462
J Korean Assoc Maxillofac Plast Reconstr Surg 2012;34(6):462-465 pISSN:1225-4207 eISSN: 2233-7296
Case Report
원고 접수일 2012년 7월 27일, 원고 수정일 2012년 8월 6일, 게재 확정일 2012년 11월 22일
책임저자 박인숙
(705-718) 대구시 남구 두류공원로 17길 33, 대구가톨릭대학교병원 치과, 구강악안면외과
Tel: 053-650-4285, Fax: 053-622-7067, E-mail: ispark@cu.ac.kr
RECEIVED July 27, 2012, REVISED August 6, 2012, ACCEPTED November 22일, 2012
Correspondence to In-Sook Park
Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Section of Dentistry, Daegu Catholic University Medical Center
33, Duryugongwon-ro, 17-gil, Nam-gu, Daegu 705-718, Korea Tel: 82-53-650-4285, Fax: 82-53-622-7067, E-mail: ispark@cu.ac.kr
CC This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/
by-nc/3.0) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
단일치아의 심한 치조골 소실 환자에서 블록형 자가치아골이식재를 이용한 치조능증대술: 증례보고
박인숙
대구가톨릭대학교 의과대학 치과학교실 구강악악면외과
Abstract
Ridge Augmentation Using Block Type of Autogenous Tooth Bone Graft Material in Severe Alveolar Bone Resorption of Single Tooth: Case Report
In-Sook Park
Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Section of Dentistry, School of Medicine, Catholic University of Daegu
Horizontal and vertical ridge augmentation with implant placement was performed, using a block type of autogenous tooth bone graft in a 37-year old male patient. This material was very useful for the case of severe alveolar bone resorption of a single tooth. After 13 months, excellent bony healing was obtained and final restoration was performed successfully.
Key words: Alveolar ridge augmentation, Single-tooth dental implant, Autogenous tooth bone graft
서 론
심한 골결손이 있는 치조능에 임플란트를 식립할 때에는 자가 골을 이용한 치조능증대술이 좋은 결과를 보이는 것은 잘 알려진 사실이다[1]. 부족한 수직 및 수평골의 증대를 위하여 블록형 골이 식을 하거나 혹은 입자형 골이식재에 여러 가지 차단막 등을 사용하여 골증대술을 시행한다[1,2]. 그러나 상부 연조직의 열개 가 일어나거나 이식 후 심한 골흡수가 일어나기도 하여 임상적으 로 어려움을 많이 가지고 있다[1]. 또한 골증대술은 다양한 공여부 를 필요로 하므로 추가적인 시술 부위나 수술 부위의 확대가
필요하고 장시간의 시술시간이 소요되어 환자의 불편감이 증가되 기도 하는 단점도 가지고 있다. 최근 개발된 입자형 및 블록형 자가치아골이식재는 발치와의 보존, 상악동 거상 및 치조능증대 술에 간편한 방법으로 많이 이용되고 있으며 그 안정성 및 임상적 효용성에 대한 장점이 보고되고 있다[3-8].
본 교실에서는 단일치아의 심한 치조골 흡수를 보이는 환자에
서 블록형 자가치아골이식재를 사용하여 골증대술 및 임플란트식
립술을 동시에 시행하여 양호한 결과를 보였기에 증례를 보고하고
자 한다.
In-Sook Park: Ridge Augmentation Using Autogenous Tooth Bone
463
Vol. 34 No. 6, November 2012 Fig. 1. (A) Initial panoramic radiography and (B) computed
tomography images. There were severe alveolar bone resorptions on left mandibular second molar.
Fig. 2. (A) Autogenous tooth bone block was adapted and
stabilized with implant fixture. (B) Root on type autogenous tooth bone block. (C) Powder type autogenous tooth bone graft material.증례보고
38세 남자 환자가 좌측 하악 제2대구치(#37)의 동요를 주소로 내원하였다. 중등도의 만성 치주염이 전반적으로 이환되었으나
#37부위는 특별히 치근단 하방까지 진행된 심한 치주염을 보이며
치근단 농양이 발생되었으며 컴퓨터단층촬영상 단일치아의 심한
치조골 소실을 보이고 있었다(Fig. 1). 이는 며칠 뒤 자연 탈락하
였고 탈락된 치아를 가지고 즉시 내원하여 상기 치아를 한국치아
조직은행으로 보내어 root on 형태와 powder 형태의 자가치아
골이식재로 가공하였다. 약 2주 뒤 연조직의 치유상태가 양호하여
자가치아골이식재를 이용하여 치조능증대술을 시행하였고 임플
란트를 동시에 식립하였다. 우선 식립하고자 하는 부위의 하방
치조골에 drilling을 시행하여 식립 부위를 preparation한 후
464
박인숙: 자가치아골을 이용한 치조능증대술J Korean Assoc Maxillofac Plast Reconstr Surg
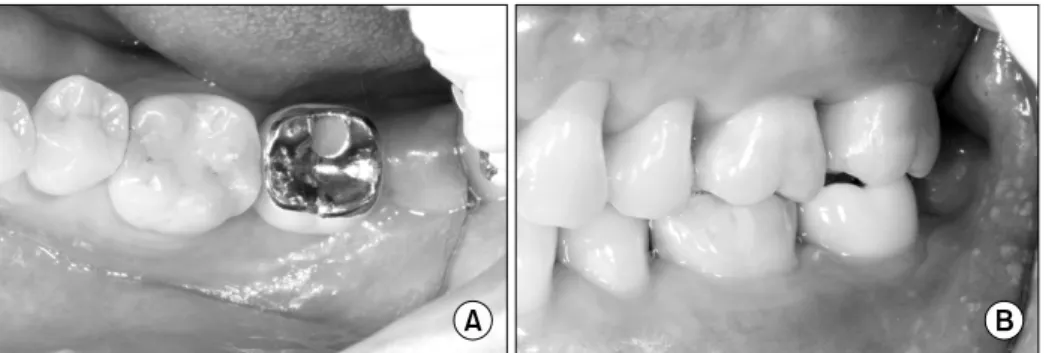
Fig. 6. The final restoration was
functionally stable. (A) Occlusal view, (B) lateral view.Fig. 5. Panoramic radiography was taken after final restoration.
Fig. 3. Postoperative panoramic radiography.
Fig. 4. Second operation was done after 13 months later. Excellent
bone healing was observed.root on 형태의 자가치아골이식재의 pulp chamber 부위를 천공 후 임플란트(Dentis S-clean Ø=4.8×12 mm) fixture를 고정한 후 그대로 prep된 치조정에 고정하였다(Fig. 2). 하방의 골에서 30 N의 충분한 초기 고정을 얻을 수 있었으며 상방에 platelet rich fibrin (PRF) membrane을 차단막으로 사용하였고 일차 봉합을 시행하고 술 후 방사선 사진을 촬영하였다(Fig. 3). 환자가 외국에서 생활하는 관계로 일차 식립 후 13개월 경과하여 2차 수술이 진행되었고(Fig. 4), 이 때 관찰한 블록형 자가골이식재의 생착은 매우 양호하였고 이 후 연조직 치유 후 최종 보철물을 장착하였다(Fig. 5, 6).
고 찰
심하게 파괴된 치조골의 골조직 재건을 위해 다양한 치조골증 대술이 이용되고 있는데 술식에 따라 ridge split technique, Ti-mesh를 이용한 ridge augmentation, block bone graft 등 다양한 술식이 이용되고 있으며 골이식재 또한 공여조직에 따라 자가골, 동종골, 이종골, 합성골 혹은 골치유 기전에 따라 골유도 성, 골전도성을 가지는 많은 골이식재가 사용되고 있다[2,9,10].
또한 골치유 능력의 향상을 위해 platelet rich plasma, PRF, concentrated growth factor (CGF) 등의 growth factor를 함유 한 여러 재료들이 부가적으로 혹은 단독으로 사용되기도 한다.
어떤 술식을 이용하든 치조골증대술은 술식의 안정성이 입증되었 고 임상적으로 유용하게 사용되고 있다.
최근 자가치아골을 이용한 골이식술은 인체 면역반응과 전염성 질환의 전이 위험성이 전혀 없이 매우 안전하며 자가골과 같은 우수한 골형성 기전을 가지고 있어 임상적으로 매우 안정성 있게 성공적으로 이용될 수 있음이 여러 연구에 의해 입증되었다 [1,3-8]. 또한 자가치아골을 이용한 골이식술은 치과계에서는 처 음으로 보건복지부로부터 보건신기술로 인증되어 그 안정성 및 유용성이 입증되었다고 볼 수 있다.
자가치아골이식재는 분말과 탈회시킨 블록의 형태로 이용되는
데 점착성이 우수하고 결손부에 잘 적합되며 블록형 자가골보다
조작이 용이하다. 또한 골유도 및 골전도성을 가지고 있어 치유가
In-Sook Park: Ridge Augmentation Using Autogenous Tooth Bone
465
Vol. 34 No. 6, November 2012
우수하여 창상의 열개로 인한 감염에 대해서도 저항성이 우수하고 2차 치유 또한 잘 이루어진다고 하였다[11,12]. 이러한 특성으로 보아 치조능의 골증대술에 유용하게 이용될 수 있으며 치아의 크기에 따라 블록형과 분말형을 동시에 만들어 사용할 경우 단일 치아의 치조골 흡수 시에는 다른 골이식재를 사용하지 않더라도 충분한 골이식재를 확보할 수 있을 것으로 보인다.
자가치아골이식재 상아질은 결정구조에 있어서 동종골과 함께 자가골에 가장 유사한 결정구조를 보이며[3], 치아의 상아질과 백악질에 보존된 유기질에는 type I collagen과 bone morpho- genic protein를 포함한 다수의 골성장 요소가 포함되어 있어 빠른 치조골 재생 및 골형성을 보인다[13]. 그러나 자가골이나 동종골 등 여타의 다른 골이식 재료와의 비교 실험은 좀 더 많은 연구가 필요하며 많은 증례에서 성공적인 골형성을 보여주고 있으 나 유의성이 있을 정도의 골형성능에 대해서는 추가적인 실험연구 들이 필요한 상태이다.
본 증례에서는 단일 치아의 심한 치조골 흡수가 발생된 증례로 인접치아의 치조골 상태가 양호할 때 블록형 자가치아골이식재 및 CGF membrane을 사용하여 임상적으로 용이하면서도 안정 적인 골증대를 획득하였다. 오랜 기간 추적검사를 할 수 없는 상황에서도 치은열개나 골이식재의 감염 없이 잘 생착되었고 임플 란트의 골유착도 우수하였으며 최종 보철물의 수복 시에도 골유착 정도는 안정적이었다. 아쉽게도 환자가 외국에서 생활하여 추적 검사가 어렵기는 하지만 현재까지 별다른 불편감의 호소 없이 잘 사용되고 있다.
References