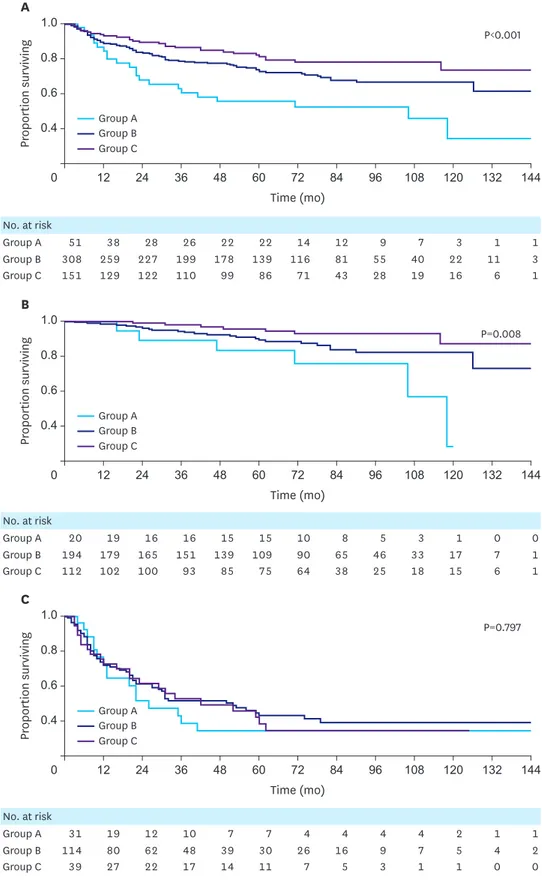
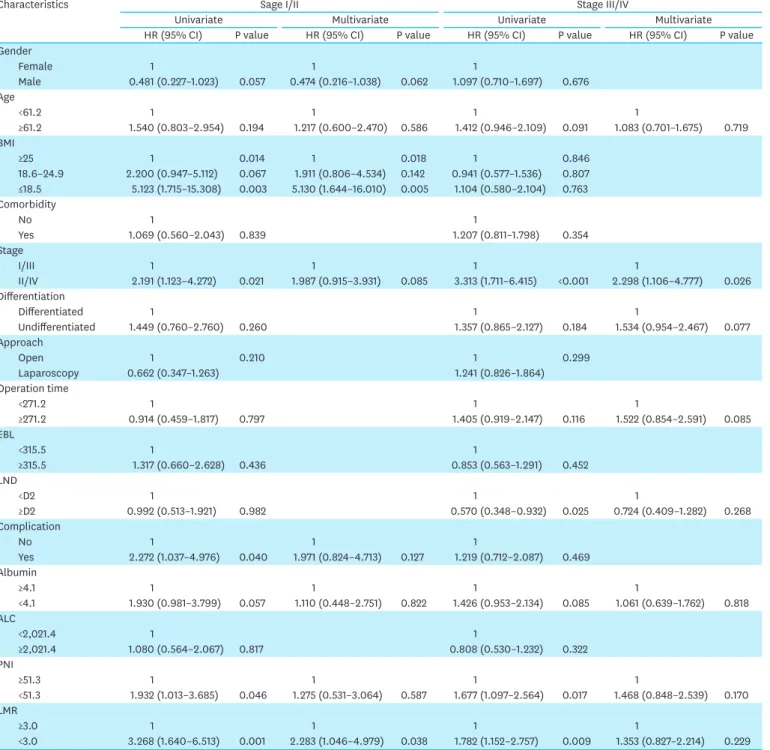
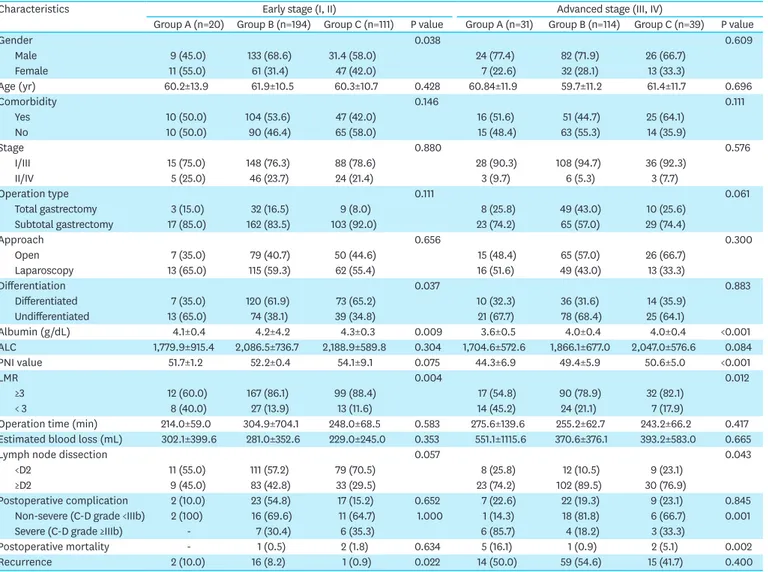
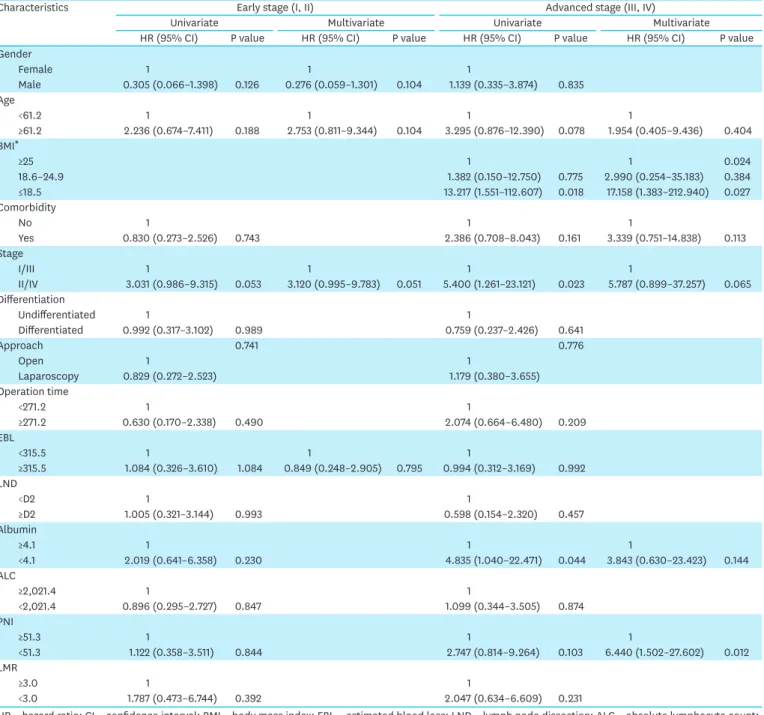
The Impact of Preoperative Low Body Mass Index on Postoperative Complications and Long-term Survival Outcomes in Gastric Cancer Patients
전체 글
수치


관련 문서
The aim of this study was not only to compare the differences of ego-resilience between students with high experience and students with low experience in
In the present study, consistent to that report, up-regulation of VEGF mRNA was observed in the colon cancer cell with the acquired resistance to 5-FU and this
Higher open conversion rate and prolonged postoperative hospital stay in LATE group were not caused by the delayed operation in this study it seems to be caused by that
One notable and important finding of the present study was that the physical function of frail older adults at baseline, with number of medications, was
In the subgroup of patients who reached ASDAS-ID 1 year after TNFi treatment ( n = 327), ASDAS-ID was observed in 66.1% of the subsequent intervals, and only the
Although visceral fat adiposity has known to be associated with clinical, pathologic, and oncologic outcomes in patients with colorectal cancer (CRC), the
In conclusion, there was no difference between the preoperative culture and postoperative culture of the oral cavity in patients undergoing TOET, and there were
For example, short-term exposure to ozone has been associated with a higher risk of pneumonia in OBJECTIVES: The aim of this study was to estimate the age-specific effects