Tuberculosis is one of the well-described infectious diseases, which has a worldwide occurrence and is asso- ciated with various clinical manifestations (1). Hepatic tuberculosis is one of the uncommon forms of extrapul- monary tuberculosis (1-4). In tuberculosis, involve- ment of liver is usually seen in association with pul- monary or miliary tuberculosis (1, 2, 5). Occurrence of isolated hepatic tuberculosis without extrahepatic mani- festations is very rare (1-5). In both, isolated hepatic and systemic tuberculosis, hepatic involvement tends to be multiple micro- or macronodular, whereas the single nodule or mass form is rare (1-3, 6). Hence, hepatic tu- berculosis can mimic primary or metastatic liver malig- nancies (1). In the present study, we have reported some unusual findings on isolated hepatic tuberculosis, which was revealed to be infiltrative type of hepatic tuberculo- sis from CT scans and ultrasonograms.
Case Report
A 49-year-old female patient was admitted to our hos- pital with abdominal pain and fever from past 20 days.
During the past four years, the patient had undergone repeated intrahepatic biliary stone removals by chole- dochoscopy. Physical examination revealed neither he- patomegaly nor splenomegaly. Laboratory tests showed an elevated level of C-reactive protein (CRP), however her other tests were normal, including alkaline phos- phatase, erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), α-feto- protein, and CA 19-9. Plain chest radiography was unre- markable. Abdominal CT revealed a very hypoattenuat- ing lesion in the right lobe of the liver (Fig. 1A). There was less enhancement of lesion when compared with rest of the liver parenchyma. There was neither lym- phadenopathy nor calcification in the abdomen.
Abdominal ultrasonography revealed a very ill-defined, heterogenous, subtle low echogenicity in the right lobe of the liver. CT and ultrasonographic findings revealed the presence of cholangiohepatitis associated with intra- hepatic biliary stones. The patient’s symptoms were re- lieved after administration of antibiotics, and after dis- charging she had no specific symptoms. Two months
J Korean Radiol Soc 2005;53:269-272
─ 269 ─
Hepatic Tuberculosis: Unusual CT and Sonographic Findings1
Jihyeon Cha, M.D., Jae Ho Byun, M.D., Seong Eon Yoon, M.D., Ye Ri Lee, M.D., Hyung Jin Won, M.D., Ah Young Kim, M.D., Yong Moon Sin, M.D., Pyo Nyun Kim, M.D.,
Hyun Kwon Ha, M.D., Moon-Gyu Lee, M.D.
A case of infiltrative type of hepatic tuberculosis is presented. Ultrasonography re- vealed a very ill-margined, heterogenously low echoic lesion in the right hepatic lobe.
CT scans demonstrated a very ill-defined, geographic, hypodense lesion with minimal contrast enhancement mimicking cholangiohepatitis or infiltrative tumor in the right hepatic lobe.
Index words :Tuberculosis Liver
Computed tomography (CT) Ultrasound (US)
1Department of Radiology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine
Received June 15, 2005 ; Accepted July 21, 2005
Address reprint requests to : Jae Ho Byun, M.D., Department of Radiology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, 388-1 Poongnap-dong, Songpa-gu, Seoul 138-736, Korea.
Tel. 82-2-3010-4400 Fax. 82-2-476-4719 E-mail: jhbyun@amc.seoul.kr
later, follow-up CT revealed the expansion of a very ill- defined, geographic, hypodense lesion with subtle con- trast enhancement in the right lobe of the liver and a new, ill-defined, low-attenuating lesion in the left lobe of the liver (Figs. 1B and C). There was neither lym- phadenopathy nor calcification and no abnormal find- ings were observed on the CT scans. The patient was readmitted and underwent sonographically guided per- cutaneous liver biopsy of a very ill-margined, heteroge-
neously low echoic lesion in the right lobe of the liver (Fig. 1D). Histologic examination showed chronic granu- lomatous inflammation with caseous necrosis, which was consistent with tuberculosis (Fig. 1E). Ziehl-Neelsen stain of the specimen for Mycobacterium tuberculosis was negative. Culture for Mycobacterium tuberculosis by employing the specimen was not performed. Anti-tu- berculous treatment with isoniazid, rifampin, ethambu- tol, and pyrazinamide was started, and the patient was
Jihyeon Cha, et al: Hepatic Tuberculosis
─ 270 ─
C D
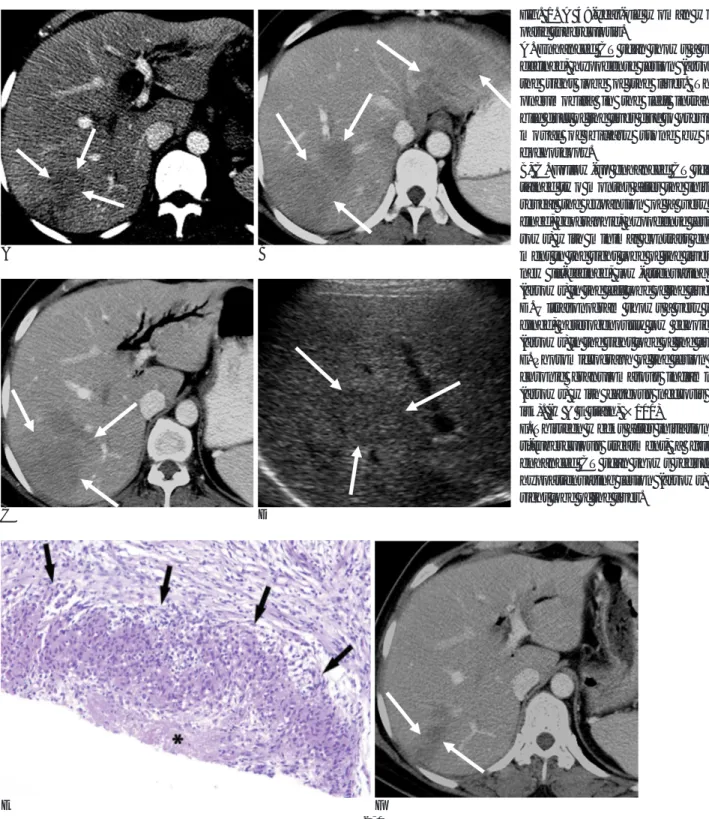
Fig. 1. A 49-year-old woman with he- patic tuberculosis.
A. Enhanced CT scan shows a very ill- defined, hypodense lesion (arrows) in the right lobe of the liver. There is pneumobilia in the left intrahepatic bile duct of the liver due to previous re- moval of biliary stone by chole- dochoscopy.
B, C. Follow-up enhanced CT scans ob- tained two months after the initial CT, reveal the expansion of a very ill-de- fined, geographic, hypodense lesion (ar- rows) with minimal contrast enhance- ment in the right lobe of the liver and a new ill-defined, low-attenuating lesion (arrows) in the left lobe of the liver.
D. Ultrasonogram shows a very ill-mar- gined, heterogenously low echoic lesion (arrows) in the right lobe of the liver.
E. Photomicrograph of the lesion shows chronic granulomatous inflammation (arrows) with caseous necrosis (aster- isk). (H & E stain, ×100)
F. Thirteen weeks after initiation of an- ti-tuberculous treatment, a follow-up enhanced CT scan shows reduction of hypoattenuating lesion (arrows) in the right lobe of the liver.
A B
E F
discharged from the hospital six days after initiation of the anti-tuberculous medication. Thirteen weeks after initiation of the anti-tuberculous treatment, follow-up abdominal CT revealed reduction of the hypoattenuat- ing lesions in both the lobes of liver (Fig. 1F). We thought that the hypoattenuating lesion in the left lobe of the liver was also hepatic tuberculosis.
Discussion
Tuberculosis can affect virtually any organ system in the body and can be devastating if left untreated. In re- cent years, the prevalence of tuberculosis in both im- munocompetent and immunocompromised individuals has increased, and this disease has become a subject of universal concern. Isolated hepatic tuberculosis without extrahepatic involvement and the macronodular or pseudotumor forms are rare (1-3). Kok and Yapp (1) re- ported that only 5 (0.3%) of 1678 new cases of tubercu- losis represented isolated hepatic tuberculosis without extrahepatic involvement of tuberculosis. Hepatic tuber- culosis can be classified as follows (3): a) primary acute pulmonary tuberculosis with liver involvement; b) mil- iary tuberculosis; c) primary tuberculosis; d) tuberculo- ma (abscess); e) chronic pulmonary tuberculosis with liver involvement; and f) tuberculous cholangitis.
Hepatic tuberculosis can be diagnosed on CT scans as micronodular (miliary) or macronodular (7). The micron- odular type manifests on CT scans as multiple, tiny, low- attenuation foci, each a few millimeters in diameter and it spreads throughout the liver. The macronodular type is rare and manifests as diffuse liver enlargement with multiple, hypodense lesions measuring from 1- to 3-cm in diameter or as a single tumor-like mass (1, 3, 6, 7).
Contrast enhancement occurs in peripheral granuloma- tous tissue, and the central low density of caseation necrosis shows less enhancement or homogenous mini- mal enhancement (5). As the time progresses, calcifica- tion of the lesion occurs and occasionally may become extensive (1). The ultrasonograms reveals the presence of the miliary form is that of a homogenous enlarged liver or a bright echo pattern, which is indistinguishable from that observed in liver cirrhosis or other cases of in- creased hepatic echogenicity (1, 8). The macronodular form is seen as multiple round hypoechoic nodules (1, 8).
In our case, CT revealed a very ill-defined, geographic, low-attenuation lesion with minimal contrast enhance- ment. There were some penetrating vessels through the hypoattenuating lesion. These CT findings were neither
micronodular nor macronodular. Ultrasonography also revealed a very heterogeneously hypoechoic lesion with ill margin. The cause of cholangitis was unclear because either tuberculosis or biliary stone could be the cause of cholangitis.
When hepatic tuberculosis is present in the macron- odular form, it is often confused with metastasis, lym- phoma, sarcoidosis, and liver abscess (1, 2, 6, 8). In our case, because of the patient’s underlying biliary stone disease, her hepatic lesion was initially mistaken for nonspecific cholangiohepatitis associated with biliary stones. It could also have been considered to be another infiltrative disease such as lymphoma, amyloidosis or fatty deposition.
Because the radiologic and clinical findings of hepatic tuberculosis have a low specificity, microbiological or histopathologic examination of such specimens is need- ed in order to make a diagnosis. Histologically, a tuber- culous lesion is composed of central caseating necrosis with surrounding epitheloid and giant cells and border- ing lymphohistiocytic cells (3, 8). The more unequivocal confirmation is the discovery of tuberculous bacilli after the use of special stains and/or on subsequent cultures.
Because the frequency of positive acid-fast smears is low, ranging from 0to 45%, the caseating necrosis can be considered to be very suggestive and sufficient for the diagnosis (8). The proper clinical setting and follow- up of liver recovery, under specific anti-tuberculosis medication, leads to final diagnosis (8).
This rare case shows the infiltrative type of hepatic tu- berculosis without extrahepatic involvement of tubercu- losis. In patients who are presented with protracted ill- ness and have an unusual lesion in the liver on cross- sectional images, biopsy must be performed for correct diagnosis and suitable treatment must be given.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Bonnie Hami, MA, Department of Radiology, University Hospitals Health System, Cleveland, Ohio, for her editorial assistance in prepar- ing the manuscript.
References
1. Kok KYY, Yapp SKS. Isolated hepatic tuberculosis: report of five cases and review of the literature. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 1999;6:195-198
2. Kawamori Y, Matsui O, Kitagawa K, Kadoya M, Takashima T, Yamahana T. Macronodular tuberculoma of the liver: CT and MR findings. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1992;158:311-313
J Korean Radiol Soc 2005;53:269-272
─ 271 ─
3. Levine C. Primary macronodular hepatic tuberculosis: US and CT appearances. Gastrointest Radiol 1990;15:307-309
4. Achem SR, Kolts BE, Grisnik J, MacMath T, Monteiro CB, Goldstein J. Pseudotumoral hepatic tuberculosis. J Clin Gastroenterol 1992;14:72-77
5. Hayashi M, Yamawaki I, Okajima K, Tomimatsu M, Ohkawa S.
Tuberculous liver abscess not associated with lung involvement.
Intern Med 2004;43:521-523
6. Tritou I, Prassopoulos P, Daskalogiannaki M, Charoulakis N,
Papakonstantinou O, Gourtsoyiannis N. Miliary hepatic tubercu- losis not associated with splenic or lung involvement. Acta Radiologica 2000;41:479-481
7. Harisinghani MG, McLoud TC, Shepard JO, Ko JP, Shroff MM, Mueller PR. Tuberculosis from head to toe. RadioGraphics 2000;
20:449-470
8. Blangy S, Cornud F, Sibert A, Vissuzaine C, Saraux JL, Benacerraf R. Hepatitis tuberculosis presenting as tumoral disease on ultra- sonography. Gastrointest Radiol 1988;13:52-54
Jihyeon Cha, et al: Hepatic Tuberculosis
─ 272 ─
대한영상의학회지 2005;53:269-272
비특이적 간 결핵1
1울산대학교 의과대학 서울아산병원 진단방사선과
차지현・변재호・윤성언・이예리・원형진・감아영・신용문・김표년・하현권・이문규
본 증례는 복부 초음파상 간 우엽에 경계가 불분명하고 불균질한 에코로 보이고 컴퓨터 전산화 촬영상 경계가 불분 명한 저음영의 조영증강이 미미한 소견을 보여 간 종괴로 오인했던 침윤적 간 결핵에 대한 예를 보고하고자 한다.