키누레닌 대사산물에 의한 신경세포 손상에 대한 Magnolol의 보호효과에 대한 연구
이창욱*·이현정*·김도희*·장영미*·이상형**·정윤화***·김대진*
정윤희*·김경용*·김성수*·이원복*†
*중앙대학교 의과대학, **서울대학교 의과대학 서울시립보라매병원, ***단국대학교 자연과학대학
Magnolol Attenuates Neuronal Cell Death Induced by Kynurenine Metabolite Chang Uk Lee
*, Hyun Jung Lee
*, Do Hee Kim
*, Yeong Mi Jang
*, Sang Hyung Lee
**, Yoonh wa Jeong
***,
Dae Jin Kim
*, Yoon Hee Chung
*, Kyung Yong Kim
*, Sung Su Kim
*, and Won Bok Lee
*†*
College of Medicine, Chung-Ang University, Seoul 156-756, Korea.
**
College of Medicine, Seoul National University, Seoul Municipal Borame Hospital, Seoul 156-707, Korea.
***
College of Natural Science, Dankook University, Yongin 448-701, Korea.
ABSTRACT : This study investigated the protective roles and mechanism of magnolol, from the stem bark of Magnolia offi- cinalis against potential neurotoxin 3-hydroxykynurenine (3-HK)-induced neuronal cell death. For the evaluation of protec- tive role of magnolol, we examined cell viability, apoptotic nuclei, change of mitochondrial membrane potential and caspase activity in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells. It was found that 3-HK induces neuronal cell death in the human neuro- blastoma SH-SY5Y cell line. The reduced cell viability produced characteristic features such as cell shrinkages, plasma membrane blebbing, chromatin condensation, and nuclear fragmentation. The cells treated with 3-HK showed an increase in the concentration of reactive oxygen species (ROS) as well as in caspase activity. In addition, both are involved in the 3- HK-induced apoptosis. Magnolol attenuated the cell viability reduction by 3-HK in both a dose- and time-dependent man- ner. Optical microscopy showed that magnolol inhibited the cell morphological features in the 3-HK-treated cells. Further- more, the increase in the ROS concentration and the caspase activities by 3-HK were also attenuated by magnolol. These results showed that magnolol has a protective effect on the 3-HK induced cell death by inhibiting ROS production and caspase activity.
Key Words : Magnolol, 3-hydroxykynureinine, Mitochondria, ROS, Caspase-3
서 언
3- 히드록시키누레닌산 (3-Hydroxykynurenine, 3-HK) 은 키누 레닌 경로의 중간산물로 , 트립토판의 이화작용에 중요하다 . 또 한 헌팅턴 병 (Pearson and Reynolds, 1992), 파킨슨 병
(Ogawa et al., 1992), 후천성 면역결핍증후군 치매 (Sardar
et al., 1995) 와 같은 신경퇴행성 질환을 가진 환자의 뇌에서 3-HK 의 농도가 증가된다는 연구결과가 알려져 있다 . 최근에
는 가쪽 뇌실에 3-HK 를 포함한 키누레닌의 중간 대사산물을
주입한 경우 경련이 유도되었음이 알려졌다 (Lapin, 1980;
Lapin, 1981). 3-HK 에 의한 질환의 병변 기작은 확실하게 밝 혀져 있지 않지만 몇 몇 연구에 의해 타당하다고 생각되는 기 전이 알려지고 있다 . Nakagami et al. (1996) 은 3-HK 에 의해
활성기 산소가 생성되고 축적되는 것을 보고하였다 . 3-HK 는
세포내의 산화적 스트레스의 발생과 세포를 운반하고 , 많은 신 경퇴행성 질환의 세포사멸특징과 관련된 병리학과 뇌 영역의 선택적인 신경세포 사멸을 유도하는 다를 연구들이 있다
(Okuda et al., 1996; Okuda et al., 1998).
우리나라 자생식물들의 한의학적 효능 특히 항산화 , 항균 ,
항염증 등의 효능은 널리 알려져 이용되고 있으나 정작 그들 의 분자적 메커니즘에 대한 연구는 미미한 상태이다 (Han et
al ., 2006; Lee et al ., 2005). 그 중 Magnolol ( 후박 ) 은 후박 나무 ( Magnolia officinalis) 껍질에서 추출하였으며 , 생물활성 을 가지고 있는 것이 알려져 있다 (Ikeda and Nagase, 2002;
Zhong et al., 2003). 또한 magnolol 이 진정 및 흥분 완화작 용 , 심장성 질병 완화 , 항산화 및 지질개선효과 , 신경통 , 중풍 ,
†
Corresponding author: (Phone) +82-2-820-5642 (E-mail) whitefox@cau.ac.kr
Received March 6, 2009 / 1st Revised April 13, 2009; 2nd Revised April 21, 2009 / Accepted April 22, 2009
고혈압 , 항암작용 등의 다양한 항염증작용을 나타내는 것이 여
러 동물과 세포 실험 결과 밝혀졌다 (Chiu et al., 1999; Lin
et al., 2002; Loong et al., 2002). 특히 , magnolol 이 hydroxyl radical 등의 ROS scavenger 로서 활성기 산소를 제거한다는 많은 결과들이 도출됨에 따라 강력한 항산화 작용을 할 수 있 는 것으로 기대되고 있어 활성기 산소가 발병기전의 주요한 원인으로 알려진 여러 가지 신경퇴행성질환의 예방 , 치료제 개 발에 있어 적절하게 이용이 가능할 것이라 생각된다 .
본 연구에서는 , 3-HK 에 의해 노출된 신경세포에서 세포 생
존율 , 활성기 산소의 발생 및 caspase 활성화에 대한 mag- nolol 의 효과를 관찰하였다 . 그 결과 3-HK 는 신경퇴행성 질환 을 야기할 수 있는 인자로 작용하며 , 후박나무 껍질 추출물인
magnolol 이 3-HK 에 의한 신경세포 손상에 대해 예방 및 치료 가능성이 있는 물질로서 작용할 수 있음을 확인할 수 있었다 .
재료 및 방법
1. 세포배양
사람의 신경모세포종 SH-SY5Y 를 10% fetal bovine serum (Gibco-BRL, CA, USA) 을 넣은 Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium (DMEM) (Gibco-BRL) 배양액으로 5% CO
2가 공급 되는 배양기에서 37 ℃ 조건으로 배양한다 . 배지는 3- 히드록시
키누레닌산 (3-HK, Sigma) 을 250 µ M 로 처리하기 2 시간 전에
1% fetal bovine serum 이 들어있는 DMEM 배지로 바꾸어준 다 . 본 연구에 사용한 magnolol 은 서울대학교 약리학교실에서 받았으며 , 10 µ M 로 고정하여 사용하였다 .
2. 세포 생존율 측정 (alarmablue assay)
SH-SY5Y 세포는 96-well plates (Nunc, Slangerup, Denmark)
에 15,000 cells/well 의 밀도로 깔아주고 24 시간 동안 배양한다 .
세포에 3-HK 처리하기 2 시간 전에 배지를 1% fetal bovine serum 이 들어있는 DMEM 으로 갈아준다 . 이후 AlarmaBlue (Serotec, Oxford, UK) 를 10 ㎕ 처리한 후 3 시간 배양하고
ELISA Reader (Molecular Devices, Sunnyvale, CA, USA)
를 이용하여 570 ㎚에서 흡광도를 측정하였다 . 배경 흡광도는
600 ㎚에서 측정하여 값을 빼준다 . 세포 생존율은 다음과 같
은 공식을 이용하였다 (Shimoke and Chiba, 2001).
세포 생존율 = × 100
3. Hoechst 33258 염색
magnolol 은 3-HK 처리 2 시간 전에 전처리하고 , 36 시간 배 양 후 SH-SY5Y 세포를 4% 파라포름알데히드에 20 분간 고정
한 뒤 , 5 분 동안 Hoechst dye 33258 을 8 ㎍ / ㎕ 넣어 염색시 킨다 . phosphate buffered saline 으로 두 번 세척하고 형광 현
미경으로 관찰한다 . 세포사멸이 일어난 세포의 형태와 크로마
틴 응축에 의해 조각난 핵 및 세포의 형태적 변화를 관찰한다 . 4. 활성기 산소 발생의 측정
2', 7'-dichlorofluorescein diacetate (DCF-DA) 형광성 염료
를 이용하여 3-HK 에 의해 발생한 활성기 산소를 측정하였다
(Kim et al ., 2008, Lee et al ., 2007). 측정하고자 하는 시간 에 SH-SY5Y 세포에 30 분 동안 DCF-DA 를 10 µM 넣어 염
색시킨다 . 세포를 모아 PBS 로 두 번 세척한다 . 세포들을 슬라
이드 글라스에 올려 고정시킨 후 세포를 형광 현미경으로 관 찰한다 .
5. 사립체 막전위차 측정
사립체 막전위 (mitochondrial membrane potential, ∆Ψ m)
의 변화를 측정하기 위하여 tetramethylrhodamine ethyl ester (TMRE; Molecular Probes, Eugene, OR, USA) 를 이용하였
다 . ∆Ψ m 을 측정하기 위하여 TMRE 100 nM 을 15 분간 37 ℃ 에서 배양하고 TMRE 형광 이미지를 fluorescence micros- copy (Olympus IX70, Olympus Optical Co. GmbH, Hamburg, Germany) 로 관찰하였다 .
6. caspase-3 활성도 측정
SH-SY5Y 세포를 10 분 동안 150 × g 으로 원심 분리시켜 모 으고 , 50 mM Tris, pH 7.5, 0.03% NP-40, 1 mM dithio- threitol (DTT) 가 포함된 lysis 완충제를 100 ㎕ 넣어 모아진 세포 펠렛을 분해한다 . 분해된 세포는 20 분 동안 얼음에서 방 치한 후 , 15,800 × g 으로 5 분간 원심분리 한다 . 이후 상층 액
만 옮겨서 단백질 정량을 실시한다 . caspase 의 잘려짐 여부를
보기 위해 세포 상층액 20 ㎍과 caspase-3 기질인 Ac-DEVD- AMC 0.25 mM 을 섞은 후 1 시간 동안 37 ℃에서 배양한다 . TECAN GENios Fluorescence microplate reader (Tecan, Switzerland) 를 이용해 380 ㎚과 460 ㎚의 파장에서 caspase-
3 의 활성을 측정한다 . 효소 활성은 임의의 값 단위로 표현하
였다 . 7. 통계처리
모든 자료는 mean ± SEM 으로 표시하였고 , 실험군 간의 차 이는 Student's t -test 를 이용하여 확인하였다 .
결 과
1. 3-HK 에 의한 세포 생존율 감소에 대한 magnolol 의 저
해효과 Fig. 1A 에서 보듯이 , 250 µM 의 3-HK 를 처리한 SH-SY5Y
세포는 시간에 따라 세포 생존율이 감소하는 것을 확인하였 test sample count
( ) – ( blank count )
untreated control count
( ) – ( blank count )
---
다 . 250 µ M 의 3-HK 를 처리한 경우 36 시간 내에 세포 생존율 이 50% 정도 감소되었다 . 그러나 이때 magnolol 을 2 시간 전
처리 한 경우 3-HK 에 의한 신경세포 사멸을 효과적으로 억제
하였다 (Fig. 1B). 이러한 magnolol 의 효과는 3-HK 에 의한 세포 사멸이 증가되어도 지속되는 것을 알 수 있었고 , 본 연 구에서는 48 시간이 지나도 magnolol 의 세포 보호효과가 유지 됨을 확인하였다 .
2. 3-HK 에 의한 어포토시스형 세포 사멸을 억제하는
magnolol 의 효과
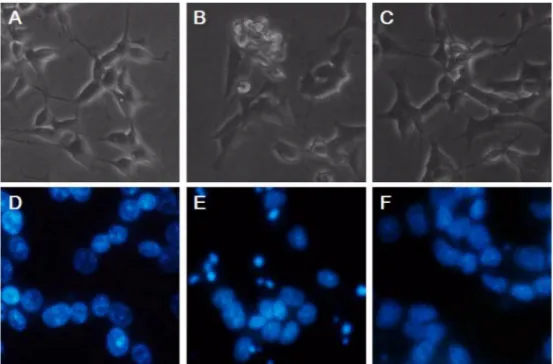
3-HK 에 의해 나타나는 신경세포 사멸의 형태학적 변화를 관
찰하기 위해 위상차 현미경으로 세포의 외형을 관찰하고 (Fig.
2A-C), 핵 형태의 변화를 확인할 수 있는 Hoechst 33258 염 색을 통해 형광 현미경 하에서 변형된 핵 모양을 관찰하였다
(Fig. 2D-F). 250 µ M 의 3-HK 에 36 시간 가량 노출된 SH-
Fig. 1.
Effect of magnolol on 3-HK-induced neuronal cell death.
(a) SH-SY5Y cells were replaced with 1%FBS/DMEM 2 h prior to the 3-HK treatment. The cells were treated with 3-HK for various time.
The cell viability was determined at indicated time points. (b) The cells were pretreated with 10
µM of magnolol for 2 h. 250
µM of 3-HK were then added. The 3-HK was dissolved in DMSO (final conc. < 0.1%). Cell viability was assessed by the alarma blue assay. The values are a mean ± SEM of three separate experiments.
Fig. 2.
Morphological assessment of apoptosis by phase-contrast and fluorescence microscopy.
The SH-SY5Y cells were either not treated (a, d) or treated (b, e) with 250
µM of 3-HK for 36 h. The magnolol pretreated (10
µM of
magnolol for 2 h) cells were treated with 250
µM of 3-HK for 36 h (c, f). The figures show the optical microscopic morphology (a,
b, c) and Hoechst 33258 stained nuclear morphology over fluorescence microscope (d, e, f). The figures are representative of
three different experiments.
SY5Y 세포는 세포막 수포화 , 세포 형태의 수축의 변화를 보
였고 , Hoechst 33258 로 염색한 핵의 형태는 DNA 분절과 핵 응축의 변화를 나타내었다 . 그러나 3-HK 처리 이전에 미리
magnolol 을 처리한 세포의 경우 3-HK 단독 처리에 의해 나타 나는 어포토시스형 세포 사멸의 양상과 형태학적 변화가 저해 되고 있는 것을 확인할 수 있었다 (Fig. 2C, F).
3. 3-HK 에 의한 세포 사멸에서 magnolol 의 항산화 효과
활성기 산소는 세포 독성을 일으킬 수 있는 산화적 스트레 스의 주요 요인이다 . 본 연구에서 250 µ M 의 3-HK 를 처리한 경우 단 시간 내에 독성이 강한 활성기 산소가 급격히 증가하 는 것을 관찰할 수 있었다 (Fig. 3). DCF 형광은 활성기 산 소 발생의 표지자로써 확인을 할 수 있는데 , 본 연구 결과 3- HK 를 처리한 지 15 분 이내에 발생한 활성기 산소는 30 분과
1 시간까지 크게 증가하고 이후 지속적인 높은 수준을 유지하
는 것을 확인할 수 있었다 . 또한 이 때 전 처리한 magnolol
이 3-HK 에 의해 발생하는 활성기 산소의 수준을 현저하게 낮
추는 것을 확인할 수 있었다 (Fig. 3). 본 연구에서는 활성기 산소의 발생량을 정량적으로 측정하기 위해 fluorometer 를 이 용하여 excitation 485 ㎚ 과 emission 535 ㎚ 의 파장에서
DCF 의 형광을 정량하였다 .
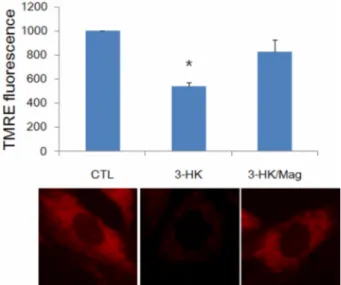
4. 3-HK 에 의한 사립체 막전위차 감소에 대한 magnolol 의
보호효과
산화적 스트레스에 의한 사립체 기능 저하에 대한 연구결과
가 알려져 있고 , 앞선 결과에서 3-HK 에 의해 활성기 산소의
발생이 급증하는 것을 관찰하였으므로 , 3-HK 에 의해 사립체 기능저하가 유도되는 지 확인하고 , 전처리한 magnolol 에 의해 보호될 수 있는 지 알아보기 위해 사립체 막전위차 ( ∆Ψ m) 를 측정하였다 . 사립체 손상은 ∆Ψ m 감소 여부를 측정하는 것으 로 판단할 수 있는데 , 본 연구에서는 ∆Ψ m 를 측정하기 위하
여 TMRE 염색을 실시하였다 . Fig. 4 그래프에서와 같이 정
상적인 배양 시 3-HK 를 처리한지 6 시간 후 ∆Ψ m 는 대조군의 절반 수준으로 감소하였다 . 그러나 magnolol 을 전처리한 후
3-HK 를 처리한 경우 3-HK 단독 처리에 의해 감소되는 ∆Ψ m
를 효과적으로 저해하여 대조군 수준의 염색을 보이는 것을 알 수 있었다 . 또한 형광현미경으로 관찰한 결과 TMRE 에 의해 강한 붉은색으로 염색되어 보이는 건강한 사립체의 대조군에
비해 , 3-HK 처리군의 경우 사립체 막전위차의 붕괴로 TMRE
염색이 거의 빠져나간 것을 관찰할 수 있었다 . 그러나 전처리 한 magnolol 과 함께 처리한 3-HK 군에서는 대조군과 거의 비슷 한 수준의 TMRE 염색 정도를 확인할 수 있다 (Fig. 4).
5. 3-HK 에 의한 세포 사멸에서 magnolol 의 caspase-3 활
성화 억제 효과
세포사멸을 관장하는 시스테인 프로테아제 패밀리 효소 중 하나인 caspase 가 3-HK 에 의한 신경세포 사멸에도 관련이 있 는 지 알아보기 위하여 pan-caspase 저해제인 zVAD-fmk 를
Fig. 3.Determination of ROS generation by 3-HK with 250
µM
after pretreatment with magnolol.
(a) Levels of ROS generation were measured using the fluore- scent probe 2', 7'-dichloroflorescein-diacetate (DCF-DA).
The effect of pretreatment of magnolol is presented. For detecting ROS generation, the cells were incubated with 10
µM DCF-DA for 30 min. And excitation at 485
㎚and emission at 530
㎚were measured with fluorometer (Materials and Methods). The difference from the cells treated with 3-HK alone was statistically significant (
P<
0.05).
Fig. 4.