서 론
요추부 화농성 척추감염은 평균적으로 10만 명당 2.4명 꼴로 발 생하는 흔치 않은 질환이나, 나이가 들어감에 따라 70세 이상에 서는 10만 명당 6.5명 수준으로 발생 빈도가 증가하며, 패혈증, 비가역적인 신경근 손상, 신경학적 장애 등의 합병증을 유발하여 사망률은 4%–29%에 이른다.
1-3)내과적 치료로 정맥 항생제 투여
Copyright © 2021 by The Korean Orthopaedic Association
“This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.”
The Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association Volume 56 Number 5 2021 Received January 25, 2021 Revised February 22, 2021 Accepted April 29, 2021 Correspondence to: Yu-Hun Jung, M.D.
Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Bundang Jesaeng Hospital, 20 Seohyeon-ro 180beon-gil, Bundang-gu, Seongnam 13590, Korea
TEL: +82-31-779-0175 FAX: +82-31-779-0176 E-mail: forsky07@gmail.com ORCID: https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9275-8710
요추부 화농성 척추염의 수술적 치료: 이환된 추체에 척추경 나사 고정이 타당한가?
나화엽 • 정유훈 • 이주영 • 김형도
분당제생병원 정형외과
Is It Appropriate to Insert Pedicle Screws at an Infected Vertebral Body in the Treatment of Lumbar Pyogenic Spondylodiscitis?
Hwa-Yeop Na, M.D., Yu-Hun Jung, M.D. , Joo-Young Lee, M.D., and Hyung-Do Kim, M.D.
Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Bundang Jesaeng Hospital, Seongnam, Korea
Purpose: In the surgical treatment of pyogenic lumbar spondylodiscitis, screw insertion at the affected vertebra has been avoided because
of biofilm formation, and the risk of infection recurrence. The authors analyzed the success rate of infection treatment while minimizing the number of instrumented segments by inserting pedicle screws into the affected vertebrae. Therefore, this study examined the usefulness of this technique.
Materials and Methods: From January 2000 to June 2018, among patients with pyogenic lumbar spondylodiscitis treated surgically,
group A consisted of patients with pedicle screws inserted directly at the affected vertebrae (28 cases), and group B underwent fusion by inserting screws at the adjacent normal vertebrae due to bone destruction of the affected vertebral pedicle (20 cases). The classified clinical results were analyzed retrospectively. All patients were treated via the posterior-only approach, so the affected disc and sequestrum were removed. Posterior interbody fusion was performed with an autogenous strut bone graft, and the segments were then stabilized with pedicle screw systems. The hospitalization period, operation time, amount of blood loss, EQ-5D index, duration of intravenous antibiotics, and the clinical and radiological results were analyzed.
Results: In group A, the number of instrumented segments, operation time, blood loss, and EQ-5D index at one month postoperatively
showed significant improvement compared to group B. There were no significant differences in the duration of antibiotic use, hospitalization, radiological bone union time, sagittal angle correction rate, and recurrence rate.
Conclusion: Minimal segmental fixation, in which pedicle screws were inserted directly into the affected vertebrae through the posterior
approach, reduced the surgery time and blood loss, preserved the lumbar motion by minimizing fixed segments and showed rapid recovery without spreading or recurrence of infection. Therefore, this procedure recommended for the surgical treatment of lumbar pyogenic spondyodiscitis.
Key words: lumbar spine, pyogenic spondylodiscitis, interbody fusion, pedicle screw insertion at the infected vertebral body
와 침상 안정을 시행하며, 적절한 항생제 투여에도 증상의 호전 이 없거나, 골 파괴로 인한 척추의 후만 변형 발생, 신경학적 증 상, 견딜 수 없는 심한 통증, 임상적 증상을 유발하는 농양이 형성 된 경우 등에서는 수술적 치료를 요하나 최근에는 수술적 치료를 선호하는 경향이다.
4-6)수술적 방법으로는 예로부터 전방 도달법 을 통한 소파술 및 자가골 이식술이 표준적인 수술법으로 이용되 었으나 후만 변형, 이식된 골편의 이탈, 장기간의 침상안정 등의 문제점으로, 이를 보완하고자 전방 혹은 후방 기기 고정술을 추 가적으로 시행하는 수술법이 사용되었으며, 최근에는 수술 시간, 출혈량 및 합병증의 발생을 줄이기 위해 후방 도달법만을 이용한 소파술과 유합술 및 기기 고정술이 시행되고 있다.
6,7)하지만 지 금까지도 후방 유합술 및 기기고정술 시에 이환된 추체에 대한 척추경 나사를 삽입하는 것은 이물질 삽입으로 인한 감염의 확 산, 균막 형성으로 인한 항생제 저항성 및 감염 치료 재발의 위험 성 등으로 기피되고 있다.
7-9)저자들은 이환된 추체에 척추경 나
사를 삽입하여 고정 분절수를 최소화하여 수술적 위험성을 줄이 고 요추부의 움직임을 보전하면서도 감염 치료의 실패나 재발 없 이 골유합을 얻고 환자가 일상생활에 복귀하였는바, 기존의 인접 정상 추체에 척추경 나사를 삽입하는 장분절 고정술에 대비한 해 당 술식의 유용성에 대하여 연구하고자 하였다.
대상 및 방법
2000년 1월부터 2018년 6월까지 본원 척추센터에서 화농성 요 추부 척추 감염 진단으로 제1저자에 의해 후방 접근법으로 이환 된 추간판의 제거, 부골화된 추체 소파술 및 추체 간 자가 지주골 이식술 후 척추경 나사 고정술을 시행한 환자 중 1년 이상 추시 가 가능했던 총 48명(이환된 추체에 직접 척추경 나사를 삽입하 여 고정술을 시행한 28명, 인접 정상 추체에 척추경 나사를 삽입 하여 고정술을 시행한 20명)을 대상으로 하였다. 이 중 이환된 추
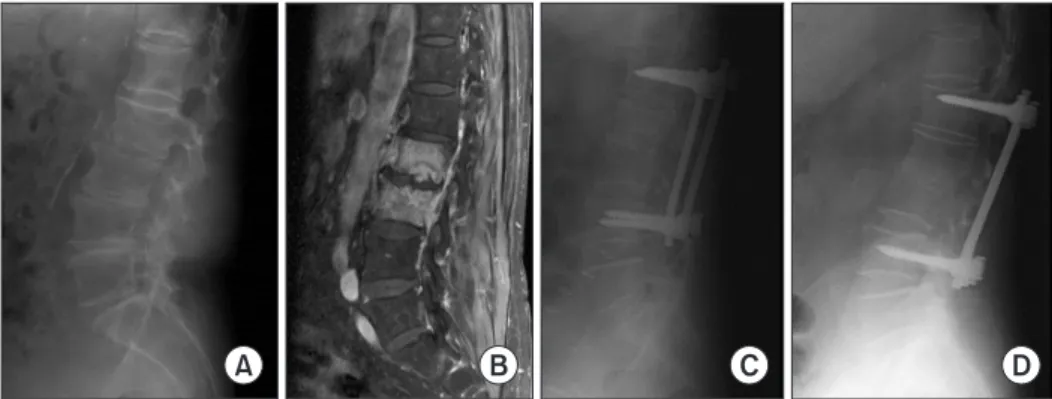
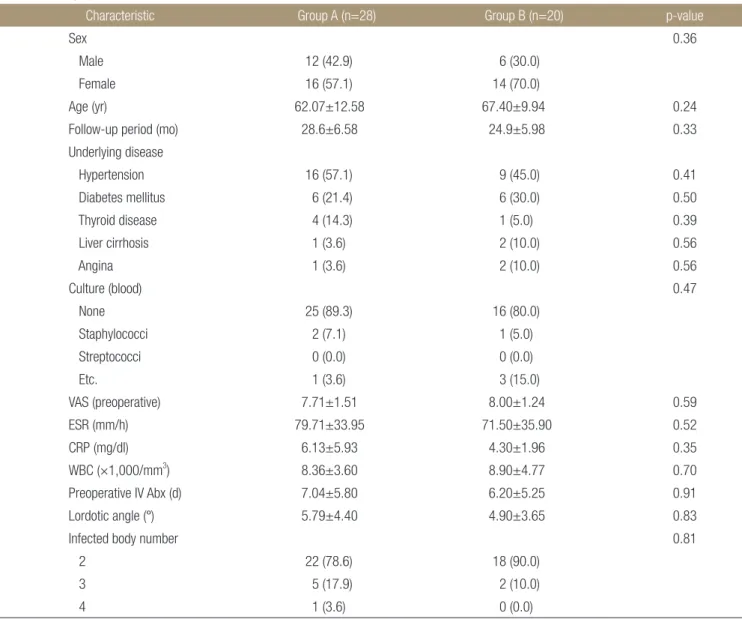
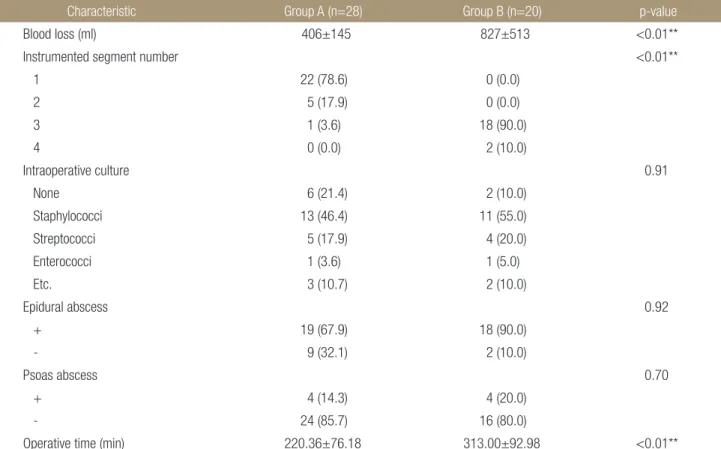
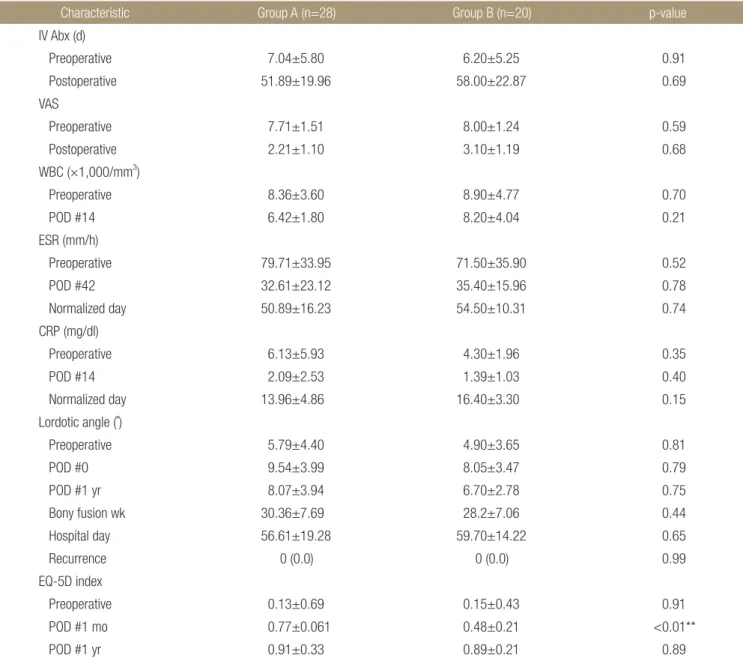
A B C D
Figure 1. A 78-year-old female with pyogenic spondylodiscitis, L2-3. (A) Initial lumbosacral lateral radiograph in the standing position. (B) Preoperative contrast-enhanced T1-weighted magnetic resonance image showing diffuse bone marrow signal changes, and enhancement with fluid collection in intervertebral disc space, L2-3. (C) Immediately postoperative lumbosacral lateral radiograph in the standing position. (D) Fifteen years after surgery, lumbosacral lateral radiograph in the standing position showing a bony union state.
A B C D E F
Figure 2. A 78-year-old female with pyogenic spondylodiscitis, L2-3. (A) Initial lumbosacral spine lateral radiograph with standing position showing
destructive changes to the end plate and intervertebral space narrowing in L2-3. Preoperative T1-weighted (B), and contrast-enhanced (C) magnetic
resonance image showing diffuse bone marrow signal change, bone destruction and enhancement with fluid collection in intervertebral disc space,
L2-3. (D) Preoperative computed tomography scan of a sagittal image showing destructive vertebral body, L2-3. (E) Immediately postoperative
lumbosacral spine lateral radiograph showing a posterior lumbar interbody fusion state in L2-3 with an autologous strut bone graft from the posterior
superior iliac spine. (F) One year after surgery, lumbosacral spine lateral radiograph in the standing position showing a bony union state.
체에 직접 척추경 나사를 삽입하여 고정술을 시행한 환자군을 A 그룹으로(Fig. 1), 인접 정상 추체에 척추경 나사를 삽입하여 고정 술을 시행한 환자군을 B그룹으로(Fig. 2) 분류하였으며, 술 전 컴 퓨터 단층 촬영 검사상에서 이환된 추체 척추경의 골파괴로 인하 여 척추경 나사 삽입 시 안정성이 보장되지 않는 경우에 한해 인 접 정상 추체에 척추경 나사를 삽입하였다. 척추체 나사못 고정 분절 이외에 두 그룹 간의 수술 술기상의 차이는 없었으며, 후향 적 분석방법을 통한 연구로 IRB 심의는 면제되었다.
평균 추시 기간은 28.1개월(A그룹 28.6개월, B그룹 24.9개월), 평균 나이는 64.34세(A그룹 62.07세, B그룹 67.40세)였고, 성별 은 남자 18명(A그룹 12명, B그룹 6명), 여자 30명(A그룹 16명, B그룹 14명)이었다. 동반 질환으로 고혈압 25명(A그룹 16명, B
그룹 9명), 당뇨 12명(A그룹 6명, B그룹 6명), 갑상선질환 5명(A 그룹 4명, B그룹 1명), 간경화 3명(A그룹 1명, B그룹 2명), 협심 증이 3명(A그룹 1명, B그룹 2명)이었으며, 술 전 시행한 혈액 배 양검사상 비검출 41명(A그룹 25명, B그룹 16명), 포도상구균 3 명(A그룹 2명, B그룹 1명), 기타 4명(A그룹 1명, B그룹 3명)이었 다. 균이 동정된 경우에는 감수성이 있는 항생제를 사용하였고, 균이 동정되지 않은 경우에는 경험적인 항생제를 사용하였다.
수술 전후 요통 및 하지 방사통의 정도는 시각통증점수(visual analogue scale, VAS)로 수치화하여 비교하였으며, A그룹 7.71, B그룹 8.00으로 양 그룹에서 모두 심한 술 전 통증을 호소하였 고, 혈액학적 검사로 백혈구, 적혈구 침강 속도 및 C 반응성 단백 (C-reactive protein, CRP)을 측정하여 술 전 환자 상태 평가 및
Table 1. Demographic and Clinical Characteristics of the Patients
Characteristic Group A (n=28) Group B (n=20) p-value
Sex 0.36
Male 12 (42.9) 6 (30.0)
Female 16 (57.1) 14 (70.0)
Age (yr) 62.07±12.58 67.40±9.94 0.24
Follow-up period (mo) 28.6±6.58 24.9±5.98 0.33
Underlying disease
Hypertension 16 (57.1) 9 (45.0) 0.41
Diabetes mellitus 6 (21.4) 6 (30.0) 0.50
Thyroid disease 4 (14.3) 1 (5.0) 0.39
Liver cirrhosis 1 (3.6) 2 (10.0) 0.56
Angina 1 (3.6) 2 (10.0) 0.56
Culture (blood) 0.47
None 25 (89.3) 16 (80.0)
Staphylococci 2 (7.1) 1 (5.0)
Streptococci 0 (0.0) 0 (0.0)
Etc. 1 (3.6) 3 (15.0)
VAS (preoperative) 7.71±1.51 8.00±1.24 0.59
ESR (mm/h) 79.71±33.95 71.50±35.90 0.52
CRP (mg/dl) 6.13±5.93 4.30±1.96 0.35
WBC (×1,000/mm
3) 8.36±3.60 8.90±4.77 0.70
Preoperative IV Abx (d) 7.04±5.80 6.20±5.25 0.91
Lordotic angle ( °) 5.79±4.40 4.90±3.65 0.83
Infected body number 0.81
2 22 (78.6) 18 (90.0)
3 5 (17.9) 2 (10.0)
4 1 (3.6) 0 (0.0)
Values are presented as number (%) or mean±standard deviation. VAS, visual analog scale; ESR, erythrocyte sedimentation rate; CRP, C-reactive
protein; WBC, white blood cell; IV Abx, intravenous antibiotics.
치료 반응에 대한 지표로 사용하였다.
두 술식의 비교를 위해 수술 시간, 출혈량, 고정 분절 수를 비 교하였으며, 방사선학적 평가를 위하여 수술 전, 수술 직후, 및 술 후 12개월째, 이후 최대 1년 주기로 직립 상태에서 전후방, 측면 단순 방사선 사진을 촬영하여 고정물의 전위와 파단 유무, 지주 이식골의 단축과 전위 및 추체 유합 여부를 관찰하였다. 후만각 의 교정 정도는 직립상태에서 촬영한 측면 단순 방사선 사진에서 이환된 부위의 근위 추체의 상부 골단판과 이환 부위의 원위 추 체의 하부 골단판의 연장선을 이용한 Cobb의 방법으로 측정하였다.
임상적 결과를 평가하기 위하여 입원 기간, 재발률 및 일상생 활 삶의 질의 척도로 수술 전, 술 후 1개월, 1년째의 EuroQol-5 Dimensions 지수(EQ-5D index)를 이용해 정량화하여 비교하 였다.
수술 전후 각 그룹 간의 통계적 차이는 독립표본 t 검정과 카이 제곱 검정으로 비교하였고, 기대빈도가 작아 Pearson 카이 제곱 값을 쓸 수 없을 경우에는 Fisher 정확 검정 값의 p-value를 사 용하였다. 변수별로는 성별, 기저질환, 혈액 배양검사, 수술장 검 체 배양 검사, 이환된 척추체의 수, 고정 분절 수, 경막외 농양, 요 근 농양 및 재발률의 분석에는 카이 제곱 검정을 사용하였으며, 나이, 추시 기간, VAS, 적혈구 침강 속도(erythrocyte sedimen-
tation rate, ESR), CRP, 백혈구, 수술 전후 주사 항생제 투여 기 간, 시상각, 출혈량, 수술 시간, 골유합 기간, 입원 기간, EQ-5D index의 분석에는 독립표본 t검정을 사용하였다. 통계 분석은 IBM SPSS Statistics, Ver. 20 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA) 을 사용하였으며, p-value가 0.05 미만인 경우 통계적으로 유의 하다고 정의하였다.
결 과
성별, 나이, 추시 기간, 기저질환, 혈액 배양 검사상 균주, 감염 된 척추체의 수, 술 전 VAS, 혈액학적 검사, 정맥 항생제 사용 기 간, 및 단순 방사선 사진상의 후만 변형 정도를 포함하는 수술 전 두 그룹의 일반적인 특징에서 유의미한 통계학적 차이는 없었다 (Table 1).
수술 중 소견에서는 A그룹에서 출혈량(A그룹 406 ml, B그 룹 827 ml; p<0.01)이 적고, 수술시간(A그룹 220.36분, B그룹 313.00분; p<0.01)이 짧으며, 고정 분절 수(A그룹: 1분절 22, 2 분절 5, 3분절 1, B그룹: 3분절 18, 4분절 2; p<0.01)가 작았으 며, 통계적으로 유의한 차이를 보였다. 수술장 내 검체의 배양검 사상 포도구균(A그룹 13, B그룹 11), 연쇄구균(A그룹 5, B그룹
Table 2. Analysis of the Intraoperative Findings
Characteristic Group A (n=28) Group B (n=20) p-value
Blood loss (ml) 406±145 827±513 <0.01**
Instrumented segment number <0.01**
1 22 (78.6) 0 (0.0)
2 5 (17.9) 0 (0.0)
3 1 (3.6) 18 (90.0)
4 0 (0.0) 2 (10.0)
Intraoperative culture 0.91
None 6 (21.4) 2 (10.0)
Staphylococci 13 (46.4) 11 (55.0)
Streptococci 5 (17.9) 4 (20.0)
Enterococci 1 (3.6) 1 (5.0)
Etc. 3 (10.7) 2 (10.0)
Epidural abscess 0.92
+ 19 (67.9) 18 (90.0)
- 9 (32.1) 2 (10.0)
Psoas abscess 0.70
+ 4 (14.3) 4 (20.0)
- 24 (85.7) 16 (80.0)
Operative time (min) 220.36±76.18 313.00±92.98 <0.01**
Values are presented as mean±standard deviation or number (%). **Statistically significant.
4), 장내구균(A그룹 1, B그룹 1), 기타(A그룹 3, B그룹 2), 비검출 (A그룹 6, B그룹 2)로 그 분포에 있어 유의한 차이를 보이지 않았 으며, 모든 경우에서 메티실린 저항성 황색 포도구균(methicil- lin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, MRSA), 카바페넴 내성 장내세균속균종(carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriacea) 등의 균주는 검출되지 않았다. 균이 동정된 경우에는 감수성 있 는 항생제를 사용하였으며, 수술장 검체에서도 균이 동정되지 않 은 경우(n=8)에는 수술 방식에 관계 없이 감염 내과와 협진 후 사용할 항생제를 결정하였다. 경험적 항생제 사용 시 1차 항생 제로는 ampicillin/sulbactam (n=3, 37.5%), ciprofloxacin±
lindamycin (n=2, 25%), penicillin+gentamycin (n=2, 25%), vancomycin+penicillin (n=1, 12.5%)의 빈도 순으로 사용되 었으며, 경과 관찰 중 임상 증상, 백혈구 수, ESR, CRP 등이 호 전 양상을 보이지 않을 시에 2차, 3차 항생제로는 vancomy- cin+ceftazidime/rifampin, cephalosporin (3, 4세대), teico- planin±clindamycin, quinolone 계열 등이 단독 혹은 병용 사 용되었다. 이외에 경막 외 농양, 및 요근 농양의 유무에서도 통계 학적 차이는 없었다(Table 2).
술 후의 임상적, 방사선학적 결과에서는 정맥 항생제 사용 기 간(A그룹 51.89일, B그룹 58.00일), VAS (A그룹 2.21, B그룹
Table 3. Analysis of the Clinical and Radiological Results
Characteristic Group A (n=28) Group B (n=20) p-value
IV Abx (d)
Preoperative 7.04±5.80 6.20±5.25 0.91
Postoperative 51.89±19.96 58.00±22.87 0.69
VAS
Preoperative 7.71±1.51 8.00±1.24 0.59
Postoperative 2.21±1.10 3.10±1.19 0.68
WBC (×1,000/mm
3)
Preoperative 8.36±3.60 8.90±4.77 0.70
POD #14 6.42±1.80 8.20±4.04 0.21
ESR (mm/h)
Preoperative 79.71±33.95 71.50±35.90 0.52
POD #42 32.61±23.12 35.40±15.96 0.78
Normalized day 50.89±16.23 54.50±10.31 0.74
CRP (mg/dl)
Preoperative 6.13±5.93 4.30±1.96 0.35
POD #14 2.09±2.53 1.39±1.03 0.40
Normalized day 13.96±4.86 16.40±3.30 0.15
Lordotic angle (˚)
Preoperative 5.79±4.40 4.90±3.65 0.81
POD #0 9.54±3.99 8.05±3.47 0.79
POD #1 yr 8.07±3.94 6.70±2.78 0.75
Bony fusion wk 30.36±7.69 28.2±7.06 0.44
Hospital day 56.61±19.28 59.70±14.22 0.65
Recurrence 0 (0.0) 0 (0.0) 0.99
EQ-5D index
Preoperative 0.13±0.69 0.15±0.43 0.91
POD #1 mo 0.77±0.061 0.48±0.21 <0.01**
POD #1 yr 0.91±0.33 0.89±0.21 0.89
Values are presented as mean±standard deviation or number (%). **Statistically significant. IV Abx, intravenous antibiotics; VAS, visual analog scale;
WBC, white blood cell; POD, postoperative days; ESR, erythrocyte sedimentation rate; CRP, C-reactive protein; EQ-5D, EuroQol-5 Dimensions.
3.10), 술 후 2주째 백혈구(A그룹 6,420/mm
3, B그룹 8,200/
mm
3), 술 후 42일째 적혈구 침강 속도(A그룹 32.61 mm/h, B그 룹 35.40 mm/h) 및 정상화되기까지의 기간(A그룹 50.89일, B그 룹 54.50일), 술 후 2주째 C 반응성 단백(A그룹 2.09 mg/dl, B그 룹 1.39 mg/dl) 및 정상화되기까지의 기간(A그룹 13.96일, B그 룹 16.40일), 수술 직후의 후만각(A그룹 9.54°, B그룹 8.05°) 및 술 후 1년째 추시 관찰상의 후만각(A그룹 8.07°, B그룹 6.70°), 입원 기간(A그룹 56.61일, B그룹 59.70일), 재발률(A그룹 0%, B 그룹 0%)에서는 두 그룹 간에 통계학적 차이를 보이지 않았다.
단, 환자의 일상 생활 삶의 질을 반영하는 EQ-5D 지수에서 수 술 전(A그룹 0.13, B그룹 0.15) 및 수술 1년 후 추시관찰(A그룹 0.91, B그룹 0.89) 시에는 통계학적 차이가 없었으나, 수술 후 1 개월째의 지수는(A그룹 0.77, B그룹 0.48; p<0.01)으로 통계학 적으로 유의하게 향상된 결과를 보였다(Table 3).
고 찰
우리나라를 포함하여 전세계적으로 요추부 화농성 척추 감염의 유병률은 지속적인 증가 추세로, 추간판 내 침습적 시술 및 관련 수술, 비뇨기 및 소화기 계통의 침습적 검사, 항생제 및 면역억제 제의 오남용 등이 대표적인 원인으로 꼽히며, 고령화 사회가 진 행되면서 당뇨, 류마티스 관절염 등의 전신 질환을 동반한 원발 성 감염의 빈도 또한 적지 않다.
10,11)이에 침상 안정 및 내과적 항 생제 치료로 치료되지 않는 요추부 화농성 척추 감염 또한 증가 하는 추세로, 이에 대응하기 위한 정형외과적 수술적 치료 역시 발전하고 있다. Hodgson과 Stock
12)이 전방 접근법을 통한 소파 술 및 자가골 이식술의 유용성을 소개하였으나, 후만 변형, 지주 골편의 이탈, 장기간 침상 안정 등의 문제점이 대두되었다. 이에 척추 분절의 안정성의 확보를 위하여 전방, 혹은 후방 기기 고정 술을 같이 시행하는 술식이 발달하였다. 이를 위해 전방 및 후방 도달법을 같이 시행하게 될 경우 수술 시간이 매우 길어지고, 대 량의 출혈 가능성으로 전신적 합병증의 발생 가능성이 높아져 최 근에는 후방 도달법만을 사용한 소파술, 유합술 및 기기 고정술 의 유용성이 여러 보고들에서 확인되었다.
12-16)요추부 척추 감염에서 척추경 나사를 사용한 기기 고정술은 척추 분절을 안정화시키고, 추가적인 후만 변형을 예방하여 추 체 감염을 조절하고 조기 보행을 가능케 하여 삶의 질을 높여 주 는 장점이 있으나, 결핵균에 의한 감염과 달리 화농성 세균에 의 한 척추 감염은 금속 기기 주변부로 두꺼운 다당류 균막을 형성 할 수 있어 숙주의 면역체계와 항생제에 대한 저항력이 상대적으 로 크다고 알려져 감염의 재발 및 파급 가능성으로 금기시되어
왔다.
17,18)이에 따라 기존의 후방 기기 고정술은 감염된 척추체를
피해 인접 정상 추체에 척추경 나사를 삽입하는 장분절 고정술이 시행되었다. 저자들은 술 전 검사상에서 이환된 추체 척추경의
골파괴가 심하여 척추경 나사 삽입 시 안정성이 보장되지 않는 경우를 제외한, 28예에서 이환된 추체에 직접 척추경 나사를 삽 입한 최소분절 고정술을 시행하였다. 술 전 두 그룹 간의 일반적 인 특징에 있어서 통계학적 차이는 없었으며, 술 후 혈액학적, 임 상적 치료경과 및 재발률에 더하여 방사선학적 유합과 후만각의 교정에 있어 두 그룹 간 대등한 결과를 나타내면서도, 이환된 추 체에 직접 척추경 나사를 삽입하여 최소분절 고정술을 시행한 그 룹에서 출혈량, 수술시간, 고정분절 수, 및 환자의 삶의 질의 빠른 회복에 있어 통계학적으로 유의하게 향상된 결과를 보였다. 이는 의학적인 수술 술기의 향상에 더불어 티타늄 등을 이용한 감염에 저항성이 큰 금속기기의 발달, 항생제의 진보한 균막 침투성 및 항균 효과 등의 요인이 복합적으로 작용하여 나타난 결과라고 생 각된다.
19,20)본 연구는 후향적으로 진행되었다는 점에 더불어, 질환의 특성 상 유병률이 적어 본원에서 19년간 누적되었음에도 그 수가 적 으며, MRSA 표본이 없다는 한계점이 있다. 따라서 추후 정확한 임상적, 방사선적 결과를 비교하기 위해 여러 센터에서 환자 표 본을 충분히 모아 시행하는 전향적 연구가 필요하다고 생각된다.
결 론
보존적 치료에 반응하지 않는 요추부의 화농성 감염 환자에서 후 방 도달법으로 이환된 추간판 및 추체 부골을 제거하고, 자가 지 주골 이식 후, 이환된 추체에 직접 척추경 나사를 삽입하는 최소 분절 고정술은 기존의 인접 정상 추체에 척추경 나사를 삽입하는 장분절 고정술과 비교할 때, 출혈량을 줄이고 수술 시간을 단축 시키며 고정 분절을 최소화하여 요추부의 움직임을 보전하면서 도, 감염의 확산이나 재발 없이 빠른 임상적 회복을 보였기에, 요 추부의 화농성 감염 환자의 수술적 치료 시 권장될 수 있는 술식 으로 사료된다.
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
The authors have nothing to disclose.
ORCID
Hwa-Yeop Na, https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9740-7039
Yu-Hun Jung, https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9275-8710
Joo-Young Lee, https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5541-6132
Hyung-Do Kim, https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4151-9779
REFERENCES
1. Zimmerli W. Clinical practice. Vertebral osteomyelitis. N Engl J Med. 2010;362:1022-9.
2. Grammatico L, Baron S, Rusch E, et al. Epidemiology of ver- tebral osteomyelitis (VO) in France: analysis of hospital-dis- charge data 2002-2003. Epidemiol Infect. 2008;136:653-60.
3. Almansour H, Pepke W, Akbar M. Pyogenic spondylodis- citis: the quest towards a clinical-radiological classification.
Orthopade. 2020;49:482-93.
4. Arnold PM, Baek PN, Bernardi RJ, Luck EA, Larson SJ.
Surgical management of nontuberculous thoracic and lum- bar vertebral osteomyelitis: report of 33 cases. Surg Neurol.
1997;47:551-61.
5. Eismont FJ, Bohlman HH, Soni PL, Goldberg VM, Freehafer AA. Pyogenic and fungal vertebral osteomyelitis with paraly- sis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1983;65:19-29.
6. Hadjipavlou AG, Mader JT, Necessary JT, Muffoletto AJ.
Hematogenous pyogenic spinal infections and their surgical management. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2000;25:1668-79.
7. Rath SA, Neff U, Schneider O, Richter HP. Neurosurgical management of thoracic and lumbar vertebral osteomyelitis and discitis in adults: a review of 43 consecutive surgically treated patients. Neurosurgery. 1996;38:926-33.
8. Ha KY, Shin JH, Kim KW, Na KH. The fate of anterior autogenous bone graft after anterior radical surgery with or without posterior instrumentation in the treatment of pyogenic lumbar spondylodiscitis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).
2007;32:1856-64.
9. Lee JS, Suh KT. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion with an autogenous iliac crest bone graft in the treatment of pyogenic spondylodiscitis. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2006;88:765-70.
10. Kim YJ, Zun WB, Choi CS, Kim BS. 3 cases of pyogenic spondylitis. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 1976;11:477-82.
11. Lee KY, Sohn SK, Hwang KS. Comparison of pyogenic and
tuberculous spondylitis. J Korean Soc Spine Surg. 1999;6:443- 50.
12. Hodgson AR, Stock FE. Anterior spinal fusion. A preliminary communication on the radical treatment of Pott's disease and Pott's paraplegia. 1956. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1994;300:16- 23.
13. Lee JS, Suh KT. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion with an autogenous iliac crest bone graft in the treatment of pyogenic spondylodiscitis. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2006;88:765-70.
14. Ahn DK, Jeong KW, Kwon BK, Cha SK, Park KY, Cho KH.
Operative treatment of lumbosacral spondylitis through a posterior-only approach. J Korean Orthop Assoc.
2005;40:868-74.
15. Dickman CA, Fessler RG, MacMillan M, Haid RW. Tran- spedicular screw-rod fixation of the lumbar spine: oper- ative technique and outcome in 104 cases. J Neurosurg.
1992;77:860-70.
16. Nasto LA, Colangelo D, Mazzotta V, et al. Is posterior per- cutaneous screw-rod instrumentation a safe and effective alternative approach to TLSO rigid bracing for single-level pyogenic spondylodiscitis? Results of a retrospective cohort analysis. Spine J. 2014;14:1139-46.
17. Chung YG, Ha KY. Adherence and biofilm formation of Staphylococcus epidermidis and Mycobacterium tuberculo- sis on spinal implant. J Korean Soc Spine Surg. 1999;6:47-56.
18. Oga M, Sugioka Y, Hobgood CD, Gristina AG, Myrvik QN.
Surgical biomaterials and differential colonization by Staphy- lococcus epidermidis. Biomaterials. 1988;9:285-9.
19. Orapiriyakul W, Young PS, Damiati L, Tsimbouri PM. Anti- bacterial surface modification of titanium implants in ortho- paedics. J Tissue Eng. 2018;9:2041731418789838.
20. Algburi A, Comito N, Kashtanov D, Dicks LMT, Chikindas ML. Control of biofilm formation: antibiotics and beyond.
Appl Environ Microbiol. 2017;83:e02508-16.
요추부 화농성 척추염의 수술적 치료: 이환된 추체에 척추경 나사 고정이 타당한가?
나화엽 • 정유훈 • 이주영 • 김형도
분당제생병원 정형외과
목적:
화농성 요추부 추체 감염의 수술적 치료 시 이환된 추체에 척추경 나사를 삽입하는 수술법은 균막의 형성 및 감염 치료 실패 의 위험성으로 기피되었다. 저자들은 이환된 추체에 척추경 나사를 삽입하여 고정 분절수를 최소화하면서도 감염 치료에 성공하 였는바, 이를 분석하여 해당 술식의 유용성에 대하여 알아보고자 하였다.
대상 및 방법:
2000년 1월부터 2018년 6월까지 본원 척추센터에서 제1저자에 의해 수술적으로 치료한 화농성 요추부 척추 감염 환자 중, 이환된 추체에 직접 척추경 나사를 삽입하여 유합술을 시행한 환자군을 그룹 A, 이환된 추체 척추경의 골파괴 소견으로 인접 정상 추체에 척추경 나사를 삽입하여 유합술을 시행한 환자군을 그룹B로 분류하여 임상적 결과를 후향적으로 연구하였다.
모든 환자들은 후방 접근법으로 수술하였으며, 이환된 추간판을 제거하고 부골화된 추체의 소파술 및 추체 간 자가 지주골 이식술 후 척추경 나사 고정술을 시행한 48예(그룹A 28예, 그룹B 20예)를 대상으로 두 그룹 간의 입원 기간, 수술 시간, 출혈량 및 수술 후 1개월째 EQ-5D 지수, 주사 항생제 투여 기간, 혈액학적 결과, 임상적 결과, 방사선학적 결과를 종합적으로 분석하였다.
결과:
그룹 A에서 고정 분절 수, 수술 시간, 출혈량 및 술 후 1개월째 EQ-5D 지수에서 그룹 B에 비하여 통계적으로 유의하게 향상 된 결과를 보였으며, 항생제 사용 기간, 입원 기간, 방사선학적 골유합의 시기, 시상각의 교정률 및 재발률에서는 유의한 차이를 보 이지 않았다.
결론:
후방 도달법을 통한 이환된 추체에 직접 척추경 나사를 삽입하는 최소 분절 고정술은 수술 시간 및 출혈량이 줄어들고, 고정 분절을 최소화하여 요추부의 운동성을 보전하면서도, 감염의 확산이나 재발 없이 빠른 회복을 보였기에, 요추부 화농성 척추염 환 자의 수술적 치료 시 권장할 만한 술식으로 생각된다.
색인단어: 요추, 화농성 척추염, 추체 간 유합술, 이환된 추체에 척추경 나사 고정
접수일 2021년 1월 25일 수정일 2021년 2월 22일 게재확정일 2021년 4월 29일 책임저자 정유훈
13590, 경기도 성남시 서현로 180번길 20, 분당제생병원 정형외과
TEL 031-779-0175, FAX 031-779-0176, E-mail forsky07@gmail.com, ORCID https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9275-8710
Copyright © 2021 by The Korean Orthopaedic Association
“This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.”
대한정형외과학회지:제 56권 제 5호 2021