Corresponding Author : Sung-Ho Hahn, M.D.
Department of Orthopedic Surgery, National Police Hospital 58 Karak-dong, Songpa-gu, Seoul, Korea
Tel : 02-3400-1247, Fax : 02-449-2120, E-mail : hsh@nph.go.kr
Volume 13, Number 1, June 2001
서 론
전방 슬관절 통증의 원인으로 슬개골의 아탈구, 경 사 및 사두근 위축이 관련되어있다고 알려져있으며1 9 ) 가장 많은 원인은 슬개대퇴 관절의 부정정렬과 관련된 망상조직의 스트레스와 관련된다고 한다2 1 ).그러나 4 5°
굴곡 Merchant view에서의 슬개골 정렬에 대해서는 어느 정도의 외측으로의 전위와 경사를 정상범위로 인 정하고 있으며 이 때문에 전방슬관절 통증과 슬개골 부정렬과의 연관을 짓는 문제에 어려움이 있다.
본 연구의 목적은 전방슬관절 통증이 없고 이학적 소견상 이상이 없는 대조군을 대상으로 0°및 2 0°슬
관절 굴곡상태에서 슬개골의 정렬을 전산화 단층 촬 영을 이용해 측정하여 정상 범위를 알아보는 것이다.
또한 전방슬관절 통증이 있고 외측지대인대가 긴장 상태에 있는 환자의 슬개골 정렬을 대조군과 비교하 고, 외측지대 절개술후 슬개골 정렬을 다시 계측하여 술후 정상범위로 교정되는지를 알아보는 것이다.
연구 대상 및 방법
1 9 9 9년 1월부터 1 9 9 9년 1 2월까지 본원에서 전방 슬관절 통증으로 치료 받은 환자 2 1명 3 2례의 슬관 절과 전방 슬관절 동통의 병력이 없고 수동 슬개 경 사 검사(passive patellar tilt test)와 슬개 미끄러
전산화 단층 촬영상을 이용한 슬개골 정렬의 평가
국립경찰병원 정형외과학교실
한성호・양보규・이승림・정선욱・김형식
= 국문 초록=
목적 : 전산화 단층 촬영으로 측정된 슬개골 정렬이 전방 슬관절 동통과 연관이 있는지를 알아보는 것이다.
대상 및 방법 : 1999년 1월부터 1 9 9 9년 1 2월 사이에 본원에서 전방 슬관절 동통과 연관된 외측 지대의 긴장이 있는 환자 2 1명 3 2례 슬관절을 환자군으로 하였고 전방 슬관절 동통의 병력이 없고 이학적 검사상 특이 소견이 없는 1 8명 3 6례의 슬관절을 대조군으로 하였다. 전산화 단층 촬영을 실시하여 구각, 일치각, 슬개골 경사각을 측정하여 슬개골 정렬을 평가하였으며 대조군과 환자군의 슬개골 정렬을 통계적으로 비교하 였다. 모든 환자군 3 2례의 슬관절에 대해 관절경을 이용한 외측 지대 절개술을 시행하였으며 술후 슬관절 신 전 및 2 0°굴곡 전산화 단층 촬영으로 슬개골 정렬 재측정을 실시하여 변화 양상을 알아보았다.
결과 : 대조군과 환자군 간에 슬개골 정렬 평가상 슬관절 신전 및 2 0°굴곡 전산화 단층 촬영상 대조군과 환자군 사이의 슬개골 정렬 측정 평균치가 유의할만한 차이를 보여 환자군과 대조군의 슬개골 정렬은 통계적 의미있는 차이가 있었다. 환자군에 대해 외측 지대 절개술 시행후 전산화 단층 촬영 소견상 술전,후 슬개골 정렬 측정 평균치가 유의할만한 차이를 보여 슬개골 정렬이 통계적으로 유의성 있게 교정되었다.
결론 : 0°및 2 0°슬관절 굴곡 상태에서 전산화 단층 촬영을 시행하여 외측으로 치우친 슬개골의 부정정렬 이 관찰된다면 정상 현상으로 이해하기보다는 전방 슬관절 동통과 연계된 병적 현상으로 봐야할 것이다.
색인단어 : 슬개골 정렬, 전산화 단층 촬영
짐 검사(patellar glide test)상 외측지대인대 긴장 이 없다고 판단되는 1 8명 3 6례의 슬관절을 대조군으 로 하였다.
연령 분포는 2 0세에서 3 2세였으며 평균 2 3세 였으 며 모두 남자를 대상으로 하였으며 환자군의 증상발 현 기간은 평균 8개월 최소 3개월 이상을 대상으로 하였으며 1 3명 환자는 양측성이었다.
전향적 연구 방법에 의하였으며 슬관절 신전 및 2 0°굴곡 상태에서 표준화 작업으로 사두근 이완된 정위적 자세(neutral rotation)로 전산화 단층 촬영 을 실시하였다36). 촬영 조각상 선택은 슬개골 정중 선 부위에서 내측 대퇴과의 최후방 지점을 연결하는 선으로 하였고(Fig. 1)1 3 , 3 4 ) 구각(sulcus angle),일 치각(congruence angle), 슬개골 경사각( l a t e r a l patellofemoral angle) 를 측정하여 슬개골 정렬을 평가하였으며 대조군과 환자군의 슬개골 정렬은 통계 적으로 비교하였다.
모든 환자군 3 6례의 슬관절에 대해 관절경으로 외 측 지대 절개술을 실시하였으며 술후 평균 3개월에 이학적 재검사와 슬관절 신전 및 2 0°굴곡 전산화 단 층 촬영을 실시하여 슬개골 정렬 재측정 실시하여 (Fig. 2) 변화 양상을 알아보았고 증상 호전여부에
대해 추시관찰하였다 . 결 과
대조군과 환자군 간에 슬개골 정렬 평가상 슬관절 신 전 및 2 0°굴곡 전산화 단층 촬영상 슬개골 정렬 측정 평균치가(Table 1) 대조군과 환자군 사이의 구각을 비 교 기준으로 하여 일치각이 각각 -2 . 7°와 1 4 . 1°및
FIGURE 1.Tomographic slice was taken at the mid portion of patella and post. condyle lowerest point lining level.
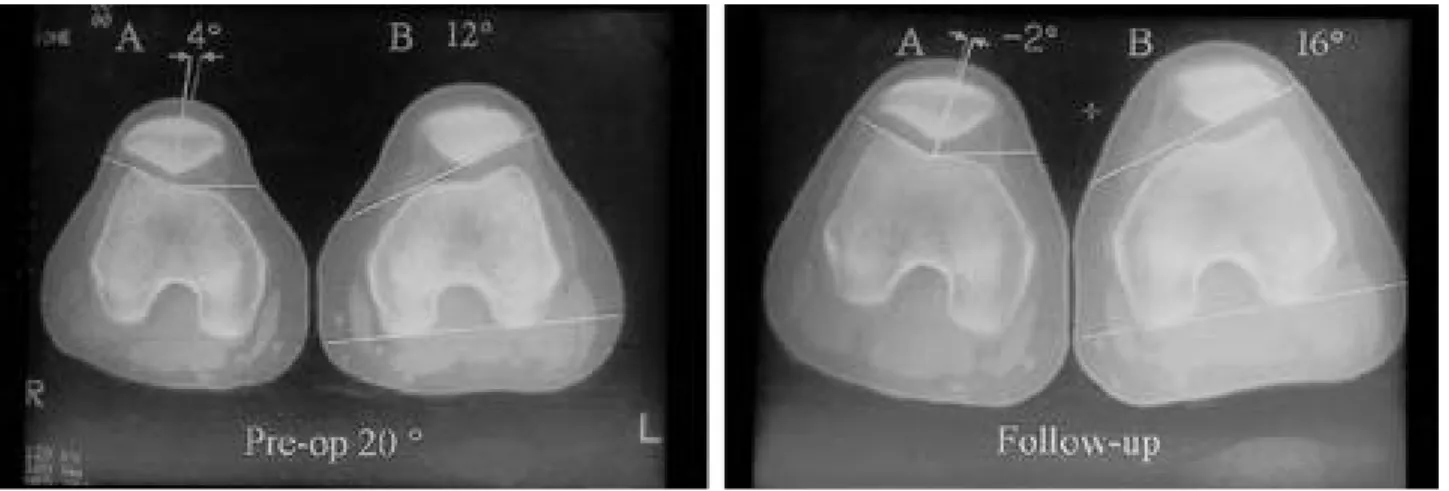
FIGURE 2. Computed tomographic images demonstrate dramatic relief of tilt and subluxation following arthroscopic lat. release of a 22-year-old patient.
FIGURE 2.2-1: pre-op 20˚ C.T. scan 2-2: post-op follow up C.T. scan
FIGURE 2.A: congruence angle: 4˚, B: lateral patellofemoral angle: 12˚ A: congruence angle: –2˚, B: lateral patellofemoral angle: 16˚
Table 1. Patellofemoral alignment in control group and patient group Full extension
P value 20˚flexion
P value
Control group Patient group Control group Patient group
Sulcus angle 155.6˚ 155.4˚ >0.05 150.2˚ 148.8˚ >0/05
Congruence angle –2.7˚ 14.1˚ 0.00 –2.8˚ 6.5˚ 0.00
Lateral patello femoral angle 16.9˚ 11.7˚ 0.00 16.1˚ 12.1˚ 0.00
-2 . 8°과 6 . 5°였으며 슬개골 경사각이 1 6 . 9°와 1 1 . 7°
및 1 6 . 1°과 1 2 . 1°로 통계적 의미있는 차이가 있었다.
환자군의 외측 지대 절개술 시행시 발견된 병리 소 견으로는 내측 추벽이 가장 많았으며(Table 2)
술전 관절경상 대퇴 활차 외측으로 치우친 슬개골 이(Fig. 3) 외측지대 절개술후 대퇴 활차 중심에 슬 개골이 위치함으로 슬개골 정렬이 교정되었음을 알수 있다(Fig. 4).
환자군에 대해 외측 지대 절개술 시행후 전산화 단 층 촬영 소견상 술전,후 슬개골 정렬 측정 평균치가
(Table 3) 술전과 술후 사이의 구각을 비교 기준으 로 하여 일치각이 각각 1 4 . 1°에서 7 . 3°및 6 . 5°에서
-1 . 8°로 교정되었으며 슬개골 경사각이 1 1 . 7°에서 1 4 . 6°및 1 2 . 1°에서 1 4 . 3°로 슬개골 정렬이 통계적 으로 의미있게 교정되었음을 알수 있다.
외측지대 절개술후 주관적 평가로 환자의 활동정도 를 기초로 한 만족도를 알아보았는데 평균 1년 추시 에서 3 6례 중 2 4례가 통증없이 운동을 할 수 있고 양호의 만족도를 보였고 7례에서는 경미한 동통이 운동 중 지속되었고 5례에서는 술후 사두고근 위축 이 심하여 아직도 근육강화운동이 필요하였다. 불량 의 5례중 4례에서 술후 일시적인 슬혈관절증이 있었 다(Table 4).
고 찰
슬개 대퇴 관절 부정정렬에 관여되는 요인으로는 과도한 대퇴골두의 전방경사, 과도한 슬관절의 외반 변형, 경골 근위부 회전 변형 및 대퇴사두고근의 과 Table 2. Associated pathology in patient group
Pathology Number of cases(%)
Pathologic medial plica 9(25.0)
Pathologic suprapatella membrane 2(5.5)
Discoid lateral meniscus 1(2.8)
Bipartite patella 2(5.5)
Cartilage change
(Outerbridge type II and III) 2(5.5)
FIGURE 3. Before proceding lateral release, patella facet is tilted laterally to the trochlear center and sub- l u x a t e d .
FIGURE 4. After proceding lateral release, patella facet is located to the trochlear center and the alignment is corrected.
Table 3. Patellofemoral alignment before and after lateral release in patient group Full extension
P value 20˚ flexion
P value
Pre-op. follow up Pre-op. follow up
Sulcus angle 155.4˚ 152.3˚ >0.05 144.8˚ 143.5˚ >0.05
Congruence angle 14.1˚ –7.3˚ 0.00 6.5˚ –1.8˚ 0.00
Lateral patello femoral angle 11.7˚ 14.6˚ 0.00 12.1˚ 14.3˚ 0.02
도 긴장 또는 불균형 등이 관여된다1 4 ).
정확한 진단을 위해서는 세밀한 임상적 검사와 환 자에게 다음 사항 즉 연관통이나 슬개골 주위의 연부 조직에 통증의 원인이 없는지, 단순 방사선상 슬개골 의 아탈구, 기울기 등이 있는지 혹은 전산화 단층 촬 영에서 슬개골의 아탈구, 기울기 또는 이들 모두가 0°및 2 0°슬관절 굴곡시 나타나지 않는지, 관절연골 의 변화는 이미 생겼는지 만약 있다면 통증이 관절 연골의 변화와 관련이 있는지 없는지 분석해야한다2 1 ).
많은 저자들이 2 5 ~ 3 0°이상 굴곡 상태에서 슬개 대퇴 부정 정렬 환자에서 대퇴 슬개관절 양상 관찰이 가능함을 보여 줬다1 2 , 2 4 . 2 6 , 2 7 , 3 6 ).
축성 영상 상 외측으로 치우친 슬개골을 정상으로 간주되어서는 안된다는 보고도 있다1 8 ).
생역학 조사에서 슬관절 굴곡시 슬개골과 대퇴골 사이의 압박력이 증가하며1 7 ) R e i l y , M o r t e n s3 1 )는 활 동중 대퇴 슬관절에 작용하는 힘을 증명하였으며 비 정상적 궤적( t r a c k i n g )은 대퇴 슬개관절에 더 큰 힘 을 발생시킨다고 알려져 있다.
부정정렬의 가능성에서 동적 현상의 가능성이 고려
되면서1 1 , 3 6 )전통적인 접선 방사선은 다양한 기술적인
문제로-대퇴슬개관절 2 5°굴곡 이내의 관찰이 어렵다 든지 사두근 수축 평가문제, 적당한 기준면 결정의 어 려움, 영상중첩, 미미한 회전 불위치 탐지 곤란 등-대 퇴슬개관절을 평가하는데 신뢰가 떨어짐이 지적되었
으며2 4 , 3 3 - 3 6 ), 전산화 단층 촬영 사용은 3 0°이하 슬관절
굴곡 평가 가능 및 기준면으로의 대퇴과 사용은 슬개 골의 축성 영상의 변형없이 획득 가능하게 되었다1 0 , 3 6 )
. 그래서 대퇴 슬개관절 평가에서 전산화 단층 촬영 이 전통적인 접선 방사선보다 더 민감하고 특이하다 고 인정되게 되었으며1 , 3 , 2 0 , 3 6 )슬개골의 경사나 아탈구 평가에서 슬개골 재정렬술 전후로 정확한 진단 수단 으로 여겨지며1 3 , 1 5 )
, 후방 기준선(대퇴후과를 가로질 러 그은 선)이 전방 기준선(내,외 활차의 두드러진 면을 가로질러 그은 선)보다 슬개골 경사각 측정시 더 정확하다1 3 ).
대퇴 슬개관절 정렬의 평가에 사용되는 잣대로는 구각, 일치각, 슬개골 경사각도가 사용된다.
구각은 대퇴 활차 깊이를 평가해서 슬개골 평가에
도움주는데 각도가 클수록 구각이 얕을수록 슬개골 불안정성의 잠재성을 증가시키고 재발성 아탈구와 연 관 될 수 있다2 , 1 7 , 2 7 ).
일치각은 아탈구를 평가하고 비정상적 각도는 재발 성 아탈구와 연관된다1 7 , 2 7 )
.
슬개골 경사각도는 슬개골 아탈구의 잣대로 L a u r i n2 5 ) 에 의해 기술되었으나 경사의 잣대로 더 정확하다.
관절경하 외측 지대 절개술은 w i l l n e r3 7 )에 의해 처 음으로 기술되었으며 적응증으로는 긴장된 외측지대, 슬개골 경사 및 슬개 관절증, Q 각의 명확한 변화없 이 발생한 아탈구, 재발성 아탈구와 미미한 슬개골 관절증 동반한 대퇴 슬관절 부정정렬 등으로1 7 )이학적 검사상 음성 수동적 슬개 경사 검사와 내측 및 외측 슬개 미끄러짐 검사상 2구획 이하를 들 수 있다3 0 ).
s c h u t z e r3 3 )등은 일치각이 1 0°슬관절 굴곡시 0°이 상이면 부정정렬로 본다고 기술하고 전방 슬개골 통 증을 가진 환자에서 대퇴 슬개관절 부정정렬 양상을 1 )경사 없는 아탈구 2 )경사 동반한 아탈구 3 )아탈구 없는 경사로 나누었을 때 외측 지대 절개술시 3형에 서 정상 정렬의 회복 및 양호한 결과를 나타낸다고
한다1 3 ).슬개골 경사각도가 외측 지대 절개술로 전산
화 단층 촬영상 교정 효과를 보여주며 일치각도 약간 호전됨을 보여준다1 3 ).
외측 지대 절개술 후 사두근력의 회복과 부종 감소 를 위해 최소 3 ~ 4개월을 추시해야하며 가장 흔한 합병증은 혈관절증이라 한다4 , 6 , 7 , 1 7 ).
슬개골 불안정성 없는 전방 슬관절 통증의 경우의 치료로 관절경하 외측지대 절개술의 효과에서 양호한 보고를 하는 경우도 있지만9 , 1 6 , 2 2 , 2 3 , 2 8 , 2 9 )
효과면에서의 문점이 많이 제기되고 있다1 7 , 3 2 ).
연골 양상은 Outerbridge 분류를 주로 사용하는 데 통증과 수술소견상 슬개관절 연골 양상과의 연관 성 관계는 뚜렷하지 않다5 , 8 , 9 , 1 7 ).
결 론
전방 슬관절 통증 없는 대조군은 슬관절 신전 및 2 0°굴곡 전산화 단층 촬영상 외측으로 치우치지 않 았으며 환자군에서 외측으로 치우친 슬개골 부정정렬 은 관절경을 이용한 외측 슬개 지대 절개술 시행 후 교정되었다.
이상으로 0°및 2 0°의 슬관절 굴곡시 외측으로 치 우친 슬개골을 부정정렬은 정상범위로 간주하기보다 는 전방슬관절 통증과 연관된 병적현상으로 이해해야 할 것이다.
이러한 병적 소견이 임상적으로 발현되지 않거나 Table 4. Functional evaluation after lateral release in patient
group
Number of case(%) Result
24(66.7) good to excellent
7(19.4) well(minimal pain on exertion) 5(13.9) poor(similar pain to pre-op state)
경미할 경우 예방 및 치료 목적으로 활동양식 변화 및 근육강화 운동등의 보존적 치료를 요하며 증상이 심한 경우 선택적으로 수술요법이 필요할 수 있으리 라 사료된다.
REFERENCES
01) Aglientti P,Buzi R and Pisaneschi A : Patella pain.
J Sports Traumatol, 12:131-149, 1990.
02) Aglientti P,Indall J and Cerulli G : Patellar pain and incongruence: Measurements of incongruence.
Clin Orthop, 176:217, 1983.
03) Aglietti P, Pisaneschi A, Allegra M, et al : Patellar pain. Comparison between conventional radiology and computed tomography. Ital J Sports Traumatol, 10:7-12, 1998.
04) Aglientti P,Pisaneschi A, Buzzi R, et al : Arthro- scopic lateral release for patellar pain or instability.
Arthroscopy, 5:176, 1989.
05) Benetley G and Down G : Current concepts of eti- ology and treatment of chondromalacia pateeae. Clin orthop, 189:209, 1984.
06) Bentz R, Lonegran R, Paterson R,et al : The per- cutaneous lateral retinacular release. O r t h o p e d i c s, 5:57, 1982.
07) Bigos S and McBride G : The isolated lateral reti- nacular release in the treatment of patellofemoral disorders. Clin Orthop, 186:75, 1984.
08) Casscells S : The arthroscope in the diagnosis of dis- orders the patellofemoral joint. Clin Orthop 144:45, 1979.
09) Ceder L and Larson R : Z-Plasty lateral retinacula release for the treatment of patellar compression syndrome. Clin Orthop, 144:110, 1979.
10) Delgado-Martins H : A study of the position of the patellar using computerised tomography. J Bone Joint Surg 61B:443-444, 1979.
11) Down GSE and Bentley G : Radiographic assess- ment in patellar instabillity and chondromalacia patellar, J Bone Joint Surg, 68B:297-300, 1986.
12) Ficat RP, Philippe J and Hungerford DS : chon- dromalacia patellae:a system of classification. C l i n Orthop, 144:55-62, 1979.
13) Fulkerson JP,Schutzer SF,Ramsby GR and Bern- stein RA : Computerized tomography of the patello-
femoral joint before and after lateral release or reali- gnment. Arthroscopy, 3(1):1987, 19-24.
14) Fulkerson, J.P.,Kalenak, A.,Rosenberg, T.D., and Cox, J.S. : patellofemoral pain: Instructional course lectures, vol XLI: 57-71, 1992.
15) Genant H,Wilson JS, Bovill EG,Brunelle F, Mur- ray W and Radrigo J. : Computerizeed tomogra- phy of the musculoskeletal system. J Bone Joint Surg, 1980;62A;1088.
16) Grana W, Hinkley B and Hollingsworth S : Arthroscopic evaluation and treatment of patellar malalignment. Clin Orthop, 186:122, 1984.
17) Greenfield Ma, Do and Scott WN : Arthroscopic evaluation and treatment of the patellofemoral joint.
Orthop Clin North Am, 23(4):587-598, 1992 OCNA 92.vol 23 NO4. 587.
18) Grelsamer RP,Newton PM and Staron RB : The medial-lateral position of the patella on Routine magnetic resonance imaging: When is normal not normal. Arthroscopy, 14(1):1998, 23-28.
19) Guo K,Ye Q,Lin J,Shen J and Yang X : Selective training of the vastus medialis muscle using electri- cal stimulator for chondromalacia patella. C h u n g Kuo I Hsueh Ko Hsueh Yuan Hsueh Pao 18(2):156- 160.
20) Inoue M. Shino K and Hirose H,et al : Subluxation of the patella. Computed tomography analysis of patello-femoral congruence. J Bone Joint Surg, 70A:1331-1337, 1998.
21) Jung Y.B and Park Y.J : Patellofemoral malalign- ment syndrome. Korean orthopaedic society for knee medicine, 1992.
22) Krompinger W and Wulkerson J : Lateral retinac- ular release for intrctable lateral retinacular release for intractable lateral retinacular pain. Clin Orthop, 179:191, 1983.
23) Larson R, Cabaud H,Slocum D, et a l: The patellar compression syndrome : Surgical treatment by later- al retinacular release. Clin Orthop, 134:158, 1978.
24) Laurin CA, Daussault R and Levesque HP : The tangent X-ray investigation of the patellofemoral joint : X-ray technique, diagnostic criteria and their interpretation. Clin Orthop 144:16-26, 1979.
25) Laurin CA, Dussault R and Levesque H : The tan- gential x-ray invesigation of the patellofemoral joint:
X-ray technique,diagnostic criteria and their inter-
pretation. Clin Orthop 144:16, 1979.
26) Laurin CA, Leveseque HP, Dassault R, et al : The abnormal lateral patello-femoral angle.A diagnostic roentgenographic sign of recurrent patellar subluxa- tion. J Bone Joint Surg 60A:55-60, 1978.
27) Merchant AC, Mercer RL, Jacobsen RH, et al : Roentgenographic analysis of patellofemoral con- gruence. J Bone Joint Surg 56A:1391-1396, 1974.
28) Micheli L and Stantiski C : Lateral patellar retinac- ular release. AM J Sports Med 9:330, 1981.
29) Osborne A and Fulford P : Lateral release for chon- dromalacia patellae. J Bone Joint Sur 6 4 ( B ) : 2 0 2 , 1 9 8 2 .
30) Patricia A, Kolowich,Lonnie E, Paulos, Thomas D, Rosenberg and Steve Farnsworth : Lateral release of the patella: indications and contraindica- tions. Am J sports medicine, 18(4):1990, 359-365.
31) Reilly D and Martens M : Experimental analysis of the quadriceps muscle force and patellofemoral joint reaction force for various activities. Acta Orthop Scand 43:126, 1972.
32) Schonholtz G,Zahn M and Magee C : Lateral reti- nacular release of the patellar. A r t h r s c o p y 3 : 2 6 9 , 1987.
33) Schutzer SF. Ramsby GR and Fulkerson JP : Computed tomographic classification of patellofemoral pain patients. Orthop Clin North Am 17:235-248, 1986.
34) Schutzer SF. Ramsby GR and Fulkerson JP : The evaluation of patellofemoral pain using computer- ized tomography.Clin Orthop 204:286-293, 1986.
35) Vainionpaa S,Eaasonen E,patlala H,et al : Acute dislocation of the patella. Clinical,radiographic and operative findings in 64 consecutive cases. A c t a Orthop Scand, 57:331-333, 1986.
36) Vincenzo Guazzanti,Antonio Gigante,Lazzaro AD and Carlo Fabbriciani : Patellofemoral malalignment in adolescents. Am J sports medicine, 22(1):55-60, 1994.
37) Willner P : Recurrent dislocation of the patellar.
Clin Orthop, 69:213, 1970.
─ Abstract ─
Evaluation of Patella Alignment using Computed Tomographic Image
Sung-Ho Hahn M.D. Bo-Kyu Yang M.D. Seung-Rim Yi M.D. Shun-Wook Chung M.D.
Hyoung-Sik Kim M.D.
Department of Orthopaedic surgery National Police Hospital, Seoul, Korea
Purpose : This study was evaluated to find out meaning of patellofemoral alignment related to anterior knee pain using computed tomographic image.
Material and Method : This study include 32 cases, 21 persons as a patient group which had been treated due to anterior knee pain related to tight lateral retinaculum from Jan. 1999 to Dec. 1999 and 36 cases, 18 persons as a control group which had no history of anterior knee pain and no abnormal finding malalignment by physical examination. Patellofemoral alignment was evaluated by measuring sulcus angle, congruence angle and lateral patellofemoral angle using computed tomographic images in 0°and 2 0°knee flexion patellofemoral alignment of the patient group was compared with that of the control group statistically. All 32 cases of the patient group had an arthroscopic lateral release and the patellofemoral alignment was rechecked on computed tomographic images.
Result : There was statistically difference between the average measurement of patient group and that of the control group on the computed tomographic images in 0°and 20°flexion of the knee. Also the average measurement after lateral release in patient group was
corrected significantly.
Conclusion : Laterally aligned patella during 0°and 20°knee flexion in computed tomographic should not be considered as normal variation but as pathologic condition related to anterior knee pain.
Key Words : Patellofemoral alignment, Computed tomographic image