696
The Meaning of Metabolic Syndrome X in Patients Suffering with Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
Jeong Seon Park, Jong Kwan Park
From the Department of Urology, Chonbuk National University Medical School, Jeonju, Korea
Purpose: We wanted to evaluate if metabolic syndrome X affects voiding symptoms and erectile function in those patients suffering with benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).
Materials and Methods: Between January 2003 and May 2006, we analyzed 68 patients suffering with both BPH and metabolic syndrome X and 112 patients suffering with BPH, but not metabolic syndrome as controls. The diagnosis of metabolic syndrome was made according to the recent consensus report of the National Cholesterol Education Program's Third Adult Treatment Panel. The blood pressure, obesity, maximal flow rate, residual volume, International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS), and the International Index of Erectile Function (IIEF) were all measured. The biochemical analyses included determining the levels of serum glucose, total cholesterol, triglycerides, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) and prostate-specific antigen (PSA). The total prostate volume and transitional zone volume were measured via transrectal ultrasound. Statistical analysis was performed by using Student's t-test.
Results: There were statistical differences between the two groups with respect to total cholesterol (p=0.045), triglycerides (p<0.001), HDL-C (p<
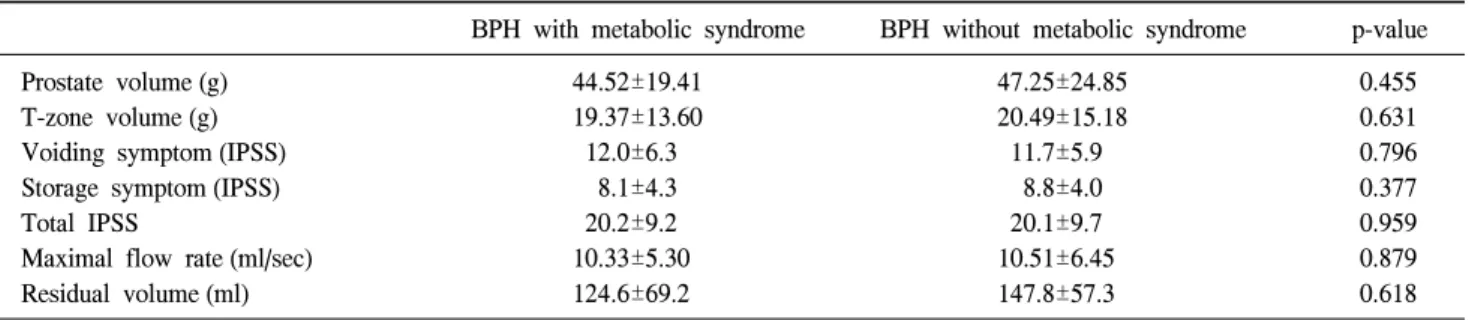
0.001), glucose (p<0.001), blood pressure (p<0.001) and obesity (p<0.001), respectively. However, there was no significant difference on comparison of the total prostate volume and transitional zone volume, the maximal flow rate, the residual volume, IPSS, IIEF, PSA and LDL-C.
Conclusions: The results of this study suggest that BPH patients with metabolic syndrome X have higher total cholesterol, triglycerides, glucose, blood pressure and obesity, and lower HDL-C. Yet there was no significant difference in the voiding symptoms and erectile function between the patients with BPH who had or didn’t have metabolic syndrome X. (Korean J Urol 2007;48:696-700)
Key Words: Benign prostatic hyperplasia, Metabolic syndrome X, Erectile dysfunction
대한비뇨기과학회지 제 48 권 제 7 호 2007
전북대학교 의과대학 비뇨기과학교실
박정선ㆍ박종관
접수일자:2007년 4월 5일 채택일자:2007년 6월 4일
교신저자: 박종관
전북대학교병원 비뇨기과 전북 전주시 덕진구 금암동 634-18
561-712
TEL: 063-250-1510 FAX: 063-250-1564 E-mail: rain@chonbuk.
ac.kr
서 론
전립선비대증은 노인에서 발생하는 가장 흔한 양성 질환 의 하나로 31-40세에 8%인 유병률이 71-80세 이상에서는 82%에 이르고, 생존연령이 증가함에 따라 유병률이 더욱 증가하여 삶의 질에 악영향을 미친다.1 전립선비대증은 기
질세포와 상피세포가 과형성되는 병태생리를 가지는 질환 으로 노화와 남성호르몬이 주요 원인이고, 이외에도 가족 력, 인종, 고혈압, 인슐린 저항성 당뇨, 비만, 키, 흡연, 낮은 고밀도 리포 단백질-콜레스테롤 (high density lipoprotein chole- sterol; HDL-C), 높은 인슐린 농도와 관련이 있다.2-6 특히 전 립선비대증에 의한 하부요로증상의 병리기전 중의 하나인 방광경부 및 전립선 교감신경의 활성도 증가는 배뇨증상을
유발하며, 대사증후군의 교감신경 항진과 관련이 있다.5,7 또한 비만은 여성호르몬과 남성호르몬의 변화를 일으켜 전 립선 용적을 증가시켜서 배뇨증상을 악화시킨다.8 전립선 비대증에서 당뇨를 동반하는 경우가 단독으로 발병하는 경 우보다 많고, 이 두 질환은 나이에 따라 발병 빈도가 증가하 여 배뇨증상에도 영향을 미칠 수 있다.9 증상이 심한 전립선 비대증은 삶의 질을 떨어뜨리고 치료에 드는 비용 또한 만 만치 않다.10
인슐린 저항성과 고인슐린혈증이 특징인 대사증후군은 제2형 당뇨, 고혈압, 비만, 이상지질혈증으로 정의하는데, 인슐린 매개성 포도당 흡수장애로 인한 인슐린저항성에 따 른 2차적 고인슐린혈증 및 교감신경계의 과활성이 대사증 후군의 병태생리이다.7 이러한 요소들은 역시 전립선비대 증 발달의 위험인자로 전립선비대증과 대사증후군은 유사 한 병태생리학적 기전을 공유하는 것으로 추정되고 있다.
노년기 남성에서 나타나는 배뇨증상의 원인으로 전립선비 대증이 가장 중요한 역할을 하는 것으로 알려져 있고, 대사 증후군에서도 역시 교감신경 과활성, 당뇨, 비만 등의 요인 들이 하부요로증상의 발현에 연관이 있을 것으로 보인다.
또한 발기불능과 심혈관계 질환은 공동의 위험인자를 가지 고 있고, 이상지질혈증, 인슐린 저항성과 고혈압 등으로 구 성되는 대사증후군도 심혈관계 질환의 병태생리에 중요한 영향을 미친다.11-15 저자들은 전립선비대증이 있는 환자에 서 대사증후군 동반 유무가 배뇨증상, 발기능력에 영향을 미치는지와 총콜레스테롤, 중성지방, 고밀도 리포 단백질- 콜레스테롤, 저밀도 리포 단백질-콜레스테롤 (low density lipoprotein cholesterol; LDL-C), 혈당, 전립선특이항원, 전립 선 용적 및 전환대 용적에 있어서 차이가 있는지 알아보고 자 하였다.
대상 및 방법
2003년 1월부터 2006년 5월까지 전립선비대증으로 본원 비뇨기과에 내원한 환자 180명을 대상으로 하였고, 이들 중 대사증후군이 동반된 군 68명 (37.8%)과 동반되지 않은 대 조군 112명 (62.2%)으로 분류하여 전립선 용적 및 전환대 용적 (B&K medical. Ultrasound class 1 type-B, NE), 최대요속 및 잔뇨를 측정하였다. 국제전립선증상점수 (International Prostate Symptom Score; IPSS), 국제발기능점수 (Internatio- nal Index of Erectile Function; IIEF)는 자가설문지를 이용하 여 작성하였으며, IPSS는 저장증상, 배뇨증상으로 분류하였 고, IIEF는 erectile function (EF), orgasmic function (OF), sexu- al desire (SD), intercourse satisfaction (IS), overall satisfaction (OS)으로 분류하여 비교하였다. 또한 전립선특이항원 (pro-
state-specific antigen; PSA, Roche. Modular E-170), 혈당, 총 콜레스테롤, 중성지방, 저밀도 리포 단백질-콜레스테롤 및 고밀도 리포 단백질-콜레스테롤을 측정하여 비교하였다.
PSA가 4ng/ml 이상인 환자에서는 경직장초음파 유도하에 전립선 조직검사를 실시하여 전립선암으로 진단된 경우와 전립선비대증으로 약물치료의 과거력이 있는 경우 이 연구 에서 제외하였다.
대사증후군의 진단기준은 2001년 5월 미국에서 발표된 제3차 콜레스테롤관리지침 (Natonal Cholesterol Education Program's Third Adult Treatment Panel)의 정의에 따라 1) 고 혈압 (수축기 혈압이 130mmHg 이상 혹은 이완기 혈압이 85mmHg 이상), 2) 고혈당 (공복 혈당이 110mg/dl), 3) 비만
(허리둘레가 90cm 이상이거나 신체질량지수가 25kg/m2 이 상), 4) 저HDL 콜레스테롤혈증 (45mg/dl 미만), 5) 고중성지 방혈증 (150mg/dl 이상)에서 세 가지 이상을 만족하는 경우 로 하였다.15
통계학적 분석은 Student's t-test (unpaired)를 이용하여 두 군 간의 유의한 차이 유무를 알아보았으며, p값이 0.05 미만 을 유의한 것으로 간주하였다.
결 과
대사증후군이 동반된 전립선비대증 환자군과 대조군의 평균연령은 68.5±6.8세와 64.7±7.2세였고, 배뇨요소, 발기능 력, 생화학적 인자를 비교한 결과, 총콜레스테롤은 204.8±
31.4mg/dl과 180.2±34.2mg/dl (p=0.045), 중성지방은 186.9±
91.2mg/dl과 107.1±41.4mg/dl (p<0.001), 고밀도 리포 단백 질-콜레스테롤은 39.5±9.0mg/dl과 48.9±9.7mg/dl (p<0.001), 혈당은 133.3±54.4mg/dl과 105.1±28.8mg/dl (p<0.001), 고혈 압은 43%와 10% (p<0.001), 비만은 38.4%와 25.4% (p<
0.001)로 유의한 차이를 보였다 (Table 1).
그러나 전립선 용적은 44.52±19.41g과 47.25±24.85g (p=
0.455), 전환대 용적은 19.37±13.60g과 20.49±15.18g (p=
0.631)이었고, 최대요속은 10.33±5.30ml/sec와 10.51±6.45 (p=0.879), 잔뇨는 124.6±69.2ml과 147.8±57.3ml (p=0.618)이 었으며, 국제전립선증상점수에서 배뇨증상은 12.0±6.3점과 11.7±5.9점 (p=0.796), 저장증상은 8.1±4.3점과 8.8±4.0점 (p=0.377), 국제전립선증상점수는 20.2±9.2점과 20.1±9.7점 (p=0.959)으로 유의한 차이를 보이지 않았다 (Table 2). 국제 발기능측정설문점수는 EF가 각각 8.0±4.3점과 8.1±4.0점 (p=0.989), OF은 2.1±1.2점과 2.7±1.4점 (p=0.493), SD는 3.3±
1.8점과 3.2±1.8점 (p=0.854), IS는 3.3±2.5점과 3.6±2.3점 (p=0.797), OS은 3.7±2.1점과 3.7±2.6점 (p=0.926), 국제발기 능측정설문점수는 20.4±19.7점과 21.5±18.8점 (p=0.832)으로
Table 1. Comparison of the biochemical factors in the patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and with or without metabolic syndrome BPH with metabolic syndrome BPH without metabolic syndrome p-value
Total cholesterol (mg/dl) 204.8±31.4 180.2±34.2 0.045
Triglycerides (mg/dl) 186.9±91.2 107.1±41.4 <0.001
LDL-C (mg/dl) 108.2±27.2 109.1±28.1 0.891
HDL-C (mg/dl) 39.5±9.0 48.9±9.7 <0.001
PSA (ng/ml) 4.04±2.49 4.53±3.10 0.572
Glucose (mg/dl) 133.3±54.4 105.1±28.8 <0.001
Hypertension (%) 43 10 <0.001
Obesity (%) 38.4 25.4 <0.001
LDL: low density lipoprotein, HDL: high density lipoprotein, PSA: prostate-specific antigen
Table 2. Comparison of the voiding factors in the patients with BPH and with or without metabolic syndrome
BPH with metabolic syndrome BPH without metabolic syndrome p-value
Prostate volume (g) 44.52±19.41 47.25±24.85 0.455
T-zone volume (g) 19.37±13.60 20.49±15.18 0.631
Voiding symptom (IPSS) 12.0±6.3 11.7±5.9 0.796
Storage symptom (IPSS) 8.1±4.3 8.8±4.0 0.377
Total IPSS 20.2±9.2 20.1±9.7 0.959
Maximal flow rate (ml/sec) 10.33±5.30 10.51±6.45 0.879
Residual volume (ml) 124.6±69.2 147.8±57.3 0.618
T-zone: transitional zone, IPSS: International Prostate Symptom Score, BPH: benign prostatic hyperplasia
Table 3. Comparison of sexual function in the patients with BPH and with or without metabolic syndrome
BPH with metabolic syndrome BPH without metabolic syndrome p-value
Erectile function 8.0±4.3 8.1±4.0 0.989
Orgasmic function 2.1±1.2 2.7±1.4 0.493
Sexual desire 3.3±1.8 3.2±1.8 0.854
Intercourse satisfaction 3.3±2.5 3.6±2.3 0.797
Overall satisfaction 3.7±2.1 3.7±2.6 0.926
Total IIEF 20.4±19.7 21.5±18.8 0.832
BPH: benign prostatic hyperplasia, IIEF: International Index of Erectile Function
역시 유의한 차이가 없었다 (Table 3). 또한 전립선특이항원 은 각각 4.04±2.49ng/dl과 4.53±3.10ng/dl (p=0.572)이었고, 저 밀도 리포 단백질-콜레스테롤은 108.2±27.2mg/dl과 109.1±
28.1mg/dl (p=0.891)으로 양 군 간에 유의한 차이를 보이지 않았다 (Table 1).
고 찰
대사증후군은 인슐린 저항성과 보상성 고인슐린혈증으 로 대표되는 다발성 대사 및 심혈관질환 위험인자의 복합 체이다. 2003년 미국에서 발표된 보고에 의하면 60-69세에 해당하는 사람의 43.5%가 대사증후군에 이환되어 있고, 이
와 유사하게 전립선비대증은 50세에서 호발하여 60-70세에 서 50%가 하부요로증상을 동반하는 전립선비대증에 이환 되어 있다.16,17 최근 우리나라에서도 관상동맥질환의 유병 률이 증가하는 추세이고, 위험인자로 이상지방혈증, 비만, 고혈압, 인슐린 저항성 당뇨 등이 있다. 이러한 위험인자군 은 현재 대사증후군으로 정의되며, 우리나라에서는 20세 이상에서 21.5%의 이환율을 보이고 있고,18 관상동맥질환으 로 인한 사망률도 증가추세에 있다. 최근 연구에 의하면 인 슐린 저항성에 의한 고인슐린혈증은 대사증후군과 전립선 비대증 발달의 위험인자이고, 대사증후군이 전립선비대증 의 병태생리에 영향을 미칠 것으로 추측된다.3,4 고인슐린혈 증은 교감신경계에 영향을 미쳐 시상하부의 배쪽 내측핵
(ventromedial nucleus)에서 당 흡수를 증가시켜 교감신경계 를 조절하고, 전립선의 폐쇄는 전립선에 의한 요로의 해부 학적 폐쇄와 전립선 피막과 방광경부에 위치하는 교감신경 계의 과활성에 의해 기능적 폐쇄가 발생한다. 대사증후군 의 구성요소인 제2형 당뇨는 배뇨장애와 관련이 있는 교감 신경 및 부교감신경계에 영향을 미쳐서 배뇨근 장애를 일 으키고, 평활근의 교감신경 수용체에도 작용하여 방광출구 폐색증상을 유발한다. 또한 고인슐린혈증은 전립선이 비대 해지는 과정에 관여하는 전신적 호르몬 분비 이상과 연관 이 있어 해부학적 폐쇄에도 관여하는 것으로 추측된다.19,20 2형 당뇨에서는 자율신경병증, 동맥 및 미세혈관병증, 성적 자극 시 증가하는 일산화질소 감소 등을 유발하여 발기능 에도 악영향을 미친다.21 전립선비대증 치료에 사용되는 알 파차단제의 원리는 방광경부의 교감신경계 활성을 감소시 켜 하부요로증상을 호전시키고, 인슐린 민감도를 증가시켜 혈중 인슐린 감소를 유발하여 전립선 성장을 억제하는 역 할을 하는 것으로 이를 뒷받침한다.22,23 최근 한 연구에서도 대사증후군이 있는 환자군에서 그렇지 않은 군에 비해 배 뇨증상의 악화뿐만 아니라 전립선용적 및 전립선 성장속도 에 있어서 유의하게 높다는 결과가 있다.6,24
대사증후군의 다른 요소인 복부비만은 혈청 내 여성호르 몬과 인슐린을 증가시키고, 성호르몬 결합 글로불린을 감 소시키고, 감소된 성호르몬 결합 글로불린에 의해 남성호 르몬과 여성호르몬이 전립선내로 진입하여 남성호르몬에 의해 전립선 용적이 증가하여 배뇨증상이 악화된다. 비만 은 인슐린 민감성을 감소시켜서 혈중 인슐린의 증가를 유 발하고, 증가된 인슐린이 인슐린양 성장인자-1 (insulin-like growth factor-1; IGF-1) 수용체와 결합하여 전립선 용적을 증가시키고, 교감신경 항진을 유발하여 배뇨증상을 악화시 킨다.4 또한 비만은 혈관내피세포의 기능장애와 인터루킨 -6, 8, 18 등의 싸이토카인을 증가시켜 발기능 장애를 초래 한다.24
고혈압이 있는 환자에서는 혈중 카테콜아민이 증가하여 요추천골 척수 (lumbosacral cord)에 영향을 미쳐 배뇨근 수 축과 관련이 있는 빈뇨 및 야간뇨 등의 증상을 유발하고, 전립선 및 방광경부 평활근 긴장도를 증가시켜 방광출구폐 색을 유발한다. 카테콜아민 농도는 밤낮에 따라 차이가 있 고, 밤에 분비가 감소하여 요량이 증가하여 야간빈뇨를 보 인다.25
이전의 연구에 의하면 대사증후군을 구성하는 고혈압, 고혈당, 비만, 저HDL-콜레스테롤혈증, 고중성지방혈증 각 각의 항목 유무에 따라 배뇨증상을 비교, 분석한 결과 대사 증후군이 있는 환자군에서 배뇨 요소가 악화된다고 하였
다.6,23,26 이와는 약간 차이를 두어 본 연구에서는 이미 전립
선비대증이 있는 환자에서 대사증후군의 동반이 배뇨증상 및 발기능력을 더욱 악화시키는지 비교하였으나 두 군 사 이에 유의한 차이는 없었다. 그러나 대사증후군이 동반된 전립선비대증에서 총콜레스테롤, 중성지방, 혈당이 유의하 게 증가하였고, 고밀도 리포단백질콜레스테롤은 감소하였 으며, 고혈압, 비만 동반이 유의하게 높았다. 또한 대사증후 군 유무와 상관없이 제2형 당뇨의 유무에 따른 배뇨증상을 비교해 보았을 때, 당뇨가 있는 군에서 없는 군보다 유의하 게 배뇨증상이 악화되었다. 앞에서 언급한 바와 같이 전립 선비대증과 대사증후군은 유사한 병태생리를 공유하는 것 으로 추정되지만, 본 연구에서는 전립선비대증과 대사증후 군이 병발한다고 해서 배뇨증상이나 발기능력이 더욱 악화 되는 것은 아니라고 생각한다.
결 론
대사증후군과 전립선비대증은 유사한 병태생리학적 기 전을 공유하는 것으로 추정되고 있다. 본 연구에서는 이미 전립선비대증이 있는 환자에서 대사증후군의 동반유무가 배뇨증상 및 발기능에 영향을 미치는지 비교하였으나 유의 한 차이는 없었다. 그러나 대사증후군 구성요소인 총콜레 스테롤, 중성지방, 고밀도 리포 단백질-콜레스테롤, 혈당, 고혈압, 비만에 있어서는 유의한 차이를 보였다.
REFERENCES
1. Kim JH, Shim BS, Hong YS. The relating factors of metabolic syndrome to benign prostatic hyperplasia. Korean J Urol 2005;
46:1046-50
2. Berry SJ, Coffey DS, Walsh PC, Ewing LL. The development of human benign prostatic hyperplasia with age. J Urol 1984;132:474-9
3. Lee C, Kozlowski JM, Grayhack JT. Etiology of benign prostatic hyperplasia. Urol Clin North Am 1995;22:237-46 4. Dahle SE, Chokkalingam AP, Gao YT, Deng J, Stanczyk FZ,
Hsing AW. Body size and serum levels of insulin and leptin in relation to the risk of benign prostatic hyperplasia. J Urol 2002;106:599-604
5. Ziada A, Rosenblum M, Crawford ED. Benign prostatic hyper- plasia: an overview. Urology 1999;53:1-6
6. Hammarsten J, Hogstedt B. Clinical, anthropometric, meta- bolic and insulin profile of men with fast annual growth rates of benign prostatic hyperplasia. Blood Press 1999;8:29-36 7. Reaven GM. Banting lecture 1988. Role of insulin resistance
in human disease. Diabetes 1988;37:1595–607
8. Matsuda T, Abe H, Suda K. Relation between benign prostatic hyperplasia and obesity and estrogen. Rinsho Byori 2004;
52:291-4
9. Boon TA, Van Venrooij GE, Eckhardt MD. Effect of diabetes mellitus on lower urinary tract symptom and dysfunction in patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia. Curr Urol Rep 2001;2:297-301
10. Holtgrewe HL. Economic issues and the management of be- nign prostatic hyperplasia. Urology 1995;46(3 Suppl A):23-5 11. Cohen PG. Aromatase, adiposity, aging and disease. The
hypogonadal-metabolic-atherogenic-disease and aging connec- tion. Med Hypotheses 2001;56:702-8
12. Guay AT. Sexual dysfunction in the diabetic patient. Int J Impot Res 2001;13(Suppl 5):S47-50
13. Ford ES, Giles WH, Dietz WH. Prevalence of the metabolic syndrome among US adults: findings from the third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. JAMA 2002;
287:356-9
14. Guirao Sanchez L, Garcia-Giralda Ruiz L, Sandoval Martinez C, Mocciaro Loveccio A. Erectile dysfunction in primary care as possible marker of health status: associated factors and response to sildenafil. Aten Primaria 2002;30:290-6
15. Expert panel on detection, evaluation, and treatment of high blood cholesterol in adults. Executive summary of the third report of the national cholesterol education program (NCEP) expert panel on detection, Evaluation, and treatment of high blood cholesterol in adults (adult treatment panel III). JAMA 2001;285:2486-97
16. Ford ES, Giles WH, Dietz WH. Prevalence of metabolic syndrome among US adults: findings from the third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. JAMA 2002;287:
356-9
17. Christensen MM, Bruskewitz RC. Clinical manifestations of benign prostatic hyperplasia and indications for therapeutic
intervention. Urol Clin North Am 1990;17:509-16
18. Nugent AP. The metabolic syndrome. BNF Nutr Bull 2004;
29:36-43
19. McNeal J. Pathology of benign prostatic hyperplasia. Insight into etiology. Urol Clin North Am 1990;17:477-86 20. Michel MC, Mehlburger L, Schumacher H, Bressel HU, Go-
epel M. Effect of diabetes on lower urinary tract symptoms in patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia. J Urol 2000;
163:1725-9
21. Fonseca V, Seftel A, Denne J, Fredlund P. Impact of diabetes mellitus on the severity of erectile dysfunction and response to treatment: analysis of data from tadalafil clinical trial.
Diabetologia 2004;47:1914-23
22. Landsberg L. Diet, obesity and hypertension: an hypothesis involving insulin, the sympathetic nervous system, and adaptive thermogenesis. Q J Med 1986;61:1081-90
23. Berne C, Pollare T, Fagius J. The sympathetic outflow in vasoconstrictor nerve fascicles to muscle is increased during euglycacemic hyperinsulinemia. Diabetologia 1989;32(Suppl):
465A
24. Hammarsten J, Hogstedt B, Holthuis N, Mellstrom D.
Components of the metabolic syndrome-risk factors for the development of benign prostatic hyperplasia. Prostate cancer Prostatic Dis 1998;1:157-62
25. Sugaya K, Kadekawa K, Ikehara A, Nakayama T, Gakiya M, Nashiro F, et al. Influence of hypertension on lower urinary tract symptoms in benign prostatic hyperplasia. Int J Urol 2003;10:569-74
26. Kim JH, Shim BS, Kim JS, Hong YS. Voiding dysfunction of men is associated metabolic syndrome. Korean J Urol 2006;47:257-62