Skeletal Muscle Dysfunction in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
전체 글
수치
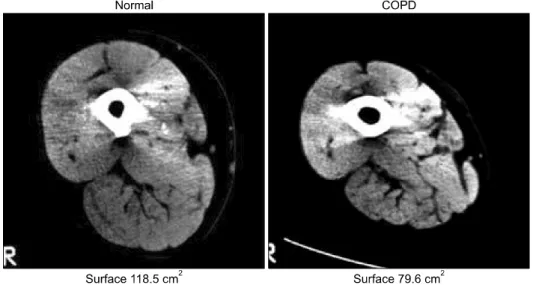
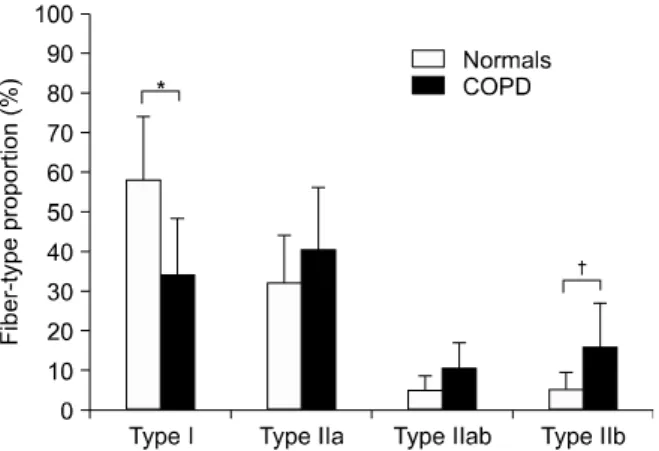
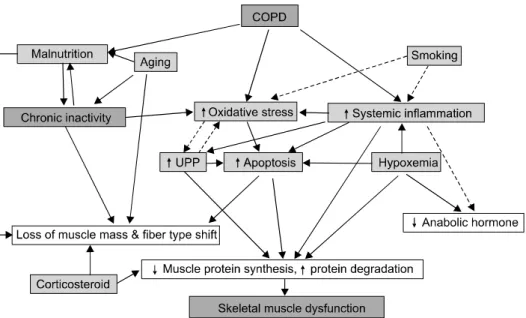

관련 문서
Our study investigated the preventive effects of resist- ance exercise on body weight, gonadal fat mass, and glucose tolerance and determined whether the ben- eficial
Also, peak to end time of T-wave, T-wave width/depth in patients with apical hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is more longer and greater than in those with stress-induced cardiomyopathy
In the change of physical strength, The exercise group showed statistically significant differences in muscle strength(right), muscle strength(left),
First, the rhythmic gymnastics exercise program improves the skeletal muscle mass of adult women in office workers and reduces body fat percentage,
Cephalometric comparisons of craniofacial and upper airway structure by skeletal subtype and gender in patients with obstructive sleep apnea.. Nasal
In conclusion, Pilates chair exercise is a positive factor in improving skeletal muscle mass among menopausal women's body composition and lower muscles EMG
Baseline characteristics of genotype 1b chronic hepatitis C patients who treated with daclatasvir and asunaprevir (n=231)... Characteristics of genotype 1b
In the health fitness category of the adult women who underwent instrument pilates exercise, they were statistically significant in muscle strength,
