Acute Cerebral Infarction Following Intravenous Glycoprotein IIb/IIIa Inhibitor for Acute Myocardial Infarction
전체 글
수치
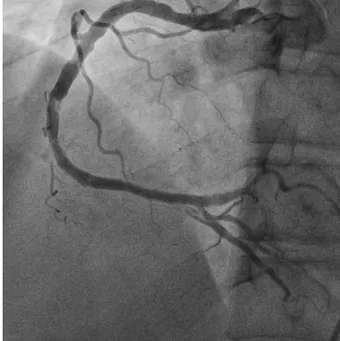
관련 문서
Prevalence of sleep-disordered breathing in acute ischemic stroke as determined using a portable sleep apnea monitoring device in Korean subjects.. Obstructive
Haemorragic fever with renal syndrome (HFRS) caused by Hantanvirus has been one of the principal acute febrile disease in Korea. Hantaviruses are carried by numerous
Therefore, cTnT is a recommended biomarker for use in the detection of myocardial infarction (MI) and in acute coronary syndromes.[8] Indeed, several authors
The positive change pattern of CK-MB according to time on acute myocardiac infarction patient.. The positive change pattern of troponin-T according to time on
The benefits and harms of intravenous thrombolysis with recombinant tissue plasminogen activator within 6 h of acute ischaemic stroke (the third
Frequency and clinical significance of the expression of the multidrug resistance proteins MDR1/P-glycoprotein, MRP1, and LRP in acute myeloid leukemia: a
Approved clinical use of bone marrow stem cells for myocardial infarction treatment... Cardiac
(Background) Gallbladder wall thickening(GWT) and gallbladder contraction are often observed in patients with acute hepatitis.. The incidence of acute hepatitis A