배양된 대뇌피질세포에서 산화성 손상에 대한 6R-Tetrahydrobiopterin의 억제작용
전남대학교 의과대학 신경외과학교실
문경섭·이제혁·강삼석·김수한·김재휴·정 신·김태선·이정길
=
=
=
= Abstract = = = =
Study on the Protective Effects of 6R-Tetrahydrobiopterin on the Oxidative Neuronal Injury in Mouse Cortical Cultures
Kyung Sub Moon, M.D., Je Hyuk Lee, M.D., Sam Suk Kang, M.D., Soo Han Kim, M.D., Jae Hyoo Kim, M.D., Shin Jung, M.D.,
Tae Sun Kim, M.D., Jung Kil Lee, M.D.
Department of Neurosurgery, Chonnam University Hospital & Medical School, Kwangju, Korea
bjective:6R-Tetrahydrobiopterin(BH4) is a cofactor for the aromatic amino acid hydroxylases which is essential for the biosynthesis of catecholamines and serotonin. It also acts as a cofactor for nitric oxide synthase, and stimulates the release of some neurotransmitters such as dopamine, serotonin, acetylcholine and glutamate.
Recently, it has been reported that BH4 could induce cellular proliferation and enhance neuronal survival. This study was performed to investigate the antioxidative effect of BH4 on the various oxidative insults in mouse cerebral cortical cell cultures.
Methods:Iron ion(FeCl2), zinc ion(ZnCl2), sodium nitroprusside(SNP) and buthionine sulfoximine(BSO, a glu- tathione depletor) were used as oxidants. Cell death was assessed by measurement of lactate dehydrogenase efflux to bathing media at the end of exposure.
Result:All 4 oxidants induced neuronal cell death associated with cell body swelling, which was markedly inhibited by trolox(100μM), a vitamin E analog. BH4(10-100μM) markedly inhibited the neuronal cell death induced by all 4 oxidants(20μM Cu 2+ , 20μM Zn 2+ , 1μM SNP or 1mM BSO). However, BH4 failed to inhibit the neuronal cell death induced by 24hr exposure to 20μM NMDA.
Conculsion:These results suggest that BH4 has antioxidative action independently of any actions of enzyme cofactor.
KEY WORDS:6R-Tetrahydrobiopterin(BH4)・Antioxidation.
서 론
6R-Tetrahydrobiopterin(BH4)은 원래 tyrosine, phe- nylalanine 및 tryptophan을 수산화(hydroxylation)시키 는 효소(hydroxylase)에 필수 보조인자(cofactor)로 작용 하는 물질로 알려져 있다 5)13)21) . 또한 최근에는 일산화질소 (NO)의 생성에 관여하는 효소인 nitric oxide synthase에
도 보조인자로 작용함이 밝혀졌다 29) . 이러한 각종 효소의 보 조인자로서의 작용이외에 BH4는 dopamine, serotonin, acetylcholine 및 glutamate 등의 신경전달물질을 유리시 키는 작용이 있음도 보고되어 있다 18)22)24)30)
.
한편 Anastasiadis 등은 BH4가 말초신경세포에서 유래 한 PC12 세포의 분열을 촉진한다고 보고하였으며 1) , Kos- himura 등은 배양액내의 혈청 제거에 의한 PC12세포의 사 멸을 BH4 처리가 억제한다고 하였다 19) . 이러한 연구결과들
OOOO
은 BH4가 신경세포의 사멸에 영향을 미칠 수 있음을 시사 하고 있다.
자유기에 의한 산화성 손상이 급성 및 만성 중추신경계 질 환의 주된 병인으로 관여함이 잘 알려져 있다 12) . 본 연구는 배양된 생쥐 대뇌피질세포에서 산화성 손상을 일으킴이 알 려진 물질들인 FeCl 2 , ZnCl 2 , sodium nitroprusside(SNP) 및 buthionine sulfoximine(BSO)에 의한 산화성 손상에 대 한 BH4의 영향을 조사하고자 하였다.
대상 및 방법
신경세포-교세포 혼합배양:신경세포-교세포의 혼합 배 양은 먼저 교세포를 배양하여 24 well 배양접시에 교세포 층을 만든 후 그 위에 다시 신경세포를 배양하였다. 교세포 배양은 생후 1~2일된 생쥐(ICR 계)에서 뇌조직을 적출하여 Ca ++ 과 Mg ++ 가 들어 있지 않은 Hanks’ balanced salt solu- tion(HBSS)에 5mg/ml glucose, 7mg/ml sucrose 및 0.35 mg/ml NaHCO 3 가 첨가된 배양액(이하 DM)에 넣고 입체현 미경하에서 뇌막을 제거하였다. 대뇌피질을 적출하여 잘게 조각을 내고 0.25% trypsin이 함유된 DM에 넣어 37℃에서 15분간 처치한 후 1,000g에서 5분간 원심분리하였다. 그후 trypsin이 들어있는 용액을 제거하고 분리된 세포를 Eagle’ s minimal essential medium(MEM)에 2mM glutamine과 10% fetal bovine serum(FBS) 및 10% horse serum(HS) 이 포함된 배양액(이하 PM) 1~2ml에 넣은 다음 구멍이 좁혀진 pipet으로 약 10회 통과하여 세포가 잘 나누어지게 하였다. 여기에 epidermal growth factor(EGF)를 10ng/
ml 농도로 첨가한 후 24 well plate(Primaria, Falcon)에 0.5 hemisphere/plate 밀도로 각 well 당 400μl씩 pla- ting하여 37℃, 5% CO 2 와 100% 습도가 유지되는 CO 2 배양 기(Forma사, 미국)에서 배양하였다. 2~4주후 교세포가 충 분히 증식하여 배양접시에 완전한 층을 만들면 임신 15~17 일된 생쥐를 halothane으로 마취하여 경추전위로 희생시키 고 전신에 70% ethanol을 분무하여 충분히 적신 후 복강을 절개하여 생쥐 태아를 꺼내어 뇌를 적출하였다. 적출된 뇌에 서 교세포 배양시와 같은 방법으로 대뇌피질을 얻어 교세포 가 배양된 plate에서 배양액을 완전히 제거한 후 2.75 hemi- sphere/plate 밀도로 각 well 당 400μl씩 plating하여 37℃, 5% CO 2 , 100% 습도하에서 배양하였다. 이때 사용한 PM 은 교세포 배양시와 다르게 5% FBS 및 5% HS로 보충하였 다. 교세포의 증식을 억제하기 위해 혼합배양 3~5일에 cy- tosine arabinoside를 10μM농도로 각 well에 처리하여 약 2일간 작용시켰다. 배양액 교체는 교세포배양의 경우 2주후
부터 1주일에 한번씩, 혼합배양에서는 일주일후부터 일주일 에 2번 시행하였다.
약물처리:신경세포의 산화성 손상을 유발하기 위하여 FeCl 2 , ZnCl 2 , SNP 및 BSO를 사용하였다. 모든 실험은 신 경세포 배양 13~15일 후에 실시하였다. 세포에 대한 약물 처리는 처리전 배양액으로 3번 씻어 주고 나서 실시하였고, 24 well 배양접시의 한 줄(4 well)에 같은 처리를 하였으며, 모든 실험에서 첫줄은 약물을 투여하지 않은 허위 처리군 (sham wash), 둘째 줄은 N-methyl-D-aspartate(NMDA, 500μM)를 처리하여 모든 신경세포를 죽이는 군(full kill) 으로 하였으며 셋째 줄에서 여섯째 줄까지를 약물 투여 군 으로 사용하였다. 모든 약물은 증류수에 녹여 원액을 만들어 각 well 당 4~8μl씩 되게 배양액에 희석하여 배양액 교환 과 함께 투여하였으며, 손상 유발 약물의 억제작용을 보기 위한 실험에서는 두 종류 약물을 동시에 같이 투여하였다.
세포사 측정:위상차 현미경으로 세포 손상 정도를 관찰 하고, 약물 투여 후 24시간 간격으로 세포막 파괴시 배양액 내로 유출된 lactate dehydrogenase(LDH)의 양을 측정하 였다. LDH 측정은 96 well plate의 각 well에 배양액(25μl) 을 넣고 buffer(125μl)와 0.3mg/ml NADH(100μl)와 22.
7mM pyruvate(30μl)를 넣어 곧 바로 Microplate reader (Molecular Device사, 미국)를 이용하여 340nm에서 흡광 도의 변동을 4분간 측정하였다. 이때 standard enzyme으 로는 Sigma사의 control enzyme을 사용하였다. 측정치는 sham wash군과 full kill군의 차이를 100으로하여 각 약물 투여군의 값과 sham wash군과 차이를 상대적 백분률로 환 산하여 평균±표준오차 (mean±SEM)로 나타내었다.
시 약:MEM, glutamine, HBSS은 Gibco사(Maryland, 미국) 제품을, HEPES control salt solution의 구성성분인 HEPES(acid), glucose, NaHCO 3 , NaCl, KCl, MgCl 2 , CaCl 2 , NaOH, phenol red와 그 외 trypsin, cytosine arabinoside, epidermal growth factor, sucrose 등은 Sigma사(Miss- ouri, 미국) 제품을 사용하였고, FBS 및 HS은 Hyclone사 (Utah, 미국) 제품을 55℃에서 30분간 비활성화 시켜 사용 하였다. BH4, FeCl 2 , ZnCl 2 , SNP 및 BSO은 Sigma사(Mis- souri, 미국) 제품을, trolox는 Aldrich사(Missouri, 미국) 제품을, NMDA 및 MK-801은 RBI사(Massachusetts, 미 국) 제품을 사용하였다.
통계처리:각 군간의 모든 값은 일측 ANOVA를 시행하
여 유의한 경우에 Student-Neuman-Keuls test로 각군
간의 유의성을 검정하였으며, p<0.05인 경우 통계학적으로
유의하다고 판정하였다.
결 과
FeCl 2 (20μM)를 배양액내에 24시간 처리시 78±5.8%
의 신경세포사를 유발하였다. 이 신경세포사는 항산화제인
trolox(100μM) 동시 처리로 현저히 억제되었으며, BH4 (30 및 100μM) 동시처리로도 현저히 억제되었다(Fig. 1, 2). ZnCl 2 (20μM)의 24시간 처리는 67±34.0%의 신경세 포사를 유발하였다. 이 신경세포사는 항산화제인 trolox(100 μM) 처리로 현저히 억제되었으며, BH4(10, 30 및 100μM)
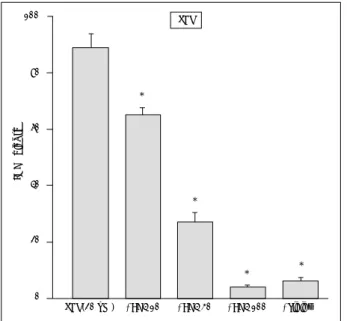
Fig. 2. Effects of 6R-tetrahydrobio-pterin(BH4:10, 30, 100μM) or trolox(100μM) on the 20μM FeCl2-induced neuronal death at the end of 24 hr exposure. Mean±SEM from 8-12 wells. As- terisks indicate significant difference from FeCl2-treated control group(p<0.01).
Fig. 3. Effects of 6R-tetrahydrobiopterin(BH4:10, 30, 100μM) or trolox(100μM) on the 20μM ZnCl
2-induced neuronal death at the end of 24 hr exposure. Mean±SEM from 8-12 wells.
Asterisks indicate significant difference from FeCl2-treated control group(p<0.01).
Fe(20 uM) +BH4 10 +BH4 30 +BH4 100 +Trolox FeCl
2100
80
60
40
20
0
% LDH Re le as e
*
*
*
Zn(20 uM) +BH4 10 +BH4 30 +BH4 100 +Trolox ZnCl
280
60
40
20
0
% LDH Re le as e
*
*
*
*
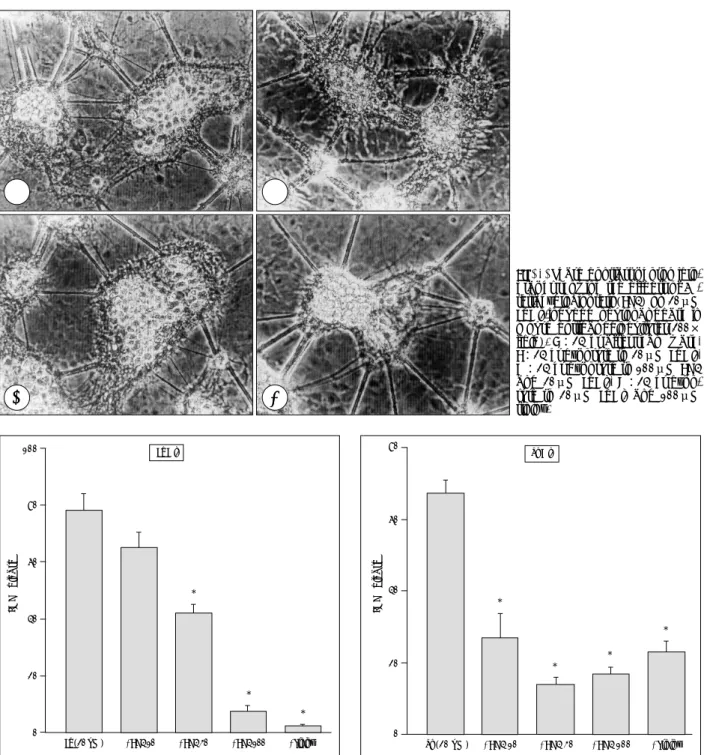
Fig. 1. Phase contrast photomicro- graphs showing the effects of 6R- tetrahydrobiopterin(BH4) on 20μM FeCl
2-induced neuronal death in mouse cortical cell cultures(200×
field). A:24 hr after sham wash, B:24 hr exposure to 20μM FeCl
2, C:24 hr exposure to 100μM BH4 and 20μM FeCl
2, D:24 hr expo- sure to 20μM FeCl
2and 100μM trolox.
A A A
A B B B B
C C C
C D D D D
동시 처리로도 현저히 억제되었다(Fig. 3). 일산화질소(NO) 를 유리하여 산화성 손상을 유발하는 SNP(1μM) 24시간 처리는 심한 신경세포사(89±5.1%)를 일으켰다. 이 SNP에 의한 신경세포사는 항산화제인 trolox(100μM) 동시 처리 로 현저히 억제되었으며, BH4(10, 30 및 100μM) 동시처
리로도 현저히 감약되었다(Fig. 4). 세포내 내인성 항산화물 질인 glutathione의 생합성을 억제하여 신경세포의 산화성 손상을 유발하는 BSO(1mM)의 48시간처리도 심한 신경세 포사(91±6.7%)를 유발하였으며, trolox 동시처리에 의해 현저히 억제되었고 BH4(10, 30 및 100μM) 동시처리에 의해서도 신경세포사가 현저히 억제되었다(Fig. 5)
한편 흥분독성을 일으키는 NMDA(20μM)의 24시간 처리 역시 심한 신경세포사(80±4.1%)를 유발하였으며, NMDA 수용체 길항제인 MK-801(10μM) 처리로 소실되었으나 BH4(10, 30 및 100μM) 동시처리에 의해서는 영향받지 않 았다(Fig. 6).
고 찰
본 실험에서 사용한 철이온은 Fenton 반응에 의해 hyd- roxyl radical을 생성하여 산화적 손상을 유발하는 물질로 알려져 있고 12) , 이러한 철이온이 중추신경세포 배양에서 산 화성 손상을 일으킴은 잘 알려져 있다 6)8) . 한편 아연이온은 허혈성 뇌손상시 신경세포사멸에 관여한다는 보고 16) 후 이 의 신경세포사멸작용 기전에 대한 많은 연구가 진행중이다.
최근 Kim 등은 본 실험과 같은 실험모형에서 아연이온이 신경세포사를 일으키며 이 과정에 산화성 손상이 관여함을 보고하였다 15) . SNP는 일산화 질소를 유리시키는 작용을 갖 는 약물로 각종 세포에서 산화성 손상을 유발함이 알려져
Fig. 4. Effects of 6R-tetrahydrobiopterin(BH4 10, 30, 100μM) or trolox(100μM) on the 1μM SNP-induced neuronal death at the end of 24 hr exposure. Mean±SEM from 8-12 wells. Asterisks indicate significant difference from SNP-treated control group (p<0.01).
Fig. 5. Effects of 6R-tetrahydrobiopterin(BH4:10, 30, 100μM) or trolox(100μM) on the 1mM BSO-induced neuronal death at the end of 48hr exposure. Mean±SEM from 8 wells. Asterisks indicate significant difference from BSO-treated control group (p<0.01).
SNP(20 uM) +BH4 10 +BH4 30 +BH4 100 +Trolox 100 SNP
80
60
40
20
0
% LDH Re le as e
*
* *
*
Fig. 6. Effects of 6R-tetrahydrobiopterin(BH4:10, 30, 100μM) or MK-801(10μM) on the 20μM NMDA-induced neuronal death at the end of 24 hr exposure. Mean±SEM from 8 wells. Aste- risks indicate significant difference from NMDA-treated control group(p<0.01).
NMDA(20 uM) +BH4 10 +BH4 30 +BH4 100 +Trolox NMDA
100
80
60
40
20
0
% LDH Re le as e
*
BSO(20 uM) +BH4 10 +BH4 30 +BH4 100 +Trolox 100 BSO
80
60
40
20
0
% LDH Re le as e
* *
있다 3)23)25) . BSO는 세포내 내인성 항산화물인 glutathione 의 생합성에 중요한 효소인 γ-glutamylcysteine synth- etase를 억제하여 산화성 손상을 유발하며 중추 신경세포 배양에서 산화성 손상을 일으킴이 잘 알려져 있다 8)14) . 본 실험성적에서 이들 4가지 약물에 의한 신경세포사가 세포막 지질과산화를 억제하는 대표적 항산화제인 trolox 6) 에 의해 서 억제된 점도 이들 약물이 산화성 손상을 일으킴을 가리 키고 있다.
한편 활성산소가 일부 퇴행성 신경 질환의 병인으로 작용 할 수 있음을 시사하는 많은 연구들이 보고되어 있다 2)7)11)26) . 즉, 외상성 뇌 손상 17) 과 척수 손상 4)27) 의 동물 모형에서 활 성산소 생성이 병인으로 작용함이 보고되어 있을 뿐아니라 중추신경계의 허혈 및 재관류시에도 활성산소의 생성 및 내 인성 항산화물이 소실되며 10) , 항산화제 처리가 허혈과 외상 에 의한 신경손상을 억제함이 알려져 있다 9)20)27) . 따라서 신 경세포에서 활성산소에 의한 산화성 손상을 억제하는 물질 이 각종 중추신경계 질환의 예방 및 치료제로서 개발되고 있다.
본 실험에서 BH4는 철 이온, 아연 이온, SNP 및 BSO에 의한 신경세포사를 현저히 감약시켰으나, NMDA에 의한 신 경세포사에는 전혀 영향을 미치지 못하였다. BH4의 항산화 작용은 100μM농도에서 그 억제작용이 trolox 100μM과 비슷하였다. 이 결과는 BH4가 강력한 항산화작용을 갖고 있 음을 나타내고 있다. 이러한 BH4의 항산화작용의 기전에 대 해서는 본 실험성적 만으로는 해석이 어려우나, 적어도 BH4 의 전술한 효소의 보조인자로서의 작용은 아닌 것으로 사료 된다. 왜냐하면 본 실험에서 사용한 대뇌피질세포배양에는 적어도 catecholamine이나 serotonin을 함유하는 신경세포 가 없으며, 산화질소를 유리하는 특성을 갖는 SNP에 의한 신경세포손상도 BH4가 강력하게 억제하기 때문이다. Shi- mizu 등은 배양된 내피세포에서 산화질소에 의한 내피세포 사멸을 BH4가 억제하며 이는 BH4의 항산화작용에 기인한 다 28) 고 하여 본 실험 성적과 일치하는 결과를 발표하였다.
이상의 성적은 BH4는 각종 효소의 보조인자로서의 작용 과는 상관없이 그 자체가 항산화제로 작용하여 산화성 손상 에 의한 신경세포손상을 억제할 수 있음을 가리키고 있으며, 흥분독성은 억제하지 못함을 시사하고 있다.
결 론
본 연구는 배양된 생쥐 대뇌피질세포에서 산화성 손상을 일으킴이 알려진 물질들인 FeCl 2 , ZnCl 2 , sodium nitrop- russide(SNP) 및 buthionine sulfoximine(BSO)와 흥분
독성유발 물질인 NMDA 의한 신경세포사멸에 미치는 BH4 의 영향을 조사하였다. FeCl 2 (20μM), ZnCl 2 (20μM) 혹은 SNP(1μM) 24시간 처리 및 BSO(1mg) 48시간 처리는 현 저한 신경세포사멸을 일으켰다. 이 신경세포사멸은 모두 vi- tamin E 유도체 항산화제인 trolox(100μM) 동시 처리로 현저히 억제되었으며, BH4(10-100μM) 동시처리로도 현 저히 억제되었다. 한편 NMDA(20μM) 처리에 의한 신경세 포사는 BH4(10-100μM) 동시처리에 의해서 영향받지 않 았다.
이상의 성적은 BH4는 그 자체가 항산화제로 작용하여 산 화성 손상에 의한 신경세포손상을 억제할 수 있음을 시사하 고 있다.
•
논문접수일:2001년 4월 4일•
심사완료일:2001년 6월 14일•
책임저자:문 경 섭501-746 광주광역시 동구 학1동 8번지 전남대학교 의과대학 신경외과학교실
전화:062) 220-6606, 전송:062) 224-9865 E-mail:herhuz@hanmail.net
References
1) Anastasiadis PZ, States CJ, Imerman BA, Louie MC, Kuhn DM, Levine RA:Mitogenic effects of tetrahydrobiopterin in
PC12 cells. Mol Pharmacol 49
:149-155, 1996
2) Beal MF:Does impairment of energy metabolism result in
excitotoxic neuronal death in neurodegenerative illness? Ann Neurol 31
:119-130, 1992
3) Blackburn RV, Galoforo SS, Berns CM, Motwani NM, Corry PM, Lee YJ:Differential induction of cell death in human
glioma cell lines by sodium nitroprusside. Cancer 82
:1137- 1145, 1998
4) Braughler JM, Hall ED:Central nervous system trauma and
stroke. I. Biochemical considerations for oxygen radical for- mation and lipid peroxidation. Free Radic Biol Med 6
:289- 301, 1989
5) Brenneman AR, Kaufman S:The role of tetrahydropteridines
in the enzymatic conversion of tyrosine to 3,4-dihydroxyphe- nylalanine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 17
:177-183, 1964
6) Chow HC, Lynch Ⅲ, JJ, Rose K, Choi DW:Trolox attenu-ates cortical neuronal injury induced by iron, ultraviolet light, glucose deprivation, or AMPA. Brain Res 639
:102-108, 1994
7) Gurney ME, Pu H, Chiu AY, Dal Canto MC, Polchow CY,Alexander DD, et al:Motor neuron degeneration in mice
that express a human Cu, Zn superoxide dismutase mutation.
Science 264
:1772-1775, 1994
8) Gwag BJ, Koh JY, Chen MM, Dugan LL, Behrens MM, Lobner D:BDNF or IGF-Ⅰ
potentiates free radical-mediated injury
in cortical cell cultures. Neuroreport 7
:93-96, 1995
9) Hall ED, Pazara KE, Braughler JM:21-Aminosteroid lipid
peroxidation inhibitor U74006F protects against cerebral isch- emia in gerbils. Stroke 19
:997-1002, 1988
10) Halliwell B:Oxidants and the central nervous system:
some fundamental questions. Is oxidant damage relevant to Parkin- son’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, traumatic injury or stroke?
Acta Neurol Scand Suppl 126
:23-33,1989
11) Halliwell B:Reactive oxygen species and the central nervous
system. J Neurochem 59
:1609-1623, 1992
12) Halliwell B, Gutteridge J MC:What is free radical? In Free
radicals in biology and medicine. 2nd Ed. Oxford University Press, New York, 1989, pp10-19
13) Kaufman S:The structure of phenylalanine-hydroxylation co-
factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 50
:1085-1093, 1963
14) Kim IH, Lee JK, Kim TS, Jung S, Kim JH, Kim SH, et al:Effect of trolox, cyclohexamide or MK-801 on the neuronal cell death induced by FeCl2, buthionine sulfoximine or KCN in primary murine mixed cortical cell culture. J Korean Neurosurg 26
:1342-1350, 1997
15) Kim YH, Kim EY, Gwag BJ, Sohn S, Koh JY:Zinc-induced
cortical neuronal death with features of apoptosis and nec- rosis
:mediation by free radicals. Neurosci 89
:175-182, 1999
16) Koh JY, Suh SW, Gwag BJ, He YY, Hsu CY, Choi DW:Therole of zinc in selective neuronal death after transient global cerebral ischemia. Science 272
:1013-1016, 1996
17) Kontos HA, Wei EP:Superoxide production in experimental
brain injury. J Neurosurg 64
:803-807, 1986
18) Koshimura K, Miwa S, Lee K, Kujiwara M, Watanabe Y:En-
hancement of dopamine release in vivo from the rat striatum by dialyticperfusion of 6R-L-erythro-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobiopterin.
J Neurochem 54
:1391-1397, 1990
19) Koshimura K, Tanaka J, Murakami Y, Kato Y:Enhancement
of neuronal survival by 6R-tetrahydrobiopterin. Neurosci 88
:561-569, 1999
20) Liu TH, Beckman JS, Freeman BA, Hogan EL, Hsu CY:Pol-
yethylene glycol-conjugated superoxide dismutase and cata- lase reduce ischemic brain injury. Am J Physiol 256
:H589- H593, 1989
21) Lovenberg W, Jequier E, Sjoerdsma A:Tryptophan hydroxy-
lase
:measurement in pineal gland, brain stem and carcinoid
tumor. Science 155
:217-219, 1967
22) Mataga N, Imamura K, Watanabe Y:6R-Tetrahydrobiopterin
perfusion enhances dopamine, serotonin, and glutamate out- puts in dialysate from rat striatum and frontal cortex. Brain Res 551
:64-71, 1991
23) Niknahad H, O’Brien PJ:Involvement of nitric oxide in ni-
troprusside-induced hepatocyte cytotoxicity. Biochem Phar- macol 51
:1031-1039, 1996
24) Ohue T, Koshimura K, Lee K, Watanabe Y, Miwa S:A novel
action of 6R-L-erythro-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobiopterin, a cofactor for hydroxylases of phenylalanine, tyrosine and tryptophan
:enhancement of acetylcholine release in vivo in the rat hip- pocampus. Neurosci Lett 128
:93-96, 1991
25) Rauhala P, Khaldi A, Mohanakumar KP, Chiueh CC:Appa-
rant role of hydroxyl radicals in oxidative brain injury indu- ced by sodium nitroprusside. Free Radic Biol Med 24
:1065- 1073, 1998
26) Rosen DR, Siddique T, Patterson D, Filewicz DA, Sapp P, Hentati A, et al:Mutations in Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase
gene are associated with familial amyotrophic lateral sclero- sis. Nature 362
:59-62, 1993
27) Saunders RD, Dugan LL, Demediuk P, Means ED, Anderson DK, Horrocks LA:Effects of methylprednisolone and the com-
bination of alpha-tocopherol and selenium on arachidonic acid metabolism and lipid peroxidation in traumatized spi- nal tissue. J Neurochem 49
:24-31, 1987
28) Shimizu S, Ishii M, Kawakami Y, Momose K, Yamamoto T:
Protective effects of tetrahydrobiopterin against nitric oxide- induced endothelial cell death. Life Sci 63
:1585-1592, 1998
29) Werner ER, Werner-Felmayer G, Fuchs D, Hausen A, Reibneg- ger G, Yim JJ, et al:Tetrahydrobiopterin biosynthetic ac-tivities in human macrophages, fibroblasts, THP-1 and T24 cells.
GTP-cyclohydrolase I is stimulated by interferon-gamma, and 6-pyruvyl tetrahydropterin synthase and sepiapterin reductase are consistently present. J Biol Chem 265
:3189-3192, 1990
30) Wolf WA, Ziaja E, Jr Arthur RA, Anastasiadis PZ, Levine RA,Kuhn DM:Effect of tetrahydrobiopterin on serotonin synth-