Recurrent Pneumomediastinum and Subcutaneous Emphysema Complicating Chronic Graft versus Host Disease after Allogeneic Bone Marrow Transplantation
전체 글
수치
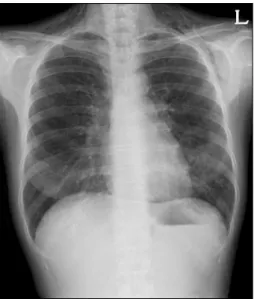
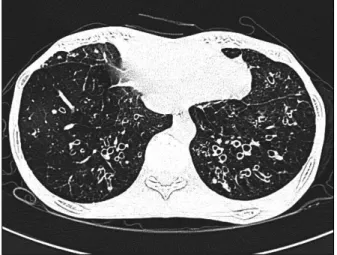
관련 문서
Clinical and histomorph ometric evaluation of extraction sockets treated with an autologous bone marro w graft... Barone A, Aldini NN, Fini M, Giardino R, Calvo Guirado
5) After GBR, the membrane was removed i n i ni ti al ti me, the usage of nonabsorbabl e membrane and autogenous bone resul ted i n the mostfavorabl e bone formati
success rates of dental implants placed at the time of or after alveolar ridge augmentation with an autogenous mandibular bone graft and titanium mesh: a 3-to
In 4-week group, the group filled with bone graft with decortication revealed larger new bone formation area than shown in the group that had a defect area
Approved clinical use of bone marrow stem cells for myocardial infarction treatment... Cardiac
The result of using PLGA nanofiber membrane with bone graft material showed that the PLGA nanofiber membrane in the experimental group of 2 weeks were ten times more new
of mineralized cancellous bone allograft(Puros) and anorganic bovine bone matrix(Bio-oss) for sinus augmentation: Histomorphometry at 26 to 32 weeks after
The defect area was filled with new-bone formation around the graft material hydroxy-apatite (open stars) at the periphery and chronic inflammation with