Cement Mantle Thickness at the Bone Cement Interface in Total Knee Arthroplasty: Comparison of PS150 RP and LPSFlex Knee Implants
전체 글
수치
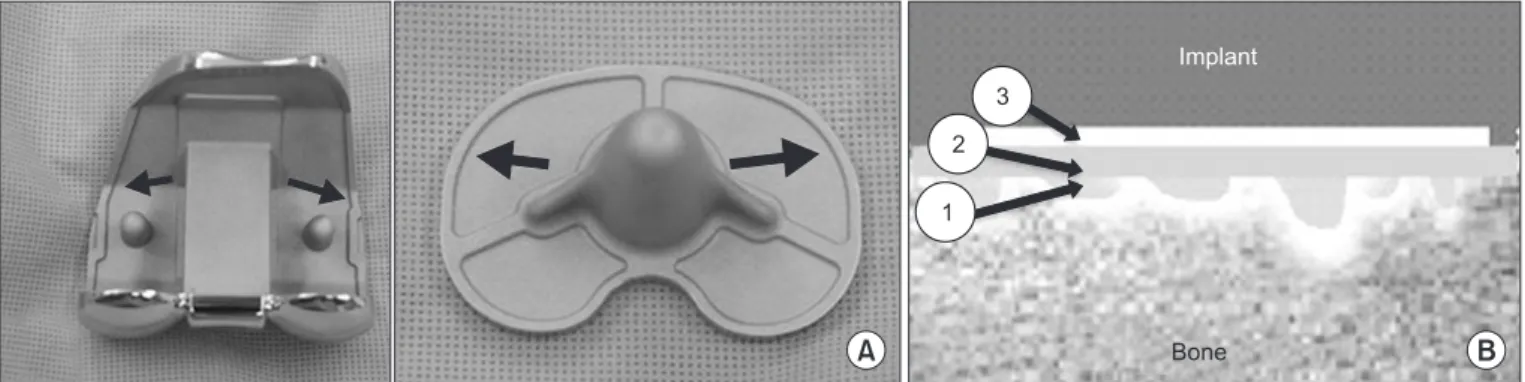

관련 문서
A and E, In control group, a small amount of new bone was observed at the margin of bone defect (40×); B and F, In experimental group 1, a large amount of new bone was formed
3 Mean percentages of bone implant contact ratio in the control group and experimental groups at 6 and 12 weeks after placement of the
Methods to overcome insufficient bone due to poor bone quality, the pneumatization of a maxillary sinus and other anatomical limitations of implant placement
Histopathologic findings of control group at 4 weeks show little bone- implant contact (BIC) around the implant (asterisks) and new-bone formation in the defect
The purpose of this study is to compare the degrees of conversion of light curing resin cement specimens cured by the light transmitted different thickness of zirconia
success rates of dental implants placed at the time of or after alveolar ridge augmentation with an autogenous mandibular bone graft and titanium mesh: a 3-to
Biochemical markers of bone turnover can be classified according to the process that underlie in markers of bone formation, products of the osteoblast
Higher power view of the box area of the left figure showed poor new-bone formation around the implant (asterisk) and low BIC. Villanueva