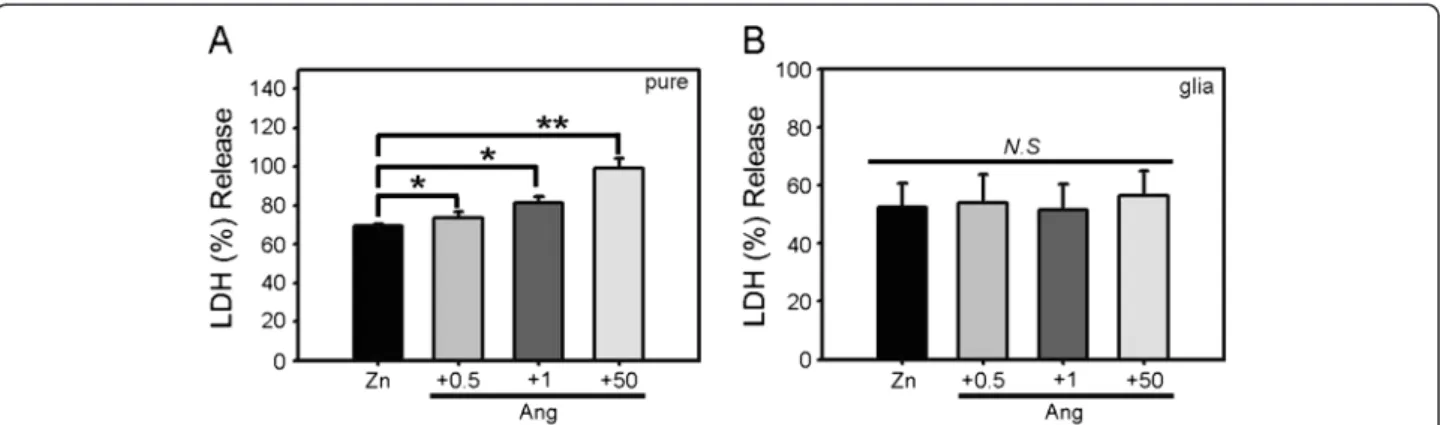
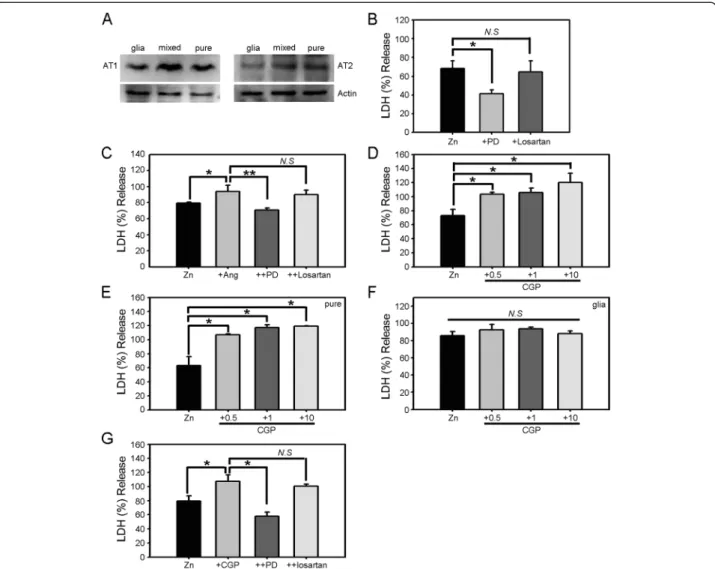
Angiotensin II potentiates zinc-induced cortical neuronal death by acting on angiotensin II type 2 receptor
전체 글
수치


관련 문서
1 John Owen, Justification by Faith Alone, in The Works of John Owen, ed. John Bolt, trans. Scott Clark, "Do This and Live: Christ's Active Obedience as the
interaction with anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 family members, we investigated whether Mcl-1 can inhibit the Noxa-induced cell death.. As expected, Mcl-1 significantly inhibits
a second phase forms because of the limited solubility of zinc in
Glutamate excitotoxicity induced by excessive activation of NMDA receptor causes various damage to cells, which leads to cell death.. In previous studies, increased ROS
n The magnitude of the buoyant force acting on a floating body in the fluid is equal to the weight of the fluid which is displaced by
Moreover, based on the fact that nuclear localization of FoxO1 is regulated by SIRT1 deacetylase, we were further interested in whether a potent SIRT1 inhibitor, Amurensin
The aim of this study was to evaluate the sealing ability in Type II root canal obturation by comparing the presence of voids between single cone technique using Endoseal MTA
These results suggest that the bilobalide inhibits the cell proliferation and induces the apoptotic cell death in FaDu human pharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma via both