193
Change of the Patellar Height and Tibial Inclination after Opening- and Closing-Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy
Se Hyun Cho, M.D., Ph.D., Sun Chul Hwang, M.D., Jin Sung Park, M.D. and Sang Hyuk Lee, M.D.
Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Gyeong-Sang National University School of Medicine, Jinju, Korea
Received: May 23, 2010 Revised: August 6, 2010 Accepted: August 6, 2010
Corresponding author: Se Hyun Cho, M.D., Ph.D.
Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Gyeong-Sang National University Hospital, 90 Chiram-dong, Jinju 660-702, Korea
TEL: 82-55-750-8100, FAX: 82-55-755-8365 E-mail: shcho@gnu.kr
Purpose: We wanted to evaluate the patella height, the tibial inclination and the joint height changes after closing-wedge high tibial osteotomy (CW HTO) and opening-wedge high tibial osteotomy (OW HTO).
Materials and Methods: The lateral radiographs taken with 30o flexion of the knees for 46 CW HTOs and 32 OW HTOs were assessed regarding the patellar height by the Insall-Salvati index (ISI) and the Blackburne-Peel index (BPI) and for the tibial inclination by the Moore-Harvey (MH) method. The average follow up period was 3.6 years (range: 2.0 to 4.7 years). Spearman correlation analysis was used to determine the influence of the two types of HTO with the amount of correction in the frontal plane Hip-Knee-Ankle (H-K-A) axis. The joint height was measured between the fibular head and the lateral tibial plateau.
Measurements were made at the preoperative, postoperative and final follow-up periods.
Results: In the CW group, both the ISI and BPI were increased at the postoperative and final follow-up periods, while the BPI showed a statistically significant increase (p=0.046). In the OW group, both the ISI and BPI were decreased, while the BPI showed a statistically significant decrease (p=0.007). There was a tendency of a decrease of the tibial inclination in the CW HTO group without statistical significance. But in the OW HTO group, there was a statistically significant increase of the tibial inclination (p=0.012). The frontal plane H-K-A axis correction did not influence the change of the patellar height and tibial inclination in both groups (r<0.3). The joint height measured between the fibular tip and the lateral tibial plateau showed a significant decrease in the CW group (p=0.000), while there was no significant change in the OW group.
Conclusion: The anatomical alteration of the patellar height was significantly influenced in opposite ways by the two methods of HTO. The BPI was more statistically significant then the ISI for the measurement of the patellar height after HTO. The joint height was significantly decreased in the CW HTO group. These changes should be kept in mind when converting HTO to total knee arthroplasty.
Key Words: Patellar height, Tibial inclination, High tibial osteotomy, Insall-Salvati index, Blackburne-Peel index, Moore-Harvey method
서 론
경골 근위 절골술은 1958년 Jackson에 의해 처음 소개 되어 중년 이후의 내반성 골관절염 환자에서 슬관절 내측 에 집중되어있는 관절염을 완화하고 슬관절 전치환술을 대 치하거나 지연시킬 수 있는 치료법으로 시행되어 왔다1,5,18). 하지만 경골 근위 절골술을 시행한 환자의 경우 술 후 발
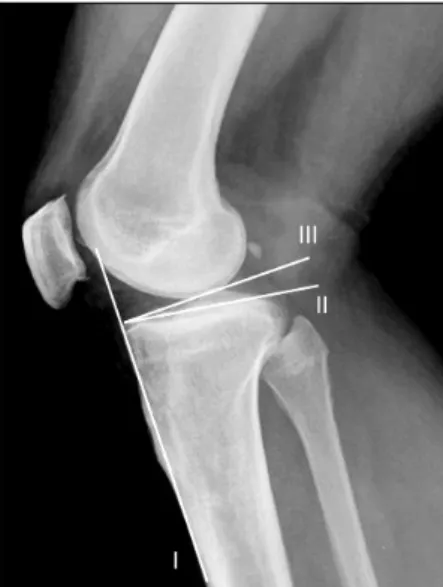
Fig. 1. Radiograph showing determination of the patellar height according to the Insall-Salvati index. The length of the patellar tendon (LT) is divided by the longest length of the patella (LP).
Fig. 2. Radiograph showing determination of the patellar height according to the Blackburne-Peel index. The distance (I) from the distal pole of the articular surface of the patella to perpendicular at the level of the tibia plateau (II) is devided by the length of the patellar articular surface (III).
Fig. 3. Radiograph showing the angle of inclination of the tibial plateau according to the Moore-Harvey method using three lines. This first (I) is tangential to the tibial crest, the second (II) is tangential to the proximal tibial articular surface and the third (III) line is perpendicular to the line of the tibial crest. The angle formed by the second and the third lines is equivalent to the posteroinferior slope of the plateau.
생한 외반 변형, 슬개골의 높이 및 경골 경사도 변화 등의 해부학적 변화가 슬관절 전치환술로 전환시 문제점이 될 수 있다2,8,11,12).
이에 본 연구는 경골 근위 절골술 중 폐쇄성, 개방성 절 골술을 시행한 환자에서 술 전과 비교하여 술 후에 나타 나는 슬개골 높이, 경골 경사도 및 관절 높이 등 해부학적 변화를 방사선학적 추시를 통하여 비교 분석하였다.
대상 및 방법
2000년 2월부터 2008년 3월까지 본원에서 내반 변형을 동반한 퇴행성 슬관절염으로 진단받고, 경골 근위 절골술 을 시행한 후 최소 2년 이상 추시한 환자 70명 78 증례를 대상으로 후향 분석하였다. 모든 수술은 통신 저자에 의해 시행되었다. 46예는 폐쇄성, 32예는 개방성 절골술을 시행 했다. 남자 14명, 여자 56명이었으며 추시 기간은 24개월 에서 57개월로 평균 3.6년이었으며 평균 나이는 52세(29
∼72세)였다.
환자들은 표준화된 방사선 촬영술에 의해 수술 전과 수 술 직후, 최종 추시 시 각각 직립 장하지 전후방 및 슬관 절을 30o 굴곡시킨 상태에서 측면 촬영을 시행하였다.
측면 사진 촬영에서 Insall-Salvati index (ISI)와 Black- burne-Peel index (BPI)로 슬개골의 높이를 측정했고
Moore-Harvey (MH) 방법으로 경골 경사도를 측정하였 다(Figs. 1∼3)3,10,14). 관절의 높이는 비골 골두 첨단부와 경골 외측 고평부까지의 거리로 측정하였다. 두 수술군 간
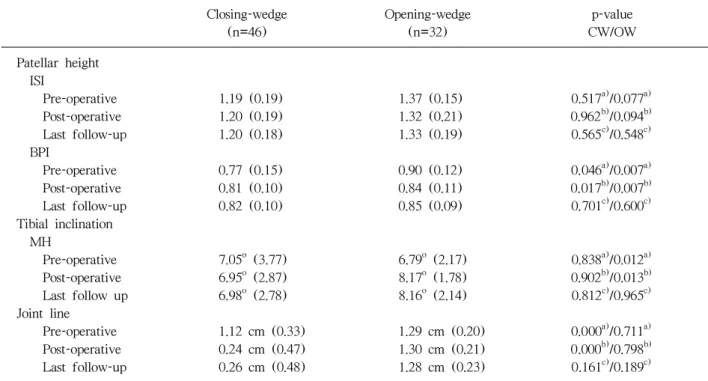
Table 1. Mean Patellar Height according to the Insall-salvati Index and Blackburne-peel Index and the Mean Inclination of the Tibia according to the Moore-harvey Method after Closing and Opening Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy
Closing-wedge Opening-wedge p-value (n=46) (n=32) CW/OW Patellar height
ISI
Pre-operative 1.19 (0.19) 1.37 (0.15) 0.517a)/0.077a)
Post-operative 1.20 (0.19) 1.32 (0.21) 0.962b)/0.094b)
Last follow-up 1.20 (0.18) 1.33 (0.19) 0.565c)/0.548c)
BPI
Pre-operative 0.77 (0.15) 0.90 (0.12) 0.046a)/0.007a) Post-operative 0.81 (0.10) 0.84 (0.11) 0.017b)/0.007b) Last follow-up 0.82 (0.10) 0.85 (0.09) 0.701c)/0.600c) Tibial inclination
MH
Pre-operative 7.05o (3.77) 6.79o (2.17) 0.838a)/0.012a) Post-operative 6.95o (2.87) 8.17o (1.78) 0.902b)/0.013b) Last follow up 6.98o (2.78) 8.16o (2.14) 0.812c)/0.965c) Joint line
Pre-operative 1.12 cm (0.33) 1.29 cm (0.20) 0.000a)/0.711a) Post-operative 0.24 cm (0.47) 1.30 cm (0.21) 0.000b)/0.798b) Last follow-up 0.26 cm (0.48) 1.28 cm (0.23) 0.161c)/0.189c)
CW: Closing-wedge, OW: Opening-wedge. ISI: Insall-salvati index, BPI: Blackburne-peel index, MH: Moore-harvey.
a)p-value for Pre-operative vs. Post-operative, b)p-value for Pre-operative vs. Last follow-up, c)p-value for Post-operavive vs.
Last follow-up.
Fig. 4. (A) Radiograph showing patella-alta and decreased tibial inclination after a closing-wedge high tibial osteotomy.
(B) Radiograph showing patella-baja and increased tibial inclination after an opening-wedge high tibial osteotomy.
의 통계적 분석은 SPSS ver. 15.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA)을 이용하여 paired t test와 Spearman correla- tion analysis를 시행하였고 p값이 0.05 이하일 때 통계적
유의성이 있는 것으로 평가하였다.
결 과
폐쇄성 절골군에서는 수술 후 평균적으로 슬개골 고위 증(patella alta)이 관찰되었다(Fig. 4A). 술 전 평균 ISI는 1.19 (Standard deviation, SD: 0.19), 평균 BPI는 0.77 (SD: 0.15)이었고 이 값은 수술 직후 평균 ISI는 1.20 (SD: 0.19)로, 평균 BPI는 0.81 (SD: 0.10)로 증가되었다.
두 측정값을 통해 폐쇄성 경골 근위 절골술 후에는 슬개 골이 상향 이동되었다. 하지만 BPI 값은 통계적으로 의미 있는 반면(p=0.046), ISI 값은 통계적으로 의미가 없었다.
ISI와 BPI 모두 수술 직후와 최종 추시 간에는 의미있는 변화가 없었다(Table 1). 반면 개방성 절골군에서는 수술 후 평균적으로 슬개골 저위증(patella baja)이 관찰되었다 (Fig. 4B). 술 전 평균 ISI는 1.37 (SD: 0.16) 평균 BPI는 0.90 (SD: 0.12)이었고 이 값은 수술 직후 평균 ISI는 1.32 (SD: 0.21)로 평균 BPI는 0.84 (SD: 0.11)로 감소되었다.
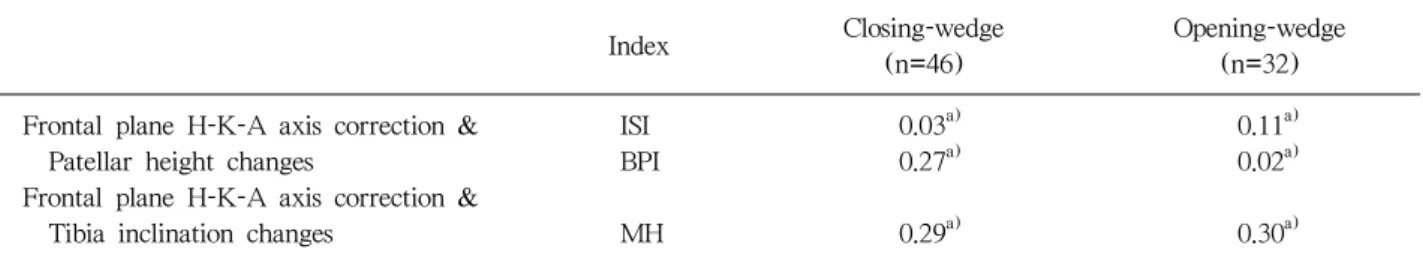
Table 2. Correlations between the Frontal Plane Hip-Knee-Ankle (H-K-A) Axis Correction, Patellar Height Changes and Tibial Inclination
Closing-wedge Opening-wedge
Index
(n=46) (n=32)
Frontal plane H-K-A axis correction & ISI 0.03a) 0.11a)
Patellar height changes BPI 0.27a) 0.02a)
Frontal plane H-K-A axis correction &
Tibia inclination changes MH 0.29a) 0.30a) ISI: Insall-Salvati index, BPI: Blackburne-Peel index, MH: Moore-Harvey method.
a)Values are given for Spearman correlation coefficient (r). There is a strong correlation only when this coefficient (r) is higher than 0.6.
두 측정값을 통해 개방성 경골 근위 골절술 후에는 슬개 골이 하향 이동되었다. 하지만 이번에도 BPI 값은 통계적 으로 의미있는 반면(p=0.007) ISI 값은 통계적으로 의미 가 없었다. 또한 ISI와 BPI 모두 수술 직후와 최종 추시간 에는 의미있는 변화가 없었다(Table 1). 경골 경사도는 폐 쇄성 절골군에서는 술전 평균 7.05o (SD: 3.77)에서 수술 직후 6.95o (SD: 2.87)로 감소되는 경향을 보였으나 통계 적으로 유의하지 않았고 수술 직후와 최종 추시 간에도 의미있는 차이는 없었다. 반면 개방성 절골군에서는 술전 평균 경골 경사도가 6.79o (SD: 2.17)에서 수술 직후 평균 8.17o (SD: 1.78)로 증가하였고 이는 통계적으로 의미있는 차이를 보였다(p=0.012). 하지만 수술 직후와 최종 추시 간에는 의미있는 차이는 없었다(Table 1). 관절 높이는 폐 쇄성 절골군에서 술전 평균 1.12 (SD: 0.33) (cm)에서 수 술직후 평균 0.24 (SD: 0.47) (cm)으로 통계적으로 의미 있는 감소를 보였으나(p=0.000) 수술 직후와 최종 추시간 에 의미있는 차이가 없었다. 개방성 절골군에서는 관절 높 이가 술전 평균 1.29 (SD: 0.20) (cm)에서 수술 직후 평 균 1.30 (SD: 0.21) (cm)으로 약간 증가하는 추세를 보였 으나 통계적으로 유의하지 않았고(p=0.711), 수술 직후와 최종 추시간에도 의미있는 차이가 없었다(Table 1). 경골 근위 절골술 후 고관절-슬관절-족관절각(H-K-A)의 교정 정도와 슬개골 높이, 경골 경사도의 해부학적 변화 간에는 상관 관계가 없는(r<0.3) 것으로 나타났다(Table 2).
고 찰
경골 근위 절골술은 내반 변형을 동반한 중등도의 슬관 절염의 치료에 널리 사용된다1,5,18). 경골 근위 절골술 후
발생된 슬개골 높이, 경골 경사도 및 외반 교정으로 인한 하지의 기계적 축의 변화는 향후 슬관절 전치환술로 전환 시 슬개건 유착과 단축현상, 슬개골을 외번시키거나 외측 구획 접근 시 어려움, 경골 치환물을 변형된 축의 회전과 각을 고려하여 위치시켜야 한다는 등 여러 면에서 기술적 문제를 발생시킨다2,8,11,12).
저자들의 경우 이번 연구에서 경골 근위 절골술의 두 가지 방법, 폐쇄성과 개방성 절골술에 따라 상반되는 해부 학적인 변화 소견을 관찰할 수 있었다. 폐쇄성 경골 근위 절골술 후에는 슬개골이 상향 이동하였고 경골 경사도가 감소하는 경향을 나타내었다. 반면에 개방성 경골 근위 절 골술 후에는 슬개골이 하향 이동하였고 경골 경사도가 증 가하는 경향을 나타내었다.
경골 근위 절골 수술 전, 후 슬개골의 높이 변화는 ISI 와 BPI를 이용한 측정법이 보편적으로 사용된다4,7,16,17,19). ISI는 슬개골의 대각선 길이와 슬개골 하단에서 경골 조면 까지의 거리 비로 측정한다10). 반면 BPI는 슬개골 관절면 의 길이와 슬개골 관절면 하단에서 경골 고평부에 수직으 로 그은 선의 길이 비로 측정한다3). Seil 등17)은 슬개골 관절면과 대퇴골 활차 및 대퇴경골 관절선과의 관계로 슬 개골 높낮이가 결정된다고 주장했고, 이를 정확하게 반영 하는 측정법은 슬개건의 원위부 부착 부위 및 슬개골 모 양 변이에 영향을 받지 않는 BPI라고 주장하였다. 경골 경 사도는 MH 방법으로 측정하였다.
폐쇄성 경골 근위 절골술 후에는 ISI와 BPI가 이전의 연 구4,7)에서 처럼 증가하는 경향이 나타났으며 BPI의 증가 는 통계적으로 의미가 있었다. 반면 개방성 경골 근위 절 골술 후에는 ISI와 BPI가 감소하는 경향이 나타났으며 여 러 저자들의 연구4,15,20)에서 처럼 BPI는 통계적으로 의미
있게 감소하였다. 이런 상반되는 결과는 수술방법 차이로 발생되는 경골 조면 위치의 변화로 인하여 슬개골의 위치 가 이동되기 때문이다. 두가지 절골술 모두 경골 조면보다 상부에서 절골이 시행되며 슬개골과 슬개건의 길이는 변 화되지 않는다. 다만 폐쇄성 경골 근위 절골술의 경우 경 골 조면이 상부로, 개방성 경골 근위 절골술의 경우 경골 조면이 하부로 전위되며, 이에 따라 슬개골 역시 각각 상 부와 하부로 전위된다7). 수술로 인하여 슬개골과 슬개건 의 길이는 변하지 않으므로 이론적으로 ISI 값은 변하지 않는다7). 하지만 임상적으로 수술로 초래된 슬개건의 신 장에 따른 반사적 수축과 슬개건 주위의 반흔으로 인한 섬유화 변성 및 대퇴사두근 이완 등으로 인해 슬개골의 위치가 변할 수 있다7,16).
경골 절골술 후 경골 경사도에도 변화가 관찰되었다. 폐 쇄성 경골 근위 절골술 후 경골 경사도는 이전의 연구4,6,9) 에서처럼 감소하는 추세를 나타내었으나 통계적으로 유의 하지는 않았다. 반면 개방성 경골 근위 절골술 후에는 여 러 저자들4,6,7)에 의해 경골 경사도의 증가가 보고되었고 우리의 경우에도 통계적으로 의미있는 경골 경사도 증가 가 관찰되었다. 개방성 경골 근위 절골술 후 나타나는 경 골 경사도의 변화는 해부학적으로 설명 가능하다. 경골 근 위부의 전내측 피질골은 후측 피질골과 45o각을 형성하고 있으나, 외측 피질골은 경골의 후측 경계와 거의 직각을 이루게 되므로 경골 전면과 후내측에 동일한 각으로 개방 성 절골술을 시행하면 경골 후방 경사도가 증가하게 된다6). 또 개방성 절골을 하기위해 경골 근위부에서 전내측 도달 법으로 접근 시, 후방부 신경과 혈관 손상을 염려하여 후 측면 피질골에 대해 적절한 절골술을 시행하지 못한 원인 이 작용하였을 가능성도 있다6).
하지만 슬개골 및 경골 경사도의 변화가 고관절-슬관절- 족관절각의 교정 정도와는 관련성이 낮은 것으로 보고6,9,13) 되고 있으며 이번 연구에서도 고관절-슬관절-족관절각의 교정 정도와 슬개골 및 경골 경사도의 변화는 Spearman 상관계수(r) 0.3 이하로 상관성이 없게 판명되었다. 폐쇄 성 경골 근위 절골술의 경우, 저자들은 비골두를 절제하거 나 비골 간부에서 절골하지 않는 대신 근위 경비관절의 절개 및 비골두를 후방 탈구시켜 수술하였으므로 폐쇄성 경골 근위 절골술로 인하여 비골두가 상대적으로 상부로 이동하였다. 따라서 비골 첨단부와 경골 외측 고평부 사이 의 거리가 단축되었으며 개방성 경골 근위 절골술에서는
비골두를 건드리지 않으므로 이 거리에는 변화가 없었다.
결 론
경골 근위 절골술 후 폐쇄성과 개방성의 두 방법에 따 라 슬개골의 높이와 경골 경사도에 서로 반대되는 해부학 적 변화가 발생하였다. 또한 슬개골 높이 변화를 측정하는 방법으로는 BPI가 ISI보다 통계적으로 유의한 값을 나타 내었다. 폐쇄성 경골 근위 절골술의 경우, 수술 후 의미있 는 관절 높이의 감소 소견이 관찰되었다. 경골 근위 절골 술 후 슬관절 전치환술로의 전환 시, 이러한 해부학적인 변화를 염두에 두고 수술한다면 슬관절 전치환술의 실패 와 합병증을 줄이는데 도움이 될 것으로 생각한다.
REFERENCES
1. Aglietti P, Buzzi R, Vena LM, Baldini A, Mondaini A:
High tibial valgus osteotomy for medial gonarthrosis: a 10- to 21-year study. J Knee Surg, 16; 21-26: 2003.
2. Bae DK, Song SJ, Yoon KH: Total knee arthroplasty following closed wedge high tibial osteotomy. Int Orthop, 34; 283-287: 2010.
3. Blackburne JS, Peel TE: A new method of measuring patellar height. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 59; 241-242:
1977.
4. Brouwer RW, Bierma-Zeinstra SM, van Koeveringe AJ, Verhaar JA: Patellar height and the inclination of the tibial plateau after high tibial osteotomy. The open versus the closed-wedge technique. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 87; 1227-1232: 2005.
5. Coventry MB, Ilstrup DM, Wallrichs SL: Proximal tibial osteotomy. A critical long-term study of eighty- seven cases. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 75; 196-201: 1993.
6. El-Azab H, Halawa A, Anetzberger H, Imhoff AB, Hinterwimmer S: The effect of closed- and open-wedge high tibial osteotomy on tibial slope: a retrospective radiological review of 120 cases. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 90; 1193-1197: 2008.
7. El-Azab H, Klabklay P, Paul J, Imhoff AB, Hinterwimmer S: Patellar height and posterior tibial slope after open- and closed-wedge high tibial osteotomy: a radiological study on 100 patients. Am J Sports Med, 38; 323-329: 2009.
8. Haddad FS, Bentley G: Total knee arthroplasty after
high tibial osteotomy: a medium-term review. J Arthroplasty, 15; 597-603: 2000.
9. Hohmann E, Bryant A, Imhoff AB: The effect of closed wedge high tibial osteotomy on tibial slope: a radio- graphic study. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc, 14; 454-459: 2006.
10. Insall J, Salvati E: Patella position in the normal knee joint. Radiology, 101; 101-104: 1971.
11. Kaper BP, Bourne RB, Rorabeck CH, Macdonald SJ:
Patellar infera after high tibial osteotomy. J Arthroplasty, 16; 168-173: 2001.
12. Katz MM, Hungerford DS, Krackow KA, Lennox DW:
Results of total knee arthroplasty after failed proximal tibial osteotomy for osteoarthritis. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 69; 225-233: 1987.
13. Marti CB, Gautier E, Wachtl SW, Jakob RP: Accuracy of frontal and sagittal plane correction in open-wedge high tibial osteotomy. Arthroscopy, 20; 366-372: 2004.
14. Moore TM, Harvey JP Jr: Roentgenographic measure- ment of tibial-plateau depression due to fracture. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 56; 155-160: 1974.
15. Noyes FR, Goebel SX, West J: Opening wedge tibial
osteotomy: the 3-triangle method to correct axial alignment and tibial slope. Am J Sports Med, 33;
378-387: 2005.
16. Scuderi GR, Windsor RE, Insall JN: Observations on patellar height after proximal tibial osteotomy. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 71; 245-248: 1989.
17. Seil R, Müller B, Georg T, Kohn D, Rupp S:
Reliability and interobserver variability in radiological patellar height ratios. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc, 8; 231-236: 2000.
18. Sprenger TR, Doerzbacher JF: Tibial osteotomy for the treatment of varus gonarthrosis. Survival and failure analysis to twenty-two years. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 85; 469-474: 2003.
19. Tigani D, Ferrari D, Trentani P, Barbanti-Brodano G, Trentani F: Patellar height after high tibial osteotomy.
Int Orthop, 24; 331-334: 2001.
20. Wright JM, Heavrin B, Begg M, Sakyrd G, Sterett W:
Observations on patellar height following opening wedge proximal tibial osteotomy. Am J Knee Surg, 14;
163-173: 2001.
폐쇄성과 개방성 경골 근위 절골술 후 슬개골 높이와 경골 경사도 변화
경상대학교 의학전문대학원 정형외과학교실
조세현ㆍ황선철ㆍ박진성ㆍ이상혁
목적: 본 연구의 목적은 폐쇄성 및 개방성 근위 경골 절골술 후 발생되는 슬개골 높이, 경골 경사도 및 관절 높이의 변화를 비교 분석하기 위함이다.
대상 및 방법: 46명의 폐쇄성 절골군과 32명의 개방성 절골군의 30o 굴곡 측면 방사선 사진 촬영에서 Insall-Salvati index (ISI) 방법과 Blackburne-Peel index (BPI) 방법으로 슬개골의 위치를 측정했고 Moore-Harvey (MH) 방법으로 경골 경사도를 측정하였다. 추시 기간은 2년에서 4.7년으로 평균 3.6년이 었다. 경골 근위 절골 수술 방법의 차이에 따른 해부학적 변화는 고관절-슬관절-족관절각(Hip-Knee- Aankle)의 교정 정도와 함께 Spearman 상관분석을 통해 비교 분석하였다. 관절 높이는 비골 골두 첨단부 와 경골 외측 고평부까지의 거리로 정의하여 수술 전, 수술 직후 및 최종 추시 시의 값들을 각각 측정하였 다.
결과: 폐쇄성 절골군에서 수술 전과 비교하여 수술 직후 및 최종 추시 시 측정된 ISI와 BPI 값이 모두 증가하였으나 BPI 값만이 통계적으로 의미있는 증가를 나타내었다(p=0 .046). 개방성 절골군에서는 ISI 와 BPI 값이 모두 감소하였으나 BPI 값만이 통계적으로 의미있는 감소를 나타내었다(p=0.007). 폐쇄성 절골군에서 경골 경사도가 감소되었으나 통계적으로 유의하지 못하였다. 반면에 개방성 절골군에서는 통계적으로 의미있는 경골 경사도의 증가 소견이 관찰되었다(p=0.012). 직립 장하지 방사선에서 수술로 인하여 변화된 고관절-슬관절-족관절각의 교정 정도는 슬개골의 높이와 경골 경사도 값의 변화에 영향을 미치지 않았다(r<0.3). 비골 골두 첨단부와 경골 외측 고평부까지의 거리로 측정된 관절 높이는 폐쇄성 절골군에서는 통계적으로 의미있는 감소(p=0.000)가 나타났으나 개방성 절골군에서는 변화가 없었다.
결론: 서로 다른 방법의 경골 근위 절골술에 따라 각각 상반되는 슬개골 높이의 해부학적 변화가 관찰되 었다. 경골 근위 절골술 이후 슬개골의 높이를 측정할 경우, BPI가 ISI보다 더 통계적으로 유의한 값을 나타내었다. 폐쇄성 절골군에서는 의미있는 관절 높이의 감소 소견이 관찰되었다. 슬관전 전치환술로의 전환시 경골 근위 절골술로 초래된 이러한 해부학적 변화를 염두해 둘 필요가 있다.
색인 단어: 슬개골 높이, 경골 경사도, 경골 근위 절골술, Insall-Salvati index 방법, Blackburne-Peel index 방법, Moore-Harvey 방법