혈류감염 진단을 위한 신속한 검사법 비교 분석
국민건강보험 일산병원 진단검사의학과
김영아, 이상선, 손영준
Rapid Diagnostic Tests for Bloodstream Infection
Young Ah Kim, Sang Sun Lee, Young Jun Son
Department of Laboratory Medicine, National Health Insurance Service Ilsan Hospital, Goyang Korea
Bloodstream infection (BSI) is a severe clinical state with high mortality and rapid identification of bloodstream pathogens and report of antimicrobial susceptibility play an essential role for the timely and effective treatment of patients with sepsis. Newly developed and introduced rapid tests for bloodstream infection are helpful to diagnose etiologic agents of bloodstream infection or to treat patient effectively. At the same time, it is also important to provide information that will help determine the antibiotic prescription in real time in order to improve clinical utility.
Key Words: Sepsis, Matrix assisted laser desorption ionization time-of flight mass spectrometry, Molecular method, Antimicrobial stewardship
책임저자: 김영아
10444 경기도 고양시 일산동구 일산로 100 국민건강보험 일산병원 진단검사의학과 전화 : (031)900-0908 팩스 : (031)900-0912 E-mail : yakim@nhimc.or,kr
서 론
패혈증(sepsis)은 병원균이나 독소가 혈관 속으로 들어가 순환하면서 전신에 심한 중독 증상이나, 급성 염증을 일으키 는 상태로 최근 변경된 정의에서는 패혈증을 감염으로 인한 생명을 위협하는 장기 부전으로 정의하고 있다.1 발열이나 호중구 증가증 등의 감염을 의심하는 전신염증 반응(Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome, SIRS)이 있는 경우 감염을 의심할 수 있지만, 좀더 정확한 진단을 위해서는 검사실에서 원인균을 확인하는 것이 필요하다. 미국질병관리 본부의 정 의에 따르면 관련 임상 증상이 있고, 임상적인 진단을 목적으 로 시행한 혈액배양이나, 비배양 검사에서
Staphylococcus aureus, Enterococcus
spp.Escherichia coli
,Pseudomonas
spp.Klebsiella
spp.Candida
spp. 등의 흔한 패혈증 병원균이 한번 이상 확인된 경우 검사실 확인 혈류감염(laboratory confirmed bloodstream infection)을 진단할 수 있다.2최근 비배양 검사도 많이 소개되고 있지만, 대부분의 검사 실에서 혈액배양은 혈류감염 진단에서 가장 중요한 검사이다.
하지만 혈액배양에서 병원균의 분리는 검체 채취법, 배양량, 배양 의뢰 횟수 및 배양법 등에 영향을 많이 받고, 특히 혈액 내에 1-10개 정도의 매우 낮은 농도로 존재하는3 병원균을 검출하기 위해서는 충분한 증식 과정을 거쳐야 하므로 최종 결과를 얻기까지 많은 시간이 소요되는 등의 제한점이 있다.
최근에는 세균 표면 단백질을 분석하여 균종을 동정하는 질량분석기 Matrix Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization Time- Of-Flight Mass Spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS)를 이용하여 병원균 동정을 시행하는 임상 미생물 검사실이 늘어나고 있 는데, 배양에 기반한 전통적인 생화학적 방법에 비해 패혈증 의 원인균을 평균 28시간 정도 단축하여 동정할 수 있다.4 또한 지난 10년간 눈부신 기술적 발전에 힘입어 PCR, films array 및 차세대염기분석(next generation sequencing) 등 분자 유전학적 방법을 이용하여 신속하게 패혈증을 진단하는 검사 법도 꾸준히 개발되고 있다.5
신속하게 패혈증의 원인균을 확인하고, 감수성 시험을 통 해 치료 효과가 있는 항생제를 알게 되면 적절한 항균제치료 를 빨리 시행할 수 있어 환자의 예후가 향상되고 의료비용을 절감할 수 있는 반면, 원인균의 동정 및 감수성 시험 결과가
늦어지면 광범위 항생제에 노출하는 기간이 늘어나 내성균이 분리될 위험이 높아진다.6 따라서 패혈증 환자에서 신속한 배양 결과 보고가 매우 중요하다.
저자들은 신속한 패혈증 진단을 위하여 새로 개발 진단검 사법을 전혈에서 직접 원인균을 검출하는 방법과 양성 혈액 배 양병에서의 검출하는 방법으로 나누어 알아보고, 항균제처방관 리 프로그램(antimicrobial stewardship)을 병행하여 신속 패혈증 검사법을 효과적으로 이용하는 방법을 소개하고자 한다.
전혈을 이용한 혈류감염의 신속 진단을 위한 분자유전 학적 방법
혈액을 배양하지 않고 패혈증 의심 환자의 전혈에서 직접 패혈증의 원인균을 직접 검출하는 방법은 통상적인 배양법에 비해 매우 빠르고 민감하게 배양이 어려운 미생물을 동정하 고, 내성 및 병독성 유전자도 함께 검출할 수 있는 것은 장점 이나, 고비용, 항균제 내성이나 자동화 문제로 혈액배양을 대 체하기 힘는 점, 오염, 표준화 및 임상적 유용서에 대한 증거 가 아직까지 충분하지 못한 점 등은 단점이다.5
PCR 원리를 이용하여 혈액 검체에서 직접 주요 패혈증의 원인균을 검출하도록 고안된 상품화된 검사법들로는 Sepsi- Test (Molzym, Bremen, Germany), SeptiFast (Roche Molecu- lar System, Basel, Switzerland), MagicPlex(Seegene, Seoul, Korea), VYOO(SIRS-Lab, Jena, Germany) 등이 있다.5 SeptiFast (Roche) 는 1.5 mL의 전혈을 사용하여 3.5-5시간 내에 19종의 주요 원인균과
mecA
내성유전자를 검출하여 methicillin 내성S.
aureus
를 확인할 수 있으며, 국내에서 개발된 MagicPlex (See- gene)의 경우 1 mL 전혈을 이용하여 3-5시간 내에 25종의 주요 원인균을 종 수준으로 동정할 뿐만 아니라, 내성 유전자mecA
,vanA
및vanB
내성유전자의 검출도 가능하여 methicil- lin 내성S. aureus
과 vancomycin 내성Enterococcus
spp.를 확인 할 수 있다.5패혈증 진단을 위한 혈액배양에 기반한 분자유전학적 신속검사법
양성 혈액 배양병에서 분자유전학적 검사법을 이용하여 직접 혈류감염 원인균을 동정하는 것은 앞서 설명한 전혈에 서 직접 검출하는 방법과 마찬가지로 여러가지 제한점이 있 다. 즉, 혈액 내에는 헤모글로빈 같은 PCR 억제제가 존재하 고, 인체에서 유래한 핵산의 양이 미생물에 비해 매우 많으며, 핵산에 오염에 의한 위양성 가능성 높고, 죽은 세균으로 인한 핵산이 존재한다는 점이다.5,7 최근의 추출과 증폭기술의 발
전으로 혈액에서 직접 원인균을 검출할 수 있는 여러가지 분 자유전학적 검사법들이 상품화되어 있다.
형광제자리부합법(fluorescence in situ hybridization, FISH) 을 이용한 방법으로는 PNA FISH (AdvanDx, Woburn, MA, USA)와 Quick FISH (AdvanDx)가 1-3시간 내에 총 13종의 원인균, AccuProbe (Gen-Probe, San Diego, CA, USA)가 1시간 이내에
S. aureus
,Enterococcus
spp. 및 주요Streptococcus
spp.를 검출한다.7 마이크로어레이법(microarray) 인 Verigene (Na- nosphere, Northbrook, IL, USA)는 2.5시간 내에 총 21종의 원인균과
mecA
,vanA
,vanB, bla
KPC,bla
NDM,bla
CTX-M,bla
VIM,bla
IMP,bla
OXA12를 동시에 확인하며, Prove-it Sepsis (Mobidiag, Esbo, Finland)은 3.5시간 내에 총 73종의 원인균과mecA
내 성유전자도 찾는다.7 multiplex PCR을 이용한 FilmArray (Idaho Technology, Salt Lake City, UT, USA)가 1시간 내에 총 24 종의 원인균과 내성유전자mecA, vanA, vanB, bla
KPC를 real- time PCR법인 Xpert MRSA/SA BC (Cepheid, Sunnyvale, CA, USA)가 1시간 내에S. aureus
와mecA
내성유전자를, multi- plex PCR인 StaphSR assay (BD GeneOhm, San Diego, CA, USA)가 1-2시간 내에S. aureus
와mecA
내성유전자를 검출할 수 있다.7양성 혈액배양병의 침사를 이용한 혈류감염의 신속 질량분석기 검사법
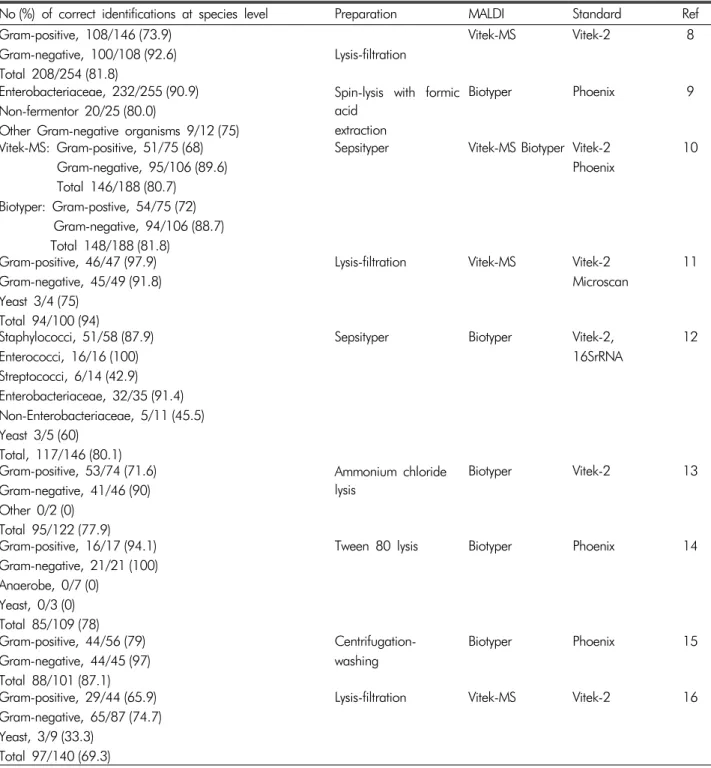
양성 혈액 배양병의 배지를 고체배지에 하루 배양하여 순 배양 집락을 얻은 후 질량분석기로 동정하는 것은 이제 많은 검사실에서 통상적으로 사용하고 있지만, 좀 더 신속한 결과 를 얻기 위해서 양성 혈액배양병에서 침사를 만들어 질량분 석기로 동정 및 항균제 감수성을 시험할 수 있다. 국내의 연구 결과는 아직 많지 않지만, 최근 한 연구에서 융해(lysis)나 여 과(filter)로 얻은 침사를 이용하여 동정하면 기존의 생화학적 방법과 81.8%의 일치하였다고 한다.8 이 연구에서 그람 음성 균의 일치도가 그람 양성균 보다 높은 것으로 보고하였는데, 저자들은
streptococci
와 coagulase 음성staphylococci
에서 동 정되지 않은 경우가 있었기 때문으로 설명하였다.8국외 보고된 주요 연구 결과를 양성 혈액병에서 미생물을 직접 전처리 질량분석기를 이용하는 방법과 자동화된 생화학 적 방법을 이용하여 미생물을 동정법과의 비교하여 Table 1 에 정리하였다.8-16 질량분석기의 검사 특성을 고려하여 혈액 에서 두 종 이상의 복합미생물이 분리된 것은 양성 혈액배 양병을 이용하여 평가한 것은 제외하였다. 그람 양성세균의 경우 종(species) 수준의 일치도가 65.9%에서 97.9%로 다양
Table 1. Comparison of identification between MALDI-TOF with the direct sample preparation method and the standard biochemical method in mono-microbial blood cultures
No (%) of correct identifications at species level Preparation MALDI Standard Ref Gram-positive, 108/146 (73.9)
Gram-negative, 100/108 (92.6) Total 208/254 (81.8)
Lysis-filtration
Vitek-MS Vitek-2 8
Enterobacteriaceae, 232/255 (90.9) Non-fermentor 20/25 (80.0)
Other Gram-negative organisms 9/12 (75)
Spin-lysis with formic acid
extraction
Biotyper Phoenix 9
Vitek-MS: Gram-positive, 51/75 (68) Gram-negative, 95/106 (89.6) Total 146/188 (80.7) Biotyper: Gram-postive, 54/75 (72) Gram-negative, 94/106 (88.7) Total 148/188 (81.8)
Sepsityper Vitek-MS Biotyper Vitek-2 Phoenix
10
Gram-positive, 46/47 (97.9) Gram-negative, 45/49 (91.8) Yeast 3/4 (75)
Total 94/100 (94)
Lysis-filtration Vitek-MS Vitek-2 Microscan
11
Staphylococci, 51/58 (87.9) Enterococci, 16/16 (100) Streptococci, 6/14 (42.9) Enterobacteriaceae, 32/35 (91.4) Non-Enterobacteriaceae, 5/11 (45.5) Yeast 3/5 (60)
Total, 117/146 (80.1)
Sepsityper Biotyper Vitek-2,
16SrRNA
12
Gram-positive, 53/74 (71.6) Gram-negative, 41/46 (90) Other 0/2 (0)
Total 95/122 (77.9)
Ammonium chloride lysis
Biotyper Vitek-2 13
Gram-positive, 16/17 (94.1) Gram-negative, 21/21 (100) Anaerobe, 0/7 (0)
Yeast, 0/3 (0) Total 85/109 (78)
Tween 80 lysis Biotyper Phoenix 14
Gram-positive, 44/56 (79) Gram-negative, 44/45 (97) Total 88/101 (87.1)
Centrifugation- washing
Biotyper Phoenix 15
Gram-positive, 29/44 (65.9) Gram-negative, 65/87 (74.7) Yeast, 3/9 (33.3)
Total 97/140 (69.3)
Lysis-filtration Vitek-MS Vitek-2 16
MALDI, Matrix assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry; N, test number; Ref, Reference; Sepsityper (Bruker Daltonik, Bremen, Germany); MALDI-TOF Vitek-MS system (bioMérieux, Marcy l'Etoile, France); Biotyper MALDI-TOF MS (Bruker Daltonik, Bremen, Germany); Vitek-2 (bioMérieux); Phoenix ((BD Diagnostic Systems, Sparks, MD, USA); Microscan (Siemens, West Sacramento, CA, USA); 16SrRNA, 16SrRNA gene sequencing
하였는데, 이는
streptococci
의 낮은 일치도가 주로 영향을 주 는 것으로 생각되었다. 그람 음성세균의 경우 종 수준의 일치도가 74.7%에서 100%를 보였는데, 장내세균(Enterobacte- riaceae)에서의 일치도는 매우 좋은 것으로 판단되었다.
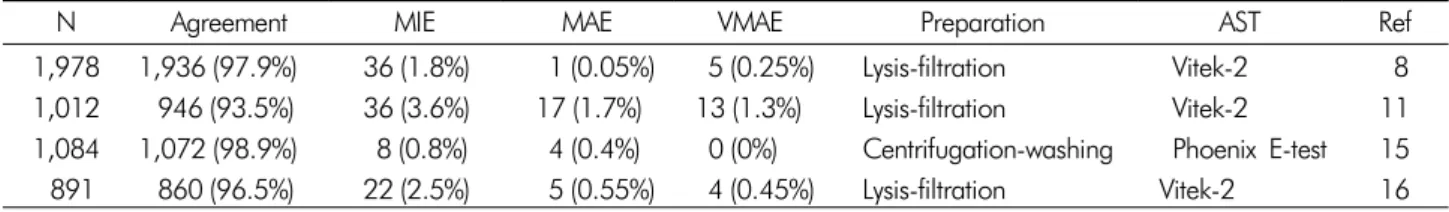
Table 2. Comparison of antimicrobial susceptibility results between the direct sample preparation and the standard method in mono-microbial blood cultures
N Agreement MIE MAE VMAE Preparation AST Ref
1,978 1,936 (97.9%) 36 (1.8%) 1 (0.05%) 5 (0.25%) Lysis-filtration Vitek-2 8 1,012 946 (93.5%) 36 (3.6%) 17 (1.7%) 13 (1.3%) Lysis-filtration Vitek-2 11 1,084 1,072 (98.9%) 8 (0.8%) 4 (0.4%) 0 (0%) Centrifugation-washing Phoenix E-test 15 891 860 (96.5%) 22 (2.5%) 5 (0.55%) 4 (0.45%) Lysis-filtration Vitek-2 16 N, number; MIE, minor error; MAE, major error; VMAE, very major error; AST, antimicrobial sensitivity test; Ref, Reference
양성 혈액배양병의 침사를 이용한 신속 항균제 감수성 시험
혈액배양 결과가 나오기 전에 선제적으로 시행한 경험적 항 균제 처방(conservative antibiotic treatment)을 최종 항균제 처방(definitive antibiotic treatment)로 변경하는 데는 최종 항 균제 감수성 시험 결과가 필수적이다. 적절한 항균제 처방이 패혈증 환자의 예후에 매우 중요한 인자임은 여러 연구에서 잘 알려져 있다.17,18 따라서 양성 혈액배양병 침사를 이용한 신속 항균제 감수성 시험은 결과 보고 시간을 기존의 검사법 보다 하루 앞당길 수 있어 임상적으로 매우 유용하리라 생각 된다. 하지만 아직까지는 정확성 문제를 간과할 수 없는데, 위내성(false resistance)으로 보고하는 major error 발생시 내 성세균의 확산을 위해 제한적으로 사용해야 하는 고가의 활 성이 높은 항균제를 남용할 위험이 있고, 위 감수성(false suscep- tible)으로 보고할 수 있는 very major error 발생시 치료 실패 를 야기할 위험이 있다.
기존의 평가에 따르면 양성 혈액배양병 침사를 이용한 신 속 항균제 감수성 시험법은 배양 후 순집락(colony)으로 시험 하는 기존 방법과 일치율이 93.5%에서 98.9%로 매우 우수하 였고, major error 0.05-1.7% , very major error 0-1.3% 수준 을 보여,8,11,15,16 기존의 방법을 대체 할 수 있을 것으로 판단되 었다. European Clinical Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST)에서도 한 종류의 세균만 자란 양성 혈액배양병에 서 agar diffusion 법으로 항균제 감수성 시험을 시행할 때 기존의 breakpoint를 적용할 수 있는지 검토하는데, 전체적인 일치율은 95.7%로 매우 좋았고, very major error는 1.3%였 다.19 이 연구에서는
Enterococcus
spp.의 고농도 gentamicin 내성과Staphylococcus
spp.의 rifampicin내성이 오류가 높았 다고 하며, major error와 minor error는 모두 3.4%이었다고 보고하였다.19결론적으로 패혈증의 임상적 중요성을 생각해 볼 때 신속 하게 원인균을 검출하고 효과적인 항생제 치료에 대한 정보
를 제공하는 혈류감염 진단을 위한 신속한 검사법을 개발하 고 검사실에 도입하는데 노력을 기울어야 하겠다. 또한 이렇 게 얻은 결과가 임상적인 결정에 실질적인 도움이 될 수 있도 록 실시간으로 항생제 처방을 결정하는데 도움이 되는 정보를 동시에 제공하는 것도 매우 중요하다. 다만 신속한 혈류감염 진단을 위해 새로 개발된 검사들은 대개 전통적인 방법보다 좀 더 신속하고 정확하지만, 검사비용이 고가인 경우가 많아 한정된 의료자원을 비용 효과적으로 이용하기 위해서는 적용 하기 전에 임상적인 효용성을 충분히 분석할 필요가 있다.
REFERENCES
1. Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW, et al. The third inter- national consensus definitions for sepsis and septic shock (sepsis- 3). JAMA 2016;315:801-10.
2. Horan TC, Andrus M, Dudeck MA. CDC/NHSN surveillance definition of health care-associated infection and criteria for specific types of infections in the acute care setting. Am J Infect Control 2008;36:309-32.
3. Wain J, Diep TS, Ho VA, et al. Quantitation of bacteria in blood of typhoid fever patients and relationship between counts and clinical features, transmissibility, and antibiotic resistance.
J Clin Microbiol 1998;36:1683-7.
4. Huang AM, Newton D, Kunapuli A, et al. Impact of rapid orga- nism identification via matrix-assisted laser desorption/ioniza- tion time-of-flight combined with antimicrobial stewardship team intervention in adult patients with bacteremia and candi- demia. Clin Infect Dis 2013;57:1237-45.
5. Opota O, Jaton K, Greub G. Microbial diagnosis of bloodst- ream infection: towards molecular diagnosis directly from blood. Clinl Microbiol Infect 2015;21:323-31.
6. Buehler SS, Madison B, Snyder SR, et al. Effectiveness of pra- ctices to increase timeliness of providing targeted therapy for inpatients with bloodstream infections: a laboratory medicine best practices systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Micro- biol Rev 2016;29:59-103.
7. Opota O, Croxatto A, Prod'hom G, et al. Blood culture-based diagnosis of bacteraemia: state of the art. Clin Microbiol Infect 2015;21:313-22.
8. Jo SJ, Park KG, Han K, et al. Direct identification and antimi-
crobial susceptibility testing of bacteria from positive blood culture bottles by Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry and the Vitek 2 system. Ann Lab Med. 2016;36:117-23.
9. Gray TJ, Thomas L, Olma T, et al. Rapid identification of Gram- negative organisms from blood culture bottles using a modified extraction method and MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. Dig Mic- robiol Infect Dis 2013;77:110-2.
10. Chen JHK, Ho P, Kwan GSW, et al. Direct bacterial identi- fication in positive blood cultures by use of two commercial matrix assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry systems. J Clin Microbiol 2013;51:1733-9.
11. Machen A, Drake T, Wang YF. Same day identification and full panel antimicrobial susceptibility testing of bacteria from positive blood culture bottles made possible by a combined lysis- filtration method with MALDI-TOF VITEK mass spectro- metry and the VITEK2 system. PlosOne 2014;9:e87870.
12. Martinez RM, Bauerle ER, Fang FC, et al. Evaluation of three rapid diagnostic methods for direct identification of microor- ganisms in positive blood cultures. J Clin Microbiol 2014;52:
2521-9.
13. Prod'hom G, Bizzini A, Durussel C, et al. Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry for direct bacterial identification from positive blood culture pellets. J
Clin Microbiol 2010;48:1481-3.
14. Leli C, Cenci E, Cardaccia A, et al. Rapid identification of bacterial and fungal pathogens from positive blood cultures by MALDI-TOF MS. Int J Med Microbiol. 2013;303:205-9.
15. Maelegheer K, Nulens E. Same-day identification and antibio- tic susceptibility testing on positive blood cultures: a simple and inexpensive procedure. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis.
2017;36:681-7.
16. Wattal C, Oberoi JK. Microbial identification and automated antibiotic susceptibility testing directly from positive blood cul- tures using MALDI-TOF MS and VITEK 2. Eur J Clin Micro- biol Infect Dis 2016;35:75-82.
17. Perez KK, Olsen RJ, Musick WL, et al. Integrating rapid patho- gen identification and antimicrobial stewardship significantly decreases hospital costs. Arch Pathol Lab Med 2013;137:1247- 54.
18. Doern GV, Vautour R, Gaudet M, et al. Clinical impact of rapid in vitro susceptibility testing and bacterial identification. J Clin Microbiol 1994;32:1757-62.
19. Stokkou S, Geginat G, Schlüter D, et al. Direct disk diffusion test using European Clinical Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tes- ting breakpoints provides reliable results compared with the standard method. Eur J Microbiol Immunol 2015;5:103-11.