VOLUME 14, NUMBER 4, December 2009
Ulna Nerve Compression Caused by a Tortuous Ulnar Artery
Young-Sang Lee, MD, Woo-Suk Song, MD, Joon-Cheol Choi, MD, Woo-Sung Kim, MD, Hyoun-Min Noh, MD, Wan-Seok Kim, MD, Hak-Soo, Kim, MD
Department of Orthopedic Surgery, BunDang Jaesang General Hospital, Seongnam, Korea
Purpose: This case report presents ulnar nerve com- pression which associated with variant distribution of ulnar artery at the proximal site of the wrist.
Materials and methods: Based on the patient's symp- toms, we could assume a neuropathy resulting from the compression of the ulnar nerve. The magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) was used to evaluate the anatomical abnormality of the ulnar artery at the site of compres- sion, and the elecromyogram (EMG) and Nerve conduc- tion velocity (NCV) were also performed to confirm the overall abnormality of the ulnar nerve.
Results: The tortuous ulnar artery of the lesion which was in the same course as that of ulnar nerve surrounded by sheath seemed to be compressed. Such finding was resolved 5 minutes after taking off tourniquet during adhesiolysis. Along with the improvement in the symp- toms of paresthesia and the numbness of the patient a day after the surgery, the atrophy of the muscle and the weakness of the affected lesion were also slightly improved 6 months after the adhesiolysis. The decrease
in abnormal spontaneous activity of the ulnar nerve was observed in both EMG and NCV, performed after the 6 month of the surgery.
conclusion: Among the patients manifesting signifi- cant symptoms of neuropathy arising from ulnar nerve compression, the tortuous ulnar artery as the source of entrapment of ulnar nerve was observed. Six months after the adhesiolysis of the sheath, the overall improve- ment of clinical symptoms was remarkable.
(J Korean Soc Hand Surg 2009;14:250-4) Key Words: Thumb reconstruction, Second toe transfer
서 론
척골 신경 마비 증상은 흔히 접할 수 있는 질환으로 상완신경총에서 수부로 주행하면서 손상 받을 수 있는 부위는 다양하며, 원인 또한 다양한 것으로 보고되고 있다. 그 중 해부학적 구조에 따른 원인으로는 주로 주관절 상방의 스트러터스 아케이드(Struther arcade)에 의한 것과 주관절의 척골 신경 포착 증후 군, 손목 관절 부근의 기용관(Guyon’s Tunnel) 에 서 기인하는 것으로 알려져 있다.
본 증례는 최근 척골 신경 압박 증상을 보이던 68세 여자환자에 있어서 전완부에서의 비정상적인 척골동맥 의 비틀림(torsion)에 따라 같은 주행경로에 있던 척 골 신경의 압박 증상을 경험하였기에 1예를 문헌 고찰 과 함께 보고하는 바이다.
증례 보고
내원 6개월 전부터 특별한 외상력 및 기저 질환 없 이 발생한 68세 여자 환자로 우측 주관절 및 전완부 척측으로의 경한 지각이상 및 통증을 호소하였다. 특 별하게 직업을 가지고 있지 않은 전업 주부로 평소 별
척
척골 골 동 동맥 맥의 의 주 주행 행 이 이상 상에 에 의 의한 한 척 척골 골신 신경 경 압 압박 박 -
- 1 1예 예 보 보고 고 - -
대진의료재단 분당 제생병원 정형외과
이영상∙송우석∙최준철∙김우성∙노현민∙김완석∙김학수
Address reprint requests to: WWoooo--SSuukk SSoonngg,, MMDD Bundang Jaesang Hospital
255-2, SeoHyun-dong Bundang-gu Seongnam, Kyungki-do TEL: 031-779-0369, FAX: 031-779-0176
E-mail: swoosuk@yahoo.co.kr
다른 운동없이 가사를 하는 주부였고, 자극을 반복적 으로 받은 적은 없으며, 이전의 골절 기왕력 또한 가 지고 있지 않았다. 기저 질환으로 만성 고혈압이 있던 환자이며, 20여년째 혈압강하제를 복용하고 있었다.
이학적 검사상 제4, 5수지의 내측 전면 및 전완부 척측의 경한 지각이상과 지각 감퇴소견 및 저림 증상 이 있었으며, 수장 소지구의 경한 위축 및 수지 굴곡 근력과 수지 외전근력의 약화 소견이 있었다. 수부의 허혈성 질환에 대한 감별을 위해 시행한 혈액순환에 대한 이학적 검사상 모세혈관 충전 검사(capillary
filling test)및 Allen test상 모두 정상이었으며, 척 골 신경에 대한 티넬 징후(Tinnel sign)는 음성이었 다. 손목의 굴곡 및 요측 편위(radial deviation)시 증상의 특별한 변화는 없었으나, 신전시 저린감을 더 욱 호소하였다.
술 전 시행한 신경 근전도 검사상 척골 신경의 운동 신경 전도에서 잠복기는 2.3 msec로 정상이었으며, 운동신경 전도검사상 증폭(ampulitude)는 6.2 uV로 저하된 소견이었다. 신경전도 속도는 주관절 상부에서 하부까지는 60 M/sec, 주관절 하부에서 수부까지는
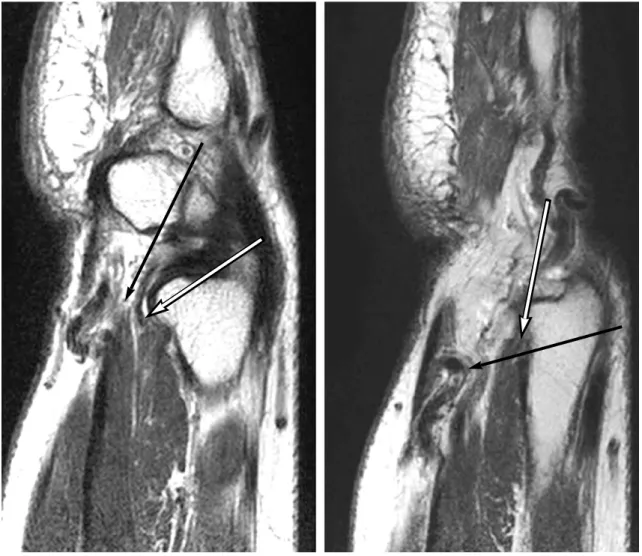
Fig. 1.Torsion of ulnar artery is noted (Black arrow) The ulnar nerve is compressed (White arrow) by the ulnar around the ulnar nerve in abnormal course.
Fig. 2. Course of the ulnar artery is noted on the level proximal to the wrist (Black arrow). Stenotic lesion is found on the ulnar artery in its course (Gray arrow). Post-stenotic dilatation of the ulnar artery following the stenotic lesion is shown (White arrow).
64 M/sec로 정상이었다.
감각신경 전도검사상 잠복기는 2.0 msec으로 정상 이었으나, 진폭(ampulitude)는 17 uV로 정상보다 낮은 소견이 나왔다. 침 근전도 검사(Needle EMG) 상 우측 소지외전근, 제 1배측 골간근에서 안정기에 세동 전위(fibrillation)와 양성 예측파(positive sharp wave)가 나타나고 동원 현상(recruitment) 이 감소되어 있는 것으로 보아 불완전 신경 차단 또는 압박의 가능성을 확인할 수 있었다.
확실한 해부학적 이상을 판별하기 위하여 자기 공명 영상 장치를 통한 검사를 시행하였으며, 손목 관절의 근위부에서 척골동맥의 비틀림(torsion)에 따른 척골 신경의 경한 압박 소견을 발견할 수 있었다(Fig. 1).
또한 척골 동맥의 비틀림 정도 및 압박되는 양상을 포 함한 정확한 병변의 소견을 파악하기 위해 CT 혈관 조영술을 시행하였으며, 병변부와 근위부와의 비교를 통한 협착 후 확장(poststenotic dilatation)소견을 통 한 척골 동맥의 이상주행을 관찰할 수 있었다(Fig. 2).
수술은 전신마취하 지혈대로 상완 근위부를 압박한 상태에서 우측 전완부의 원위부 전면, 척골측으로 종 축으로 피부 절개를 가한 후 해당 부위의 척골 신경을
추적하였다. 추적 소견상, 천골 신경이 전완부를 주행 하여 원위부로 향하다가 손목관절의 3~4 cm 근위 부 간에서 척골동맥의 비틀림(torsion)에 의해 척골 신경 을 압박하는 소견을 관찰할 수 있었다(Fig. 3). 척골 동맥과 신경을 감싸고 있는 막에 의해 척골 동맥의 비 틀림(torsion)에 따른 신경의 주행 이상 소견을 발견 하였으며, 혈관 및 신경 막을 박리(dissection)함으로 써, 신경의 압박을 제거할 수 있었다(Fig. 4).
막으로 둘러싼 척골 동맥과 척골 신경의 비정상적인 유착(adhesion)을 완전히 분리해내고 막을 가로지르 며 신경 압박의 가능성이 있는 가는 정맥에 대해서는 결찰하였으며, 주행에 방해가 되지 않는 정맥은 그대 로 놓아 두었다. 지혈대의 압력 제거 후 척골 동맥의 주행을 관찰하였으며, 지혈대의 압력 제거 5분 후 척 골동맥에 따른 척골신경의 압박이 더 이상 없는 것을 직접 확인할 수 있었다(Fig. 5).
수술 후 우측 전완 원위부의 감각 이상 및 지각감 퇴, 저린감등의 증상이 호전되었으며, 퇴원할 당시 수 부말단의 경한 지각 이상 및 감각이상, 저린감이 남아 있었다. 수술 6개월 후에 시행한 신경 근전도 검사상 손목부위에서의 비정상 자발 전위는(+++)에서 (+)로 감소하였고, 운동신경 전도검사상 증폭(ampulitude) 는 6.2 uV에서 10.2 uV로 호전되었다. 술 후 1년 째 추시 관찰 결과 손목 이하 부위의 제4, 5수지의 저 린감은 술 전보다 유의하게 증상이 호전되었으며, 지 각감퇴 및 수장의 소지구의 경한 위축 및 수지 굴곡근 력과 수지 외전근력의 약화 소견 또한 경미하게 호전 되었다.
고 찰
현재까지 보고된 전완의 원위부 및 손목 관절 부근 의 신경 압박원인들을 살펴보면, 반복적인 외상, 결절 종, 유두종, 유두골 골절, 삼각골 골절, 제4, 5중수지 저부 골절, 기용관(Guyon’s tunnel)의 해부학적 기 Fig. 3. Intraoperative photograph showing the ulnar nerve
and tortuous ulnar artery (black arrow) at the level of the wrist. Flexor carpi ulnaris tendon is located at medial side of ulnar artery and nerve (White arrow).
Fig. 4. Dissection of sheath between artery (Black arrow)and nerve (White arrow).
Fig. 5. Decreasing of tortuous artery (Black arrow) at 5min after dissecting the sheath, results in dimin- ishing of compressed ulnar nerve (White arrow).
형, 척측 수근 굴근의 비대, 척골 동맥염, 혈전 맥관 염, 반흔 조직 구축, 요골 골절, 신경 초종(Neurile- mmoma), 점액낭염, 수근 골의 골 관절염, 기용관 (Guyon’s tunnel)을 지나는 비정상적인 근육들, 두 상골 탈골 등이 있다2-4,7.
척골 신경의 압박 증상은 신경의 압박 위치에 따라 결정되어지는데,(Shea and McClain classifica- tion)1,2 첫째(type I)로 척골 신경이 전완의 원위부에 서, 후면 감각신경이 분리되는 곳로부터 기용관 (Guyon’s tunnel)까지에서의 부위에서 신경 압박이 있을 경우에는 수부에서 해당부위의 감각 신경과 운동 신경의 마비증상 소견이 같이 있게 되며(30%), 둘째 (type II)로 심부 분지만을 압박하는 경우에는 해당부 위의 운동신경 마비증세만 있게 되며(52%), 셋째 (type III)로 천부분지 만을 압박하는 경우에는 감각 신경 마비증세만 있는 것으로 분류되어진다(18%).
본 증례는 위치에 따른 분류 및 소지구의 약화와 척 골 신경 지배영역의 감각이상을 포함한 임상증세로 보 아 제 1형(type I)에 부합할 것이라고 예측하였으며, MRI소견 및 CT 혈관조영술을 통하여 확인할 수 있었 다. 수술 소견상에서는 예측한 바와 같이 전완의 원위 부에서 병변을 확인하였으며, 그에 따라 제1형에 해당 하였으며 동맥의 협착 후 확장은 CT 혈관조영검사상 에서 보이던 정도로 뚜렷하지는 않았지만 탄력성 저하 로 인해 이완되어 있는 것을 확인할 수 있었다10.
신경 근전도 검사는 척골 신경 병변의 다양한 해부 학적 위치와 원인때문에 진단의 확진 및 압박된 위치 를 찾는데 필수적인 검사임에 틀림없으며6,8 ,본 증례에 서는 술 전과 술 후 6개월 째 신경근전도 검사를 비교 하여 비정상 자발 전위의 감소를 보이며 임상증세 또 한 호전되어 치료 효과 판정에 적합하였다.
손목부근의 척골 신경 압박에 대해서는 이전의 무수 한 증례보고들이 있었지만, 혈관의 이상주행으로 인한 보고는 드물다. 수근 관절 부위에서 척골 신경마비는 주로 기용관이란 협소한 관주위의 병변에서, 주로 종 괴의 압박이나 수상 후 비정상적인 유착에 의해서 신 경마비가 오게된다.(ulnar tunnel syndrome). 또 한 Wu 등은 보고된 55례의 수근 관절 부위에서의 척 골 신경 마비를 종합하여 보고하였다. 원인은 41%에 서 결절종, 11%에서 비정상적인 근육이었고, 두상골 에의한 압박과 완관절 골절이 각각 9%였다5. 그러나 앞서 제시된 원인들 이외에 혈관의 이상 주행으로 인 해 유발된 신경마비에 대한 보고는 드물다. Kim 등은 기용관내에서 발생한 동정맥 기형으로 인한 신경병증 에 대하여 미세현미경을 이용한 제거술을 시행한 증례 를 보고한 바 있다9. 본 증례는 만성 고혈압이 있는 환 자에서 말초 혈관의 수축이 진행되던 중, 노화로 인한
혈관의 탄력성 저하 및 이완과 함께 비틀림이 발생하 여 내원 6개월전부터 증상이 시작된 척골 신경 병증에 대한 예로 저자들은 본 례의 임상소견을 토대로 척골 신경 병증 진단시 환자의 기저 질환 및 연령에 따른 혈관의 변형과 그 외의 혈관 기형 및 비정상적인 유착 을 고려해야 할 것으로 판단한다.
요 약
본 교실에서는 척골신경의 압박으로 인해 발생한 증 상(신경 주행 경로 따라 나타나는 저린감, 근위축, 감 각이상 등)을 호소하던 68세 여자 환자에서 수술 소견 상 손목의 근위부에서 비정상적으로 주행하는 척골 동 맥으로 인한 척골 신경의 압박을 관찰할 수 있었으며, 해당 부위의 척골동맥과 신경을 감싸고 있던 sheath 에 의한 유착(adhesion)을 분리해냄으로써 척골 신경 을 감압하여, 압박증상의 호전을 얻었기에 보고하는 바이다.
참고문헌
01) Shea JD, McClain EJ. Ulnar-nerve compression syn- dromes at and below the wrist. J Bone Joint Surg Am.
1969; 51:1095-103.
02) Ozdemir O, Calisaneller T, Altinors N. Compression of the ulnar nerve in Guyon’s canal by an arteriovenous mal- formation. J Hand Surg Br. 2007;32:600-1.
03) Jose RM, Bragg T, Srivastava S. Ulnar nerve compression in Guyon’s canal in the presence of a tortuous ulnar artery.
J Hand Surg Br. 2006; 31:200-2.
04) Yoshii S, Ikeda K, Murakami H. Ulnar nerve compression secondary to ulnar artery true aneurysm at Guyon’s canal.
J Neurosurg Sci. 1999;43:295-7.
05) Wu JS, Morris JD, Hogan GR. Ulnar Neuropathy at the wrist : Case report and Review of Literature. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1985;66:785-8.
06) Aguiar PH, Bor-Seng-Shu E, Gomes-Pinto F, Almeida- Leme RJ, Freitas AB, Martins RS, et al. Surgical manage- ment of Guyon’s canal syndrome, an ulnar nerve entrap- ment at the wrist : report of two cases. Arq Neuropsiquiatr.
2001;59:106-11.
07) Stuart H. Kuschner, Richard H. Gelberman, Candace Jennings. Ulnar nerve compression at the wrist . J Hand Surg, Am. 1988;13:577-80.
08) Papathanasiou ES, Loizides A, Panayiotou P, Papacostas SS, Kleopa KA. Ulnar neuropathy at Guyon’s canal : elec- trophysiological and surgical findings. Electromyogr Clin
Neurophysiol. 2005;45:87-92.
09) Kim SS, Kim JH, Kang HI, Lee SJ. Ulnar nerve compres- sion at Guyon’s canal by an Arteriovenous Malformation.
J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2009;45:57-9.
10) Michael F. O’Rourke. Arterial aging: pathophysiological principles. Vasc Med. 2007;12:329-42