성균관대학교 의과대학 삼성서울병원 이비인후과학교실장영수, 조양선, 장규선, 최나연, 박준오
Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
Young-Soo Chang, Yang-Sun Cho, Kyu-Sun Jang, Nayeon Choi, Jun Oh Park
안면신경 전방전위를 이용한 경정맥공 종양 제거 수술에서 술 후 안면신경 기능의 예후인자 분석
Prognostic factors for post-operative facial nerve function after removal of jugular foramen tumor with anterior facial nerve
rerouting
J Korean Skull Base Society 6권 1호 : 5~9, 2011
Objectives : Resection of jugular foramen tumors is limited by the intratemporal course of the facial nerve. Facial nerve rerouting techniques were developed to facilitate resection of extensive tumors occupying the skull base. Although facial nerve rerouting technique can maximize the surgical view, it may result in some degree of facial nerve paresis. We have therefore analyzed factors associated with post-operative facial nerve outcome in patients with jugular foramen tumor who were undergone surgical management including anterior facial nerve rerouting.
Study design : Retrospective study
Methods : We retrospectively enrolled 21 patients with jugular foramen tumor who underwent anterior rerouting of the facial nerve. Rerouting technique, type of mastoidectomy, operation time, completeness of tumor resection and change of facial expression were obtained from the medical records. Facial nerve function was evaluated using House-Brackmann grading system.
Results : Shorter rerouting resulted in a better outcome without statistical significance.
Operation time lesser then 12 hours had a better facial nerve outcome at immediately post- operative evaluation. However, facial nerve outcome within 6-12 months did not show the difference.
Conclusion : The facial nerve function at 12 months after operation could be preserved in 90.5 % of patients who underwent surgical management of the jugular foramen tumor including anterior rerouting of the facial nerve. We can expect better facial nerve outcome with short rerouting and after operation with short duration. The facial nerve should be minimally manipulated during even in the rerouting procedure.
논문 접수일 : 2011년 5월 10일 심사 완료일 : 2011년 5월 30일 주소 : 성균관대학교 의과대학 삼성서울병원
이비인후과학교실
서울특별시 강남구 일원동 50 Tel : 82-2-3410-3578 Fax : 82-2-3410-3879 E-mail : yscho@skku.edu
조 양 선
교신저자
Facial nerve, Jugular foramen, Anterior rerouting
Key Words
원저1 종설1 증례1 증례2 증례3 증례4
▒
서 론경정맥공에 발생하는 종양으로는 경정맥 사구종 (glomus jugulare tumor), 경정맥공 신경초종 (jugular foramen schwannoma, JFS), 경정맥공 뇌수막종 (jugular foramen meningioma) 등이 있다.12)
다양한 경정맥공 종양에 대한 치료의 원칙은 종양의 수술적 절제 이다.9)측두하와 접근법을 비롯한 외측 접근법은 경정맥공 종양의 수술 시에 넓은 시야를 제공하며 많이 쓰이는 수술적 접근방법이 다. 2, 11)
이 술식은 경정맥공에 발생하는 광범위한 종양에 대한 수술적 치 료를 용이하게 하나,5)안면신경 전방 전위에 따른 술 후 안면신경 마 비를 비롯한 뇌신경 마비의 위험성이 있으며, 중이와 유양동, 그리 고 외이도의 폐쇄로 인하여 영구적인 전음성 난청을 초래한다. 이러 한 단점들을 극복하고자 최근에 들어서는 종양의 종류나 위치에 따 라 다양한 수술적 방법들을 이용하여 뇌신경 마비나 전음성 난청을 줄이려는 시도들이 있다.1, 6-8)안면신경을 전방 으로 전위하는 과정 에서 안면신경의 허혈이나 조작으로 인한 외상으로 술 후 안면신경 마비의 위험성이 있으며, 이를 방지하기 위하여 안면신경 조작을 최 소화하면서 수술 시야를 얻은 방법들이 소개되고 있다.2)(Fig. 1)
이에 본 연구에서는 안면신경 전방전위를 이용한 경정맥공 종양 제거술을 받은 환자들에서 술 후 안면신경기능의 예후인자에 대하 여 분석하고자 하였다.
▒
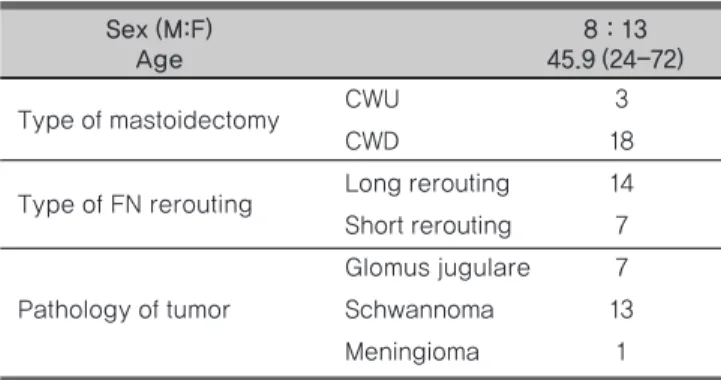
대상 및 방법1997년부터 2011년까지 경정맥공을 침범한 두개저 종양에 대하 여 A형 측두하와접근법을 포함, 안면신경 전방전위를 이용하여 종 양을 제거한 21명의 환자에 대한 의무기록을 후향적으로 검토하였 다. 병리 조직 검사 결과 경정맥 사구종 7예, 경정맥공 신경초종 13 예, 경정맥공 뇌수막종 1예 였다. 안면신경 기능의 평가는 House- Brackmann (H-B) grading system을 이용하여 평가하였으며 12 개월 이상 추적관찰 하였거나 마지막 외래 방문 시 H-B grade (Gr)
Type of mastoidectomy CWU 3
CWD 18
Type of FN rerouting Long rerouting 14 Short rerouting 7 Glomus jugulare 7
Pathology of tumor Schwannoma 13
Meningioma 1
Sex (M:F) 8 : 13
Age 45.9 (24-72)
Table 1. Patient demographics, type of surgical techniques and pathology of tumor
CWU : canal wall up mastoidecomy, CWD : canal wall down mastoidectomy, FN : Facial nerve
Intraoperative findings in each type of facial nerve rerouting procedures A. CWU-short rerouting.
B. CWD-short rerouting.
C. CWD-long rerouting. White arrows point to the rerouted facial nerves. CW : posterior wall of external auditory canal, SS : sigmoid sinus, CWU : canal wall up mastoidecomy, CWD : canal wall down mastoidecomy
A B C
Fig. 1
I 또는 II 였던 환자들을 포함하여 분석하였다. 남자가 8명, 여자가 13명이었으며, 연령은 24세에서 72세로 평균 45.9세였다. (Table 1) 수술 중 안면신경 전방전위 부위, 유양동 수술의 종류, 수술 시간, 종양의 완전절제 여부를 예후인자로 분석하였고, 수술 직후, 술 후 1, 6, 12개월 시의 안면신경 기능을 H-B grading system 으로 평 가하여 수술 후 안면신경마비 정도를 측정하였다.
모든 환자에 대하여 수술 전에 이비인후과와 신경외과에서 문진 과 뇌신경 기능 평가를 포함한 신체검사를 시행하였으며 전산화 단 층 촬영과 자기공명영상을 시행하여 병변의 위치를 평가하였다. 종 양의 완전 절제여부는 수술 중 동결절편 검사 결과를 통하여 평가하 였으며 수술 중 안면신경의 기능은 NIM-IITM (Xomed, USA) 를 이용하여 감시하였다.
안면신경마비의 정도는 수술 직후부터 1개월까지는 H-B Gr I- III 와 IV 이상의 군으로 나누었으며, 6개월에서 12개월까지는 H-B Gr II 이하와 III 이상의 군으로 나누어 비교하였다.
예후인자에 따른 안면신경마비 정도를 집단 간에 분석하기 위하 여 Pearson`s Chi-square test를 이용하였으며, 모든 경우에 유의 수준은 p < 0.05 로 하였다.
▒
결 과전방전위의 종류
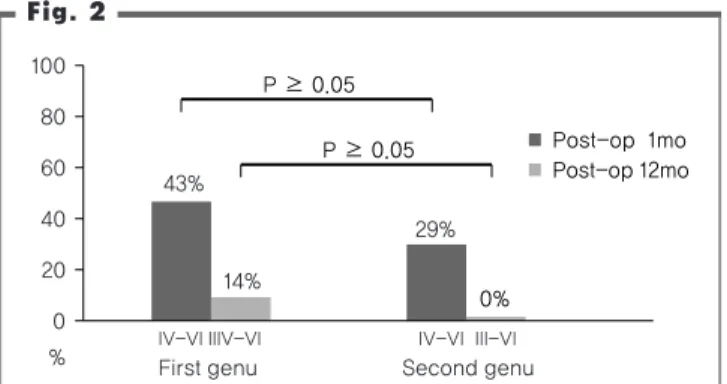
21명의 환자 중 안면신경의 슬신경절 (geniculate ganglion)에서 경유돌공 (stylomastoid foramen)까지 전방전위를 시행한 군 (Long rerouting group)은 14명 이었고, 제2슬부 (second genu) 에서 경유돌공까지 전방전위를 시행한 군 (Short rerouting group)
은 7명이었다. (Table 2.) Long rerouting group 중 6명 (43%)은 수술 직후부터 1달까지 H-B Gr IV 이상으로 중등도 이상의 안면신 경마비 소견을 보였으나 점차 호전되어 수술 후 1년 경과 시에는 2 명 (14%)만이 H-B Gr III 였고, 나머지는 모두 H-B Gr I, II 로 호 전되었다. Short rerouting group 중 2명 (29%)은 수술 직후부터 1 달까지 H-B Gr IV 이상이었으나 수술 후 1년 경과시에는 모두 H- B Gr I 으로 정상화되었다. (Fig. 2)
유양돌기 절제술의 방법
외이도 후벽을 제거 후 (canal wall down, CWD) 안면신경의 슬 신경절 (geniculate ganglion) 에서 경유돌공 (stylomastoid foramen) 까지 전방전위를 시행한 군은 14명이었으며, 제 2슬부 (second genu) 에서 경유돌공까지 전방전위를 시행한 군은 외이도 후벽을 보존한 경우 (canal wall up, CWU) 가 3명, CWD 을 시행한 경우 4명 이었다. Short rerouting group 중 CWU 과 CWD 을 시
Long I - III 14 8 8 I, II 11 12
rerouting CWD III 2 2
IV - VI 0 6 6 IV - VI 1 0
I - III 4 3 3 I, II 4 4
CWD III 0 0
Short IV - VI 0 1 1 IV - VI 0 0
rerouting
I - III 3 2 2 I, II 3 3
CWU III 0 0
IV - VI 0 1 1 IV - VI 0 0
Type of Type of
H-B Grade Pre-op Post-op Post-op
H-B Grade Post-op Post-op
FN rerouting mastoidectomy immediate 1 mo 6 mo 12 mo
Table 2. Facial nerve function according to the post-operative duration after anterior rerouting procedures
H-B : House-Brackmann, op : operative, CWU : canal wall up mastoidecomy, CWD : canal wall down mastoidectomy
Fig. 2
100
80 60
40 20
0
% IV-VI IIIV-VI IV-VI III-VI
First genu Second genu
43%
14%
29%
■Post-op 1mo
■Post-op 12mo
0%
P ≥ 0.05 P ≥ 0.05
Postoperatve facial nerve paralysis according to type of facial nerve rerouting. op : operative
행한 경우 각각 1명에서 수술 직후부터 1달까지 H-B Gr IV 이상으 로 중등도 이상의 안면신경마비 소견을 보였으나 점차 호전되어 수 술 후 1년 경과 시에는 2명 모두 H-B Gr I 으로 정상화되었다.
수술 소요 시간
12시간 이상 수술시간이 소요된 환자는 14명으로 이중 8명 (57%) 이 수술 직후부터 1달까지 H-B Gr IV 이상의 소견을 보였다. 12시 간 이하로 수술이 소요된 환자 7명은 수술 직후부터 모두 H-B Gr III 이하의 양호한 안면신경기능을 보여 두 군간에는 통계적으로 유 의한 차이가 있었다. (Pearson`s Chi-square test, p = 0.015) 그러 나 수술 후 6개월에서 1년 경과 후 안면신경 기능의 회복 정도는 두 군간에 통계적으로 유의한 차이를 나타내지 않았다. (Fig. 3)
종양의 완전절제여부
총 21명의 환자 중 17명은 수술을 통하여 종양을 완전절제 (gross total removal: GTR) 하였으며, 4명은 부분절제 (partial resection : PR) 시행하였다. 수술 직후 H-B Gr IV 이상의 안면신경 마비를 나타낸 환자는 GTR 군에서는 35%, PR 군에서는 50% 였으며, 두 군은 통계적으로 유의한 차이를 나타내지 않았다. 수술 6개월에서 1 년 경과 후 H-B Gr III 이상의 안면신경 마비를 나타낸 환자는 GTR 군에서 6%, PR 군에서 25% 였으며, 두 군의 비교에서도 통계 적으로 유의한 차이를 나타내지 않았다.
▒
고 찰경정맥공에 발생한 종양을 제거하는 데에는 측두하와 접근법을 비롯한 다양한 수술적 접근이 사용됨으로써 많은 발전이 있어왔다.
1964년 Shapiro와 Neues 가 측두하와 접극법을 비롯한 외측 접 근법을 발표하였으며,11) 1977년 Fisch는‘infratemporal fossa approach’라는 이름으로 비슷한 유형의 수술방법을 발표하였다.4)
Fisch 는 측두하와 접근법에서 종양의 절제를 용이하도록 슬신경절 에서부터의 안면신경 전방 전위술을 제안하였다. 이후 Farrior 는 안면신경 마비를 감소시키기 위하여 Fisch 가 기술한 슬신경절보다 원위부인 제 2슬부에서의 안면신경 전방 전위술을 제안하였다.3)
Selesnick 은 측두하와 접근법을 포함하여 다양한 측두개저 수술 시 제 2슬부 혹은 슬신경절에서부터 안면신경 전방전위를 시행하는 경우 단기 추적시에는 큰 차이가 없으나 장기 추적관찰시에는 제2 슬부에서 안면신경 전방전위를 시행하는 경우 93%에서, 슬신경절 에서 안면신경 전방전위를 시행하는 경우 72% 에서 H-B Gr I-II 의 안면신경 기능을 보여 유의한 차이를 보인다고 보고하였다.10)
저자들은 이번 연구에서 안면신경 전방전위를 이용한 경정맥공 종양 제거술 후 안면신경기능의 예후인자에 대하여 분석하였다. 예 후인자로서 수술 중 안면신경 전방전위 부위, 유양동 수술의 종류, 수술 시간, 종양의 완전절제 여부를 평가하였다.
수술 직후 슬신경절에서 경유돌공까지 전방전위를 시행한 군은 43% 에서 H-B Gr IV 이상으로 중등도 이상의 안면신경 마비 소견 을 보였고, 제 2슬부에서 경유돌공까지 전방전위를 시행한 군은 14%에서 중등도 이상의 안면신경 마비소견을 보여 안면신경의 전위 범위가 작은 환자에서 좋은 기능을 보였으나 두 군은 통계적으로 유 의한 차이를 나타내지 않았다.
수술 후 1년 째 평가를 했을 때 H-B Gr III 로 안면신경 마비가 남은 2명의 환자는 모두 슬신경절에서 경유돌공까지 전위를 시행 한 경우로서 분석한 증례수가 적어서 통계적 유의성을 보이지는 않 았지만 역시 전위의 범위가 작을수록 안면신경 기능이 우수함을 보 여주었다. 전체적으로 보면 수술 후 1년이 경과 후에는 90.5%에서 H-B Gr I or II로 호전되어 안면신경 전방전위술 후 안면신경 기 능은 만족할 만한 성적을 보였다. 12시간 이상 수술이 소요된 경우 57%에서 수술 직후부터 1달까지 H-B Gr IV 이상의 소견을 보였 고 이는 12시간 이하로 수술이 소요된 경우와 통계적으로 유의한 차이가 있었다. 수술시간이 길어지는 이유는 종양의 크기가 크거나 종양의 위치가 제거하기 어려운 경우, 술자의 술기 등이 있을 수 있 고 이러한 과정에서 안면신경이 외상을 받을 가능성이 높아지면서 유의한 차이가 나타났다고 생각된다. 그러나 수술 후 6개월에서 1 년 경과 후 안면신경 기능의 회복 정도는 두 군간에 통계적으로 유 의한 차이를 나타내지 않아 수술 중 안면신경의 조작의 증가는 단 기적인 안면신경 마비의 위험성을 높이지만 장기적으로는 큰 영향 을 미치지 않는다고 추정할 수 있다. 유양돌기 절제술의 종류나 종 양의 완전 절제 여부는 환자 수가 충분하지 않아 통계적 유의성을 검증할 수 없었다.
Fig. 3
100
80 60
40 20
0
% IV-VI III-VI Post-op 1mo Post-op12mo
57%
0% 14%
■Operation time ≥12hr
■Operation time 12hr
0%
P = 0.015
P ≥ 0.05
Postoperative facial nerve paralysis according to operation time.
▒
결 론안면신경 전방전위를 통한 경정맥공 종양의 제거술 후 안면신경 기능은 수술 1년 후에 90.5% 에서 H-B Gr I, II 로 회복되었다. 안 면신경전위의 범위가 적을수록 술 후 안면신경 기능이 양호한 경향 을 보였고, 특히 수술시간이 12시간 이하인 경우 수술 직후 안면신 경 기능이 좋았고, 안면마비가 발생하여도 쉽게 회복되는 경향을 보 였으나 장기적으로는 안면신경 마비의 위험에 영향을 미치지는 않 았다. 경정맥공 종양 제거술에서 가능한 한 안면신경 전방전위 정도 를 최소화하는 것이 수술 직후 안면신경 기능 보존에 도움이 될 것 으로 생각되며 안면신경 전방전위는 경정맥공 종양 수술에서 넓은 시야를 제공하면서 만족할 만한 안면신경 결과를 얻을 수 있는 좋은 수술적 술기라고 할 수 있다.
References
1 Borba LA, Ale-Bark S, London C. Surgical treatment of glomus jugulare tumors without rerouting of the facial nerve: an infralabyrinthine approach. Neurosurg Focus 17:E8, 2004
2 Cho YS, So YK, Park K, Baek CH, Jeong HS, Hong SH, et al. Surgical outcomes of lateral approach for jugular foramen schwannoma:
postoperative facial nerve and lower cranial nerve functions.
Neurosurg Rev 32:61-66; discussion 66, 2009
3 Farrior JB. Infratemporal approach to skull base for glomus tumors:
anatomic considerations. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 93:616-622, 1984 4 Fisch U. [Microsurgery of the temporal bone (author's transl)]. HNO
25:193-197, 1977
5 Fisch U. Infratemporal fossa approach to tumours of the temporal bone and base of the skull. J Laryngol Otol 92:949-967, 1978 6 Kadri PA, Al-Mefty O. Surgical treatment of dumbbell-shaped jugular
foramen schwannomas. Neurosurg Focus 17:E9, 2004
7 Kim CJ, Yoo SJ, Nam SY, Kim SY. A hearing preservation technique for the resection of extensive jugular foramen tumors. Laryngoscope 111:2071-2076, 2001
8 Lee SK, Park K, Kong DS, Cho YS, Baek CH, Nam DH, et al. Surgical tactics and outcome of treatment in jugular foramen schwannomas. J Clin Neurosci 8 Suppl 1:32-39, 2001
9 Ramina R, Maniglia JJ, Fernandes YB, Paschoal JR, Pfeilsticker LN, Neto MC, et al. Jugular foramen tumors: diagnosis and treatment.
Neurosurg Focus 17:E5, 2004
10 Selesnick SH, Abraham MT, Carew JF. Rerouting of the intratemporal facial nerve: an analysis of the literature. Am J Otol 17:793-805;
discussion 806-799, 1996
11 Shapiro MJ, Neues DK. Technique for Removal of Glomus Jugulare Tumors. Arch Otolaryngol 79:219-224, 1964
12 Vogl TJ, Bisdas S. Differential diagnosis of jugular foramen lesions.
Skull Base 19:3-16, 2009