109
임상에서 분리한 Streptococcus pneumoniae에서 Levofloxacin 내성유전자의 비교 연구
최재민1·박선희1·윤지아1·한양금2·이인수1†
1한남대학교 생명공학과, 2대전보건대학교 치위생(학)과
Comparative Analysis of Levofloxacin Resistant Genes in Clinically Isolated Streptococcus pneumoniae
Jae Min Choi
1, Seon Hui Park
1, Ji A Yoon
1, Yang Keum Han
2and In Soo Lee
1†1Department of Biotechnology, Hannam University Daejeon, 305-811, Korea
2Department of Dental Hygiene, Daejeon Health Science College Daejeon, 300-711, Korea
Abstract
One hundred seventy four Streptococcus pneumoniae clinical isolates were categorized depending on the types of specimens, the age and the gender, respectively. All isolates were analyzed the characteristics of the multi-drug resistance including levofloxacin antibiotics. In the results of analysis depending on the type of samples, it had been confirmed that sputum was the main source of pneumonia infection because 156 of 174 strains (89.7%) were isolated in sputum samples. The opportunity for isolating the S. pneumoniae that had tolerance to levofloxacin was increased in over 51 age patients group compared with other age and male group. Eight strains of isolates were evaluated higher resistant to levofloxacin, and those also showed multi-drug resistant including penicillin, tetracycline, erythromycin, clindamycin and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole. In the results of sequence analysis of quinolone resistance determining region in SP32 (MIC 64µg/mL) and SP96 (MIC 8 µg/mL) which were levofloxacin resistant strains, an amino acid substitutions were found Ser-81→Phe in both GyrA of SP32 and SP96, and Ser-11→Gly in only SP96. A Ser-79→Phe substitution of ParC was found in both.Key words
gyrA, Levofloxacin, parC, Streptococcus pneumoniae서 론
Streptococcus pneumoniae 는 폐렴을 발병시키는 가장 흔한 세균이며, 성인을 비롯하여 영유아와 소아의 세균성 수막염, 중이염, 부비동염의 주요 원인균이며
1), 65 세 이상 의 노인에게서 발병되는 폐렴의 경우에는 사망률이 비교 적 높은데, 그 이유는 고령으로 인한 면역기능의 저하, 인 후부 반사기능 저하, 기관지 점액 섬모운동의 기능저하, 심폐기능부전 등이 부가적으로 관여하기 때문이다
2,3). 또 한 S. pneumoniae 감염증 중에서 균혈증이나 늑막염을 동반하는 침습성 폐렴과 뇌수막염 등은 당뇨병과 악성종 양 환자들에서 많이 보고되고 있다
4). 지역사회획득 폐렴
은 연간 인구 10,000명당 12~90명의 빈도로 발생하고, 사 망률은 약 5% 정도이며
5), 치료법은 폐렴의 중증도, 동반 질환, 원인균 및 원인균의 항생제 내성에 따라 다르다. S.
pneumoniae 감염의 치료에 페니실린이 대표적인 항생제 로 사용되어 왔으나, 1967년부터 페니실린 내성 Strepto- coccus 가 분리된 후, 1990년대까지 급속도록 그 내성도가 증가하였고, 최근에 다제내성 S. pneumoniae도 증가하고 있다
6). 잇몸과 치아에서 분리되는 S. gordonii는 S. pneu- moniae 와 구강에서 공생적 관계로 생존하는데, 특히 pen- icillin 내성에 관여하는 High-molecular-weight (HMW) penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) 유전자는 두 균주간 상 동성이 존재하는 것으로 보고되었다
7). 이와 같이 내성 세 균의 출현과 확산으로 미생물 감염성 질환의 치료가 점점 어려워지고 있으며, 또한 최근 개발된 fluoroquinolone계 약제의 광범위한 사용으로 인하여 S. pneumoniae를 비롯 한 Gram negative bacillus에서 항생제 내성세균 출현 빈 도가 증가하고 있다
8,9). DNA gyrase 와 topoisomerase IV 의 작용을 저해하는 fluoroquinolone에 대한 세균의 방어
†
Corresponding author Tel: 042-629-8772 Fax: 042-629-8751 E-mail: inslee@hnu.kr
Citation: 최재민 등: 임상에서 분리한 Streptococcus pneumoniae에 서 Levofloxacin 내성유전자의 비교 연구. 치위생과학회지 12(2):
109-113, 2012.
ISSN: 1598-4478(Print), 2233-7679(Online)
기전은 gyrAB와 parCE 유전자 돌연변이 또는 efflux 펌 프의 작용이라고 알려져 있다
10). 실험실이나 임상에서 분 리된 항생제 내성 세균의 경우 gyrA와 parC 유전자 각각 의 특정 영역에서 점 돌연변이가 발생되어 내성이 발생된 다고 보고되었으며
11), 이 영역을 quinolone 내성 결정 부 위(Quinolone Resistance Determining Region, QRDR)로 명명하였다
12). 특히 구강 내 Streptococci 세균의 gyrase와 topoisomerase 유전자의 속간 형질전환이 보고되어
13), S.
pneumoniae 의 항생제 내성 유전자는 치아우식증 및 치주 질환 유발 viridans streptococci로 확산될 수 있는 위험성 이 있으므로
14)구강을 비롯한 상기도부 상주 세균에 대한 항생제 내성도 조사는 중요한 의미를 갖는다. 국내에서 발병되는 폐렴의 경우 항생제 내성 여부와 관계없이 경험 적으로 치료하는 경우가 많아 내성의 범위와 임상 경과 간의 추이를 살펴보는데 어려움이 있다. 즉, 지역사회획득 폐렴의 경험적 치료와 적절한 항생제를 선택하기 위하여 각 지역별 원인균 분포 및 항생제 내성 현황 등의 역학 자료가 요구되며, 이의 확보를 위한 연구의 필요성이 대 두되고 있다
15).
본 연구에서는 2008년 10월에서 2010년 5월까지 임상 에서 분리된 S. pneumoniae 균주 174개를 대상으로 levo- floxacin 에 대한 검체별, 연령별, 성별 항생제 감수성 및 다제내성 조사를 통하여 세균의 약제 내성도 및 다제내성 도 범위를 평가하며, 또한 분자유전학적 검사를 통하여 항생제 기전을 확인하고자 하였다.
연구재료 및 방법
1. 실험 균주 및 사용배지
본 연구에서 사용된 균주는 2008년 10월부터 2010년 5 월까지 구강의 점막 및 객담, 혈액, 농, 각종 도말 및 체액 검체 그리고 중추신경계로부터 분리된 174개의 S. pneu- moniae 이며, 세균의 동정은 Optochin Sensitivity Test와 Bile Solubility Test 를 통해 진행되었다
16,17). 항생제 감수성 조사의 정도관리는 S. pneumoniae ATCC49619를 사용하 였다. 세균의 증균에는 Mueller-Hinton 배지를 사용하였고, 필요에 따라 5% defibrinated sheep blood가 첨가하였다.
배양은 5% CO2 및 35
oC 환경 조건에서 진행되었다.
2. 항생제 감수성 검사
실험균주의 항생제 감수성 조사는 디스크 확산법
18)을 사용하였고, 항생제 최소억제농도(mininmal inhibitory concentration) 는 MicroScan (Siemens Healthcare Diag- nostics, USA) MICroSTREP plus antimicrobial panel 방 법
19)과 액체배지희석법을
20)사용하였다. 결과는 CLSI 기 준에 따라 감수, 중간, 내성으로 판정하였다
21). 항생제 내 성도 조사는 penicillin, cefotaxime, vancomycin, clinda- mycin, erythromycin, levofloxacin 및 trimethoprim/sul-
famethoxazole (Sigma, St. Louis, USA) 등의 항생제를 대상으로 시행하였다.
3. 항생제 내성 유전자 분석 1) PCR 및 DNA 클로닝
유전자 증폭을 위한 주형 DNA는 해당 균주를 하룻밤 생장시킨 세균의 배양액과 Genomic DNA 분리 Kit (Promega, USA) 을 사용하여 준비하였다. gyrA와 parC 유전자 증폭을 위한 primer로서 5’-TTC TCT ACG GAA TGA ATG-3’ 와 3’-GAT ATC ACG AAG CAT TTC-5’, 5’-TGG GTT GAA GCC GGT TCA-3’ 와 3’-CAA GAC CGT TGG TTC TTT C-5’ 를 각각 사용하였다. PCR 반 응 시약은 DNA Polymerase (Top-Tag
TM, CoreBio sys- tem, Korea), dNTP (CoreBio system, Korea) 및 Ther- mocycler (Dice
TM, Takara Bio, Japan) 를 사용하였다. 증 폭된 DNA 확인은 0.8% 아가로스 전기영동을 통하여 수 행되었으며, DNA 추출과 정제는 젤 추출 Kit (MGTM SVMacrogen, Korea) 를 사용하였고, 추출된 DNA는 pGEM T-easy vector (Promega, USA) 에 결합하여 E.coli DH5a 에 형질전환 시켰다
22). 재조합 plasmid DNA는 plasmid Mini Prep Kit (Dyne Bioinc Ltd. Korea) 를 사용 하여 분리하였다.
4. 염기서열 분석
gyrA 및 parC 유전자의 염기서열 결정은 (주)마크로젠 에 의뢰하였고, 분석은 NCBI (National Center for Bio- technology Information) 의 BLAST (Basic Local Align- ment Search Tool: http://ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/BLAST) 프로 그램 상에서 S. pneumoniae R6 염기서열을 대상으로 비 교 분석하였다.
결 과
1. 검체별 S. pneumoniae 분리빈도
가장 높은 S. pneumoniae 분리빈도는 총 174 균주의 89.7% 인 156 균주가 분리된 구강 내 객담 검체로 확인되
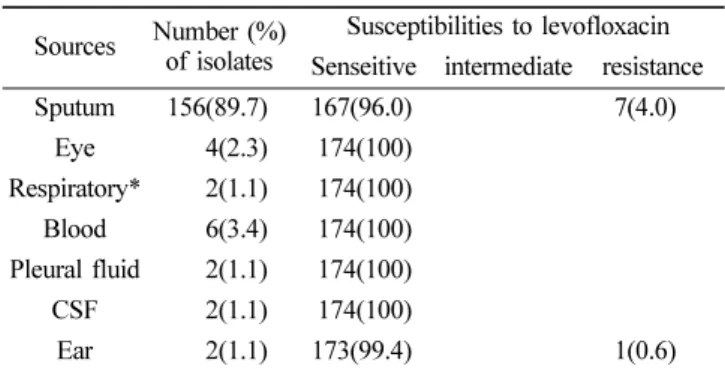
Table 1. The distribution of S. pneumoniae isolates and their susceptibility to levofloxacin antibiotics
Sources Number (%) of isolates
Susceptibilities to levofloxacin Senseitive intermediate resistance
Sputum 156(89.7) 167(96.0) 7(4.0)
Eye 4(2.3) 174(100) Respiratory* 2(1.1) 174(100) Blood 6(3.4) 174(100) Pleural fluid 2(1.1) 174(100) CSF 2(1.1) 174(100)
Ear 2(1.1) 173(99.4) 1(0.6)
*Upper respiratory; CSF, Cerebrospinal Fluid
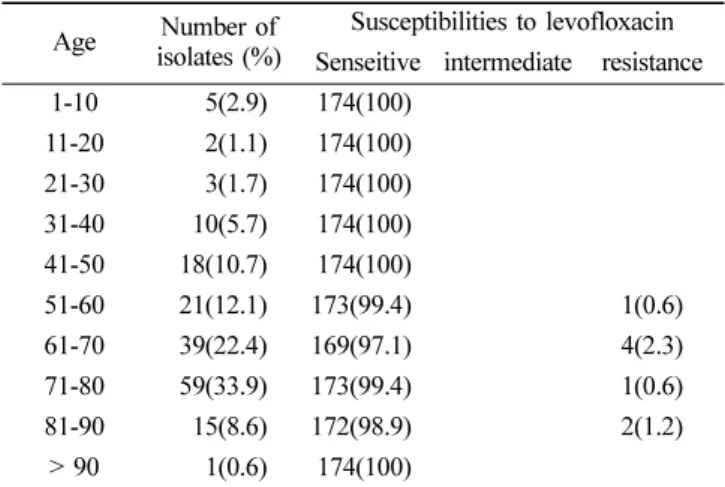
었으며, 그 중에서 levofloxaicn 내성세균은 객담과 귀에 서 각각 분리되었다(Table 1). 연령별 분리 빈도는 나이에 따라서 증가하는 경향을 나타내어, 61세 이상의 고령에서 상대적으로 검출률이 높았으나, 81세 이상부터는 오히려 감소하는 경향을 보여주었다. Levofloxacin 내성도는 51~90 세 고령 환자에게서 가장 높게 나타났다(Table 2).
성별 기준으로 S. pneumoniae의 검출 빈도는 남성이 여 성에 비하여 1.7배 높게 조사되었다(Table 3).
2. 분리된 S. pneumoniae 항생제 감수성 조사
분리된 174 균주의 S. pneumoniae를 대상으로 항생제 내성도를 조사한 결과, clindamycin, erythromycin 및 TMP/SMX 등의 macrolide계 항생제 내성세균의 분리도 가 penicillin과 비교하여 약 3배 이상 높게 조사되었다 (Table 4).
전체 분리균주의 약 4.6%만이 levofloxacin 내성도를 나타내었고, 특히 vancomycin 내성 균주는 분리되지 않 았다. 총 174 균주의 S. pneumoniae 중에서 항생제 내성 을 갖는 164 균주를 대상으로 약제 중복 내성도를 조사한 결과, 서로 다른 3 종류 항생제에 대한 내성률은 9.7%, 4 종류 항생제에 대한 내성률은 23.2%, 5 종류 항생제에 대 한 내성률은 41.5% 그리고 실험에 사용된 모든 종류의 항생제 내성률은 4.9%로 각각 분석되었다. 특히 levof- loxacin 내성세균들은 시험한 모든 항생제에 내성을 소유 하는 것으로 확인되었다(Table 5).
Table 2. Age distribution and levofloxacin susceptibilities of S. pneumoniae isolates according to the age of patients
Age Number of isolates (%)
Susceptibilities to levofloxacin Senseitive intermediate resistance 1-10 5(2.9) 174(100)
11-20 2(1.1) 174(100) 21-30 3(1.7) 174(100) 31-40 10(5.7) 174(100) 41-50 18(10.7) 174(100)
51-60 21(12.1) 173(99.4) 1(0.6)
61-70 39(22.4) 169(97.1) 4(2.3)
71-80 59(33.9) 173(99.4) 1(0.6)
81-90 15(8.6) 172(98.9) 2(1.2)
> 90 1(0.6) 174(100)
Table 3. Gender distribution and levofloxacin susceptibilities of S. pneumoniae isolates
Sex Number (%) of isolates
Susceptibilities to levofloxacin Senseitive intermediate resistance
Male 110(63.2) 105(95.5) 5(4.5)
Female 64(36.8) 61(95.3) 3(4.7)
Table 4. Susceptibility to various antibiotics in 174 isolates of S. pneumoniae
Antibiotics Susceptibilities
Susceptible Intermediate Resistant Clindamycin 69(39.7)* 2(1.5) 103(59.2) Erythromycin 40(23.0) 2(1.2) 132(75.9) Penicillin 38(21.9) 106(61.0) 30(17.3) Tetracycline 59(34.0) 24(13.8) 91(52.3)
TMP/SMX 36(20.7) 20(11.5) 118(67.8)
Levofloxacin 165(94.9) 8(4.6)
Vancomycin 174(100)
TMP/SMX, trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazoe; *, Number (%) of isolates
Table 5. Distribution of S. pneumoniae isolates according to antibiograms
Antibiotics No. of resistant drug
No.(%) of isolates
aPEN 1 8(4.9)
C 1 1(0.6)
TE 1 1(0.6)
SXT 1 4(2.4)
PEN+SXT 2 10(6.1)
C+E 2 4(2.4)
TE+SXT 2 6(3.7)
TE+ERY+SXT 3
b3(1.8)
E+P+SXT 3 1(0.6)
C+E+T 3 1(0.6)
C+E+P 3 7(4.3)
PEN+TE+ERY 3 4(2.4)
C+E+T+SXT 4
b5(3.1)
C+E+P+SXT 4 10(6.1)
PEN+TE+ERY+SXT 4 22(13.4)
PEN+TE+ERY+C 4 1(0.6)
PEN+TE+ERY+C+SXT 5 68(41.5)
PEN+TE+ERY+C+SXT+LV 6 8(4.9)
a
No.(%) of 164 strains showing resistance of 174 strains
b
Multidrug-Resistance; PEN, penicillin; TE, tetracycle; ERY, erytromycin;
C, clinda-mycin; SXT, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazoe; LV, levofloxacin Table 6. Comparison of susceptibility based on the determinating methods for evaluation in eight 8 levofloxacin resistance S. pneumoniae
Bacterial strains
Disk diffusion method (mm)
Microscan MIC ( µg/mL)
Broth dilution method MIC
( µg/mL) S I R
( ≥17 14-16 ≤13) S I R (0.25 - 4 )
S I R
( ≤2 4 ≥8)
SP4 R >4 16
SP12 R >4 8
SP16 R >4 8
SP32 R >4 64
SP35 R >4 32
SP96 R >4 8
SP109 R >4 32
SP176 R >4 32
S; Susceptible, I; Intermediate, R; Resistant
디스크법과 MicroScan 방법을 사용하였을 경우, levof- loxacin 에 가장 높은 내성도를 나타낸 SP32 (MIC 64 µg/
mL) 균주는 상대적으로 내성도가 3배 낮은 SP12, SP16 및 SP32와 동일한 MIC 값으로 평가되었다(Table 6).
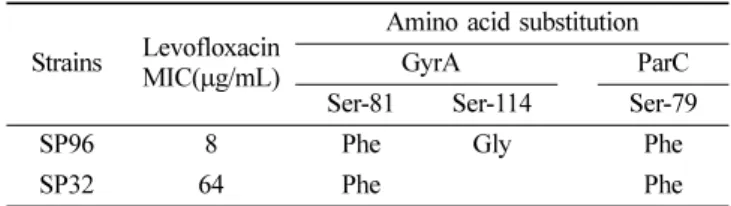
3. gyrA와 parC 유전자의 염기서열 분석
Levofloxacin 내성 S. pneumoniae는 SP32와 SP96을 대 상으로 QRDR의 염기서열 분석 및 돌연변이 유무를 조사 한 결과, SP96 균주의 ParC에서 79번 아미노산인 serine 이 phenylalanine (Ser-79
→Phe) 으로, GyrA에서 81번과 114 번 아미노산 serine이 각각 phenylalanine (Ser-81
→Phe) 과 glycine (Ser-114
→Gly) 으로 치환되었고, SP32 균 주에서는 ParC의 79번 아미노산과 GyrA의 81번 아미노 산인 serine이 각각 phenylalanine으로 (Ser-79
→Phe, Ser- 81
→Phe) 변이된 것이 확인되었다(Table 7).
고 찰
S. pneumoniae 감염성 호흡기 질환의 치료에서 문제점 으로 대두되는 것은 환자의 연령에 관계없이 원인균의 항 생제 내성도가 계속 증가된다는 것이며,
20)특히 최근 levofloxacin 에 대한 내성도가 증가하는 양상을 보여 새로 운 fluoroquinolon계 항생제 개발의 필요성이 대두되고 있다.
21)대전 지역사회에서 항생제 내성 S. pneumoniae의 출현 빈도 및 내성도를 조사하기 위하여, 2008년 10월부 터 2010년 5월까지 병원에서 분리된 174개의 S. pneumo- niae 를 검체별, 연령별, 성별에 따른 항생제 내성빈도와 내성기전을 분석하였다. S. pneumoniae가 가장 많이 분리 된 시료는 구강의 객담으로 조사되었고, 폐렴이 호흡기 질환임을 감안할 때 이와 같은 결과는 이해될 수 있으며, 또한 고령 환자의 경우에 분리 빈도 및 항생제 내성도가 증가하였는데, 이것은 노령으로 인한 면역력 감퇴 및 이 로 인한 항생제 의존도가 높았기 때문에 상대적으로 항생 제 내성 균주의 출현이 많았을 것으로 추정된다. 임상에 서 분리된 미생물의 항생제 내성도 조사는 자동화된 MicroScan MIC, 비교적 조사가 용이한 디스크 확산법 그 리고 전통적 최소억제농도법을 각각 사용한 결과, 분리된 균주의 항생제 내성도는 최소억제농도법을 사용한 결과 에서 정확하게 조사되었으며, 임상결과를 토대로 환자에 적합한 약제 처방에서 이 부분은 충분히 고려되어야할 사
안으로 진단해 본다. 표 5에서 보는 바와 같이, 본 연구에 서 분리된 8개의 levofloxacin 내성세균 모두는 6종류의 서로 다른 항생제에 대한 다제내성을 나타내어 S. pneu- moniae 에서 항생제 교차내성도 현상이 확인되었다. 현재 levofloxacin 에 대한 고도내성은 parC와 gyrA 유전자 돌 연변이 현상으로 이해되어, 세계적으로 S. pneumoniae의 DNA topology 에 관여하는 gyrase 및 topoisomerase 효소 의 아미노산 서열분석 연구가 활발하게 진행되고 있다.
최근 Optochin Test에서 전형적인 Streptococci 결과와 상 이하게 분석되는 구강의 viridans streptococci인 S. mitis 와 S. oralis 균주의 항생제 내성은 S. pneumoniae 변이유 전자의 interspecies transfer의 결과일 것이라는 가능성이 보고된 이후,
22,24)해부학적으로 상호 연계된 구강 및 상기 도에 서식하는 세균들의 약제 교차 내성도는 병원성 구강 미생물 감염의 치료와 밀접한 관계성을 갖는다고 할 수 있다. 본 연구에서도 SP96과 SP32를 대상으로 아미노산 서열을 분석한 결과 Janoir 등(1996)의 보고와 유사하게 QRDR 지역의 점 돌연변이를 관찰할 수 있었으며, 이로 인하여 분리된 S. pneumoniae는 levofloxacin에 대하여 내성을 갖는 것으로 확인되었다. 향후 구강상피 또는 객 담 등에서 분리된 fluoroquinolone 내성 S. pneumoniae의 gyrase 및 topoisomerase의 아미노산 서열 변이 현상을 S.
mutans 와 S. salivarius 등과 비교하는 후속 연구를 통하 여 Streptococci 속 세균의 항생제 내성 확산에 대한 이해 의 폭을 넓힐 수 있을 것이다.
요 약
임상에서 분리한 총 174 균주의 S. pneumoniae를 대상 으로 검체별, 연령별, 성별 분리빈도 및 levofloxacin의 내 성도를 조사하였으며, 항생제 감수성 검사를 통해 다제내 성도를 확인하였다. S. pneumoniae가 가장 많이 분리된 검체는 객담으로서 총 174 균주의 89.7%인 156 균주가 분리되었다. 특히 남성과 51세의 고령환자에서 분리빈도 가 높았으며, 분리된 levofloxacin 내성 8 균주 모두는 penicillin, tetracycle, erytromycin, clindamycin 및 trime- thoprim-sulfamethoxazoe 대한 다제내성도 함께 소유하고 있는 것으로 확인되었다. 분리된 levofloxacin 내성균주 SP32 (MIC 64 µg/mL)와 SP96 (MIC 8 µg/mL)의 QRDR 염기서열을 분석한 결과, SP32와 SP96 균주의 GyrA에서 Ser-81
→Phe 로, SP96에서 Ser-11
→Gly 으로 아미노산 치 환이 각각 확인되었고, ParC에서는 두 균주 모두 Ser- 79
→Phe 으로 치환된 돌연변이가 확인되었다.
감사의 글
이 논문은 2007년도 한남대학교 학술연구조성비 지원 에 의하여 연구되었음.
Table 7. The characteristics of point mutations of GyrA and ParC in levofloxacine resistant S. pneumoniae
Strains Levofloxacin MIC( µg/mL)
Amino acid substitution
GyrA ParC
Ser-81 Ser-114 Ser-79
SP96 8 Phe Gly Phe
SP32 64 Phe Phe
참고문헌