동정맥루의 모니터링(Monitoring)과 감시(Surveillance)
이재훈
대구가톨릭대학교 의과대학 외과학교실
Monitoring and Surveillance of Vascular Access
Jae Hoon Lee
Department of Surgery, College of Medicine, Daegu Catholic University, Daegu, Korea
서 론
식습관의 서구화, 고령화로 당뇨병과 고혈압의 유병이 늘면서 이로 인한 합병증으로 투석을 필요로 하는 말기 만성신부전을 앓 고 있는 환자도 크게 증가하고 있는 실정이다. 2018년 대한신장학 회에서 보고한 우리나라 신대체요법 현황에 따르면 말기 만성신 부전 환자수는 2017년 기준 총 98,746명에 이르며(혈액투석 환자 73,059명, 복막투석 환자 6,475명, 콩팥이식 환자 19,212명), 2017 년 한 해 동안 새롭게 발생한 환자수는 16,659명에 이른다. 신대 체요법 중 70% 이상을 차지하는 혈액투석을 지속적으로 하기 위 해 정맥을 많은 양의 혈액이 지나가도록 확장시키고 동맥처럼 튼 튼하게 하는 동맥과 표피 정맥을 연결하는 수술인 동정맥루 수술 이 필수적이다. 말기 만성신부전 환자들이 지속적 혈액투석 치료 를 받기 위해서는 적절한 동정맥루 상태를 유지하는 것이 가장 중 요하다. KDOQI 지침에서는 사전 모니터링(monitoring)과 감시 (surveillance)로 동정맥루의 협착을 조기에 진단하여 처치하는 것
을 추천한다[1]. 반면 사전 감시로 인한 혈관성형술의 증가가 동정 맥루의 수명 또는 2차 개존율을 증가시키지는 않는다는 반론을 제 기하기도 한다[2]. 이 논문에서는 모니터링과 감시의 정의 및 종류 와 방법에 대해서 알아보고자 한다.
본 론 1. 정의
KDOQI 지침에서 모니터링은 동정맥루의 기능을 신체검진을 통해 검사하고 평가하는 것으로 정의한다. 모니터링에는 Kt/V 측 정의 변화와 임상양상의 변화가 포함된다. 감시는 특별한 측정기 구를 이용해 동정맥루의 기능을 주기적으로 평가하는 것으로 정 의한다[1]. 초음파를 이용한 혈류측정, 동적 또는 정적 정맥압 측 정, 초음파 희석법(ultrasound dilution, UD)과 다른 희석법(혈류와 재순환 시 헤마토크리트(hematocrit), 전도도(conductivity), 온도 (temperature) 등의 차이 측정)이 포함된다.
대 한 투 석 혈 관 학 회 지 : 제 2 권 제 1 호
Journal of Korean Dialysis Access 2019;2(1):6-9
Review Article
Physical examination is a simple but critical test with symptoms such as increased post-dialysis hemodialysis time, urea reduction ratio, decreased Kt/V levels, and increased pressure during dialysis in monitoring. Surveillance is an important test that maintains the function of the arteriovenous fistula, avoiding dialysis through unnecessary conduits and reducing the length of hospital stay, thereby improving the quality of life of dialysis patients. Future research into the proper combination of active clinical monitoring and additional surveillance would be expected to create a formalized program of monitoring and surveillance to provide a way to maintain arteriovenous fistulas and prevent unnecessary procedures.
Key Words: Arteriovenous fistula, Hemodialysis, Stenosis
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Copyright © The Korean Society for Dialysis Access | eISSN: 2635-8603
Received: Mar 30, 2019, Revised: Apr 15, 2019 Accepted: Apr 28, 2019 책임저자 : 이재훈
우 42472, 대구시 남구 두류공원로 17길 33, 대구가톨릭대학병원 혈관외과 Tel: 053-650-4065, Fax: 053-624-7185, E-mail: vsljh@cu.ac.kr
*본 종설은 2018년 9월 9일 대한투석혈관학회 제30차 하계학술대회에서 발표한 내용을 추가 편집하였습니다.
이재훈 : 동정맥루의 모니터링(Monitoring)과 감시(Surveillance) 7
2. 모니터링(Monitoring)
모니터링에는 유출 정맥의 촉진 변화, 팔의 지속적인 부종, 측부 정맥의 존재, 투석 후 투석자리의 지속적인 출혈, 투석천자의 어려 움, 천자 시 혈전 흡입 등의 임상양상 변화와 투석양의 감소(Kt/V drop>0.2 units)를 포함한다. 전향적 연구에 따르면 Kt/V 0.2 units 이상감소와 임상양상은 각각 양성예측도가 69%, 66%를 보이며, 동정맥루 협착을 80% 정도 예측하였다[3]. 모니터링은 손쉽고 저 렴한 방법이지만 정확한 측정을 위해서는 적절한 측정방법과 임상 양상에 대한 이해와 교육이 요구된다.
3. 감시(surveillance)
1) 직접 혈류 측정(Direct access flows)
직접 혈류 측정은 초음파와 자기공명혈관촬영(magnetic resonance angiography, MRA)를 통하여 측정할 수 있지만, 상대 적으로 비싸고 환자에게 부담이 된다. 초음파는 혈관의 크기와 혈 류의 속도 측정에서 검사자 의존적인 방법으로, 주관적이다. 따라 서, 반복적인 측정을 추천한다. 초음파의 정확도는 혈관촬영과 비 슷해서 민감도는 92-100%, 특이도는 94-97%로 보고된다[4-6]. 인 조혈관 동정맥루에서 초음파를 통한 혈류 흐름이 500 ml/min 이하 일때, 투석 실패와 연관이 있었고(투석 실패의 상대위험도 40% 이 상), 반면 자가혈관 동정맥루에서는 혈류흐름이 투석 실패의 예측 인자가 되지 못했다[7]. 자기공명 혈관 촬영은 인조혈관, 자가혈관 동정맥루 모두에서 동정맥루 협착 양상과 혈류 속도 측정에 효과적 이지만 비용이나 시간적인 문제로 통상적인 감시수단으로 사용되 기에 무리가 있다[8,9].
2) 간접 혈류 측정(Indirect access flows)
동정맥루 기능부전을 예측하는 간접혈류를 측정하는 방법들 이 다양하게 소개되었다[10]. 대부분의 측정법은 투석 중 재순 환을 시켜 희석정도를 평가한다. 초음파 희석법(UD), 시간내 초 미세여과법(timed ultrafiltration methods), 이온 투석도(ionic dialysance), 온도 희석(thermal dilution), 전도도 차이(differential conductivity), 포도당 주입(glucose infusion)등의 방법으로 측정이 가능하다. 그 원리는 단위 시간당 특정 물질의 양(saline, glucose, hematocrit, sodium 등)이나 물리적 변화(temperature)가 얼마나 되 는지를 통하여 투석막의 혈류를 계산하는 것이다. 특별히 미리 정 의된 시간에 물질의 농도를 알고 있다면 특정 물질을 사용하여 계 산할 수 있다. 측정 시 정자세에서 바늘천자를 필요로 하고 이후에 추가 측정을 위해 혈류의 역전이 필요하다. 이것은 측정 시 정맥 및 동맥 투석관을 막고 방향을 바꾸어 측정하여 감염 위험이 높이는 단점이 있다. 기존 투석관을 분리하지 않고 혈류를 역전시킬 수 있 는 기구가 있지만 추가 비용이 발생하게 된다. KDOQI 지침에 따 르면 이 방법이 인조혈관 동정맥루 감시에서 초음파 또는 MRA보 다 선호된다[1].
실제로 재순환을 통해 투석 흐름을 평가하는 데 사용되는 가장
일반적인 방법 중 하나는 초음파 희석법이다. 이것은 정맥 바늘을 통해 투석기의 혈액 흐름을 전환 후 희석물질(식염수 등)을 주입하 여 동맥 및 정맥 관에서 초음파로 희석물질을 측정하여 혈류량을 평가한다. 연속적인 간접혈류측정은 동정맥루 기능이상의 예측을 위한 유용한 도구이다. 그러나 시간이 오래 걸리고 소프트웨어 비 용이 많이 들며 투석중인 환자의 적절한 측정을 위해 특별한 인력 이 필요하다는 단점이 있다[11].
3) 정적과 동적 압력 측정(Static and Dynamic pressure mea
sure ment)
인조혈관 동정맥루의 경우 혈류 측정과 정적 정맥압 측정 역시 협착을 감지하는 데 효과적이다. 그러나 동적 정맥압 측정은 예측 이 어려워 인조혈관 동정맥루 감시의 우선순위로 권장되지는 않는 다[10].
바늘의 크기나 배치에 따른 동적 정맥압 측정의 오차를 줄이기 위하여 혈액 투석 중 혈액 펌프를 150-200 mL/min로 감속 시킨 후 15 게이지 바늘로 투석기계 압력 변환기를 이용해 정맥 압력을 측정할 수 있으며, 3번 연속으로 정맥압이 125-150 mmHg 이상일 때 동정맥루 기능이상으로 판단하였다[12]. 동적 정맥압 측정은 과 거 인조혈관 동정맥루에서 연구되었다. 바늘 배치 및 튜빙(tubing) 에 의해 생성되는 상당한 오류가 있으나, 동일한 바늘 게이지 및 튜 빙을 사용한 연속적인 감시의 경우, 협착을 조기 감지할 수 있을 것 으로 여겨졌다. 또한, 쉽고 저렴하며 짧은 시간에 추가 장비없이 측 정이 가능하다는 장점이 있다. 그러나, 자가혈관 동정맥루 감시에 는 동적 정맥압 측정이 권장되지 않으며, 결론적으로 KDOQI 지침 에서도 인조혈관 동정맥루의 감시로 동적 정맥압 측정을 추천하지 않게 되었다[1].
반면에 정적 정맥압 측정은 KDOQI 지침에서 추천되는 인조혈 관 동정맥루 감시 방법이다. 정적 정맥압 측정은 동적 정맥압 측정 에 비해 추가적인 노력이 요구된다. Blood pump를 정지하고, 정맥 관을 클램핑(cross-cramping) 한 다음 정맥 또는 동맥 바늘로부터 정맥 점적 챔버(venous drip chamber) 에서 혈액 끝의 높이를 센티 미터로 측정한다. 이 압력은 혈압으로 보정하면 일반적으로 0.4 미 만이다. 동정맥루에서 정맥 분절 정적 압력이 0.5 이상이거나 인조 혈관 동정맥루에서 동맥 분절 정적 압력이 0.75 이상일 때는 추가 적인 평가가 필요하다. 비용과 전문적인 지식이 요구되지는 않지 만, 투석 중 측정을 위해 추가적인 시간이 요구되고 어느 정도 주관 적일 수 있다는 단점을 가진다. 자가혈관 동정맥루의 감시법으로 추천되지 않는다[1].
4. 동정맥루 모니터링과 감시의 연구
한 무작위 대조 시험에 대한 체계적인 문헌고찰(systemic review) 및 메타 분석(meta-analysis)에 따르면 자가혈관 동정맥루 의 혈류 측정은 혈전증의 상대적 위험 감소와 관련이 있었으나 동 정맥루 생존율의 유의한 개선은 없었다. 더욱이, 인조혈관 동정맥 루의 혈류 측정 또는 또는 초음파에 의한 감시는 혈전증 조차도 감
대한투석혈관학회지 : 제 2 권 제 1 호 2019
8
소 시키거나 그 생존율을 향상시킨다는 증거는 없었다[13].
반면에, 또 다른 메타 분석에 따르면, 협착의 진단과 치료를 위 한 무증상 동정맥루의 연속적인 감시가 혈전증의 위험을 감소시키 고 정상적인 임상 모니터링보다 동정맥루 생존을 연장시킬 수 있는 것으로 보였지만 통계적으로 유의하지는 않았다[14].
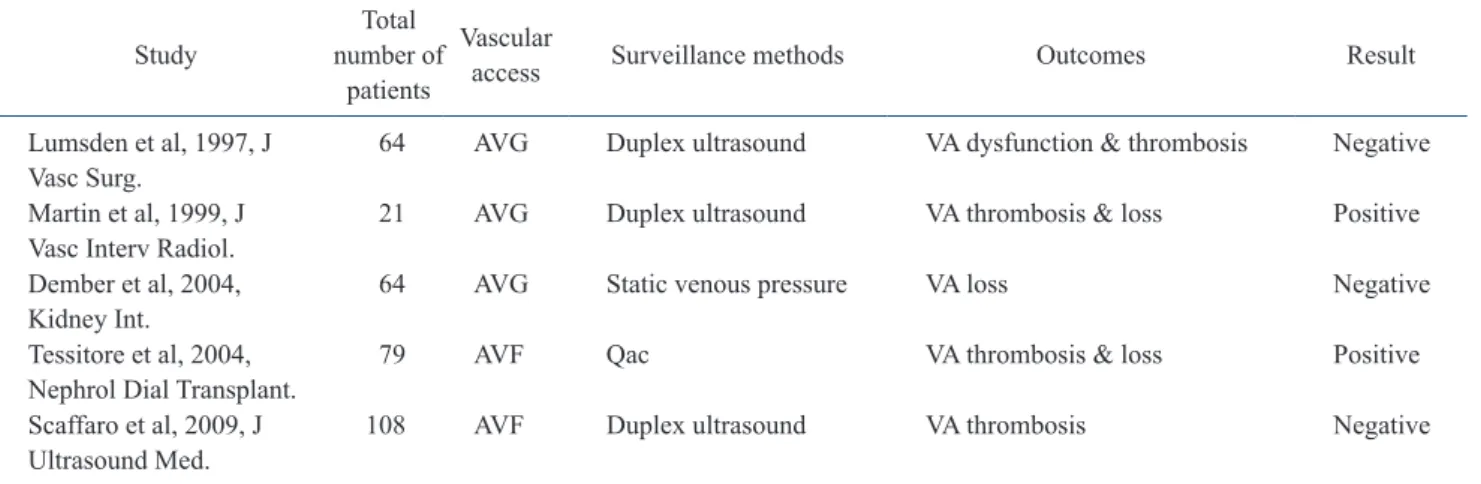
1990년도 후반기 이후로 모니터링과 감시에 대한 무작위 대조 연구(Table 1)와 감시에서 비정상 소견시 시술을 한 군과 관찰을 한 군 간의 무작위 대조연구(Table 2)가 이루어졌다. 이러한 연구들에 서, 자가혈관 동정맥루의 전향적인 연구들에서는 감시는 동정맥루 혈전을 감소시킬 수 있고 예방적인 동정맥루 시술을 통하여 동정맥 루의 장기 생존율을 증가시켰다. 반면에, 인조혈관 동정맥루에 대 한 몇몇 무작위 대조 연구는 감시가 인조혈관 동정맥루 혈전 예방 에도 도움을 주지 못하고 동정맥루 개존 결과에도 영향을 주지 못 하였다. 정적 정맥압 측정과 혈류 측정 모두가 모니터링보다 인조
혈관 동정맥루에서 그 유용성을 보이지 못하였다[15-19]. 지금까 지의 연구들의 한계는 연구에 포함된 대상자 수가 비교적 적고, 1 차 종점(primary end point)이 다양했다는 한계점이 있다. 결로적으 로 지금까지의 연구들에 따르면 감시가 동정맥루의 수명을 연장시 킨다는 확실한 근거는 명확하지 않아 다수의 대상자들을 포함하는 대규모 연구가 필요할 것으로 여겨진다.
결 론
모니터링에서 기본 신체검진과 투석 후 지혈시간 증가, 요소 환 원법 비욜(urea reduction ratio) 또는 Kt/V 수치 감소, 투석 중 압 력증가와 같은 증후 및 증상의 관찰은 단순하지만 핵심적인 검사이 다.
감시는 동정맥루의 기능을 유지하는 중요한 검사법으로 불필요
Table 1. Randomized controlled studies about surveillance versus monitoring
Study Total
number of patients
Vascular
access Surveillance
methods Outcomes Result
Sands et al, 1999, ASAIO J 103 AVF & AVG Qac, static venous pressure VA thrombosis Positive Moist et al, 2003, J Am
Soc Nephrol 112 AVG Qac, dynamic venous pressure VA thrombosis & loss Negative Ram et al, 2003, Am J
Kidney Dis 101 AVG Qac VA thrombosis & loss Negative
Roca-Tey et al, 2004,
Nefrologia 159 AVF & AVG Qac VA thrombosis Positive
Malik et al, 2005, Kidney Int. 192 AVG Duplex Ultrasound VA loss Positive Polkinghorne et al, 2006,
Nephrol Dial Transplant 126 AVF Duplex Ultrasound >50% stenosis Negative Robbin et al, 2006, Kidney
Int. 126 AVG Duplex Ultrasound VA thrombosis & loss Negative AVF, arteriovenous fistula; AVG, arteriovenous graft; VA, vascular access; Qac, access flow volume.
Table 2. Randomized Trials with abnormal surveillance results comparing intervention versus observation
Study Total
number of patients
Vascular
access Surveillance methods Outcomes Result Lumsden et al, 1997, J
Vasc Surg. 64 AVG Duplex ultrasound VA dysfunction & thrombosis Negative Martin et al, 1999, J
Vasc Interv Radiol. 21 AVG Duplex ultrasound VA thrombosis & loss Positive Dember et al, 2004,
Kidney Int. 64 AVG Static venous pressure VA loss Negative
Tessitore et al, 2004,
Nephrol Dial Transplant. 79 AVF Qac VA thrombosis & loss Positive Scaffaro et al, 2009, J
Ultrasound Med. 108 AVF Duplex ultrasound VA thrombosis Negative AVG, arteriovenous graft; VA, vascular access; AVF, arteriovenous fistula; Qac, access flow volume.
이재훈 : 동정맥루의 모니터링(Monitoring)과 감시(Surveillance) 9
한 도관을 통한 투석을 피하고, 입원시간을 감소시켜 투석환자의 삶의 질 향상을 기대할 수 있게 한다. 적극적인 임상 모니터링과 추 가적인 감시에 대한 추후 연구가 모니터링과 감시에 대한 정형화된 프로그램을 통하여 동정맥루의 개존율을 향상 시킬 뿐만 아니라 불 필요한 시술 또한 막을 수 있을 것이다.
REFERENCES
1. Gilmore J. KDOQI clinical practice guidelines and clinical practice recommendations--2006 updates. Nephrol Nurs J.
2006; 33(5): 487-8.
2. Kumbar L, Karim J, Besarab A. Surveillance and monitoring of dialysis access. Int J Nephrol. 2012; 2012: 649-735.
3. Robbin ML, Oser RF, Lee JY, et al. Randomized comparison of ultrasound surveillance and clinical monitoring on arteriovenous graft outcomes. Kidney Int. 2006; 69(4): 730- 5.
4. Finlay DE, Longley DG, Foshager MC, et al. Duplex and color Doppler sonography of hemodialysis arteriovenous fistulas and grafts. Radiographics. 1993; 13(5): 983-9.
5. Grogan J, Castilla M, Lozanski L, et al. Frequency of critical stenosis in primary arteriovenous fistulae before hemodialysis access: should duplex ultrasound surveillance be the standard of care? J Vasc Surg. 2005; 41(6): 1000-6.
6. Doelman C, Duijm LE, Liem YS, et al. Stenosis detection in failing hemodialysis access fistulas and grafts: comparison of color Doppler ultrasonography, contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance angiography, and digital subtraction angiography.
J Vasc Surg. 2005; 42(4): 739-46.
7. Bay WH, Henry ML, Lazarus JM, et al. Predicting hemodialysis access failure with color flow Doppler ultrasound. Am J Nephrol. 1998; 18(4): 296-304.
8. Smits JH, Bos C, Elgersma OE, et al. Hemodialysis access imaging: comparison of flow-interrupted contrast-enhanced MR angiography and digital subtraction angiography.
Radiology. 2002; 225(3): 829-34.
9. Laissy JP, Menegazzo D, Debray MP, et al. Failing
arteriovenous hemodialysis fistulas: assessment with magnetic resonance angiography. Invest Radiol. 1999; 34(3):
218-24.
10. Sands JJ, Jabyac PA, Miranda CL, et al. Intervention based on monthly monitoring decreases hemodialysis access thrombosis. ASAIO J. 1999; 45(3): 147-50.
11. Garland JS, Moist LM, Lindsay RM. Are hemodialysis access flow measurements by ultrasound dilution the standard of care for access surveillance? Adv Ren Replace Ther. 2002; 9(2): 91-8.
12. Schwab SJ, Raymond JR, Saeed M, et al. Prevention of hemodialysis fistula thrombosis. Early detection of venous stenoses. Kidney Int. 1989; 36(4): 707-11.
13. Tonelli M, James M, Wiebe N, et al. Ultrasound monitoring to detect access stenosis in hemodialysis patients: a systematic review. Am J Kidney Dis. 2008; 51(4): 630-40.
14. Casey ET, Murad MH, Rizvi AZ, et al. Surveillance of arteriovenous hemodialysis access: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Vasc Surg. 2008; 48(5): 48-54.
15. Tessitore N, Lipari G, Poli A, et al. Can blood flow surveillance and pre-emptive repair of subclinical stenosis prolong the useful life of arteriovenous fistulae? A randomized controlled study. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2004;
19(9): 2325-33.
16. Moist LM, Churchill DN, House AA, et al. Regular monitoring of access flow compared with monitoring of venous pressure fails to improve graft survival. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2003; 14(10): 2645-53.
17. Tessitore N, Bedogna V, Poli A, et al. Adding access blood flow surveillance to clinical monitoring reduces thrombosis rates and costs, and improves fistula patency in the short term: a controlled cohort study. Nephrol Dial Transplant.
2008; 23(11): 3578-84.
18. Dember LM, Holmberg EF, Kaufman JS. Randomized controlled trial of prophylactic repair of hemodialysis arteriovenous graft stenosis. Kidney Int. 2004; 66(1): 390-8.
19. Ram SJ, Work J, Caldito GC, et al. A randomized controlled trial of blood flow and stenosis surveillance of hemodialysis grafts. Kidney Int. 2003; 64(1): 272-80.