Functions of hepatic non-parenchymal cells in alcoholic liver disease
전체 글
수치
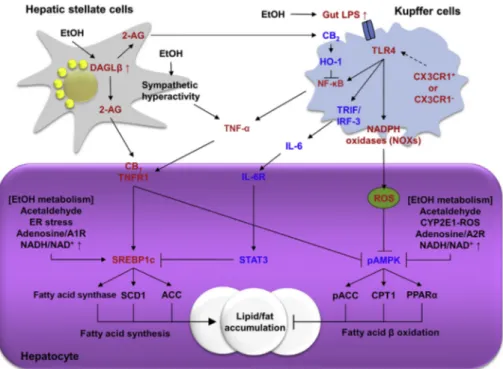

관련 문서
Convection dominant in flow channels Diffusion dominant in electrode...
– Embryonic stem cell : Pluripotent cells that can give rise to all tissue types. – Adult stem cell : Multipotent cells
• Generation of different specialized kinds of cells from zygote (fertilized egg) or other precursor cells.. – Generate blood cells, muscle
Note that the number of adjacent cells is the same as the number of input variables since it is equal to the number of bits... If we don’t use DC terms, the logic function f
In this work, processing techniques for producing microcellular silicon carbide with cell densities greater than 10 9 cells/㎤ and cells smaller than 30㎛ have
whether NME1-depleted cells impairs the Rad51 foci formation in response
Regulatory T (Treg) cells are a subset of CD4+ T cells whose function is to suppress immune responses and maintain self-tolerance, therefore they have a central
Factors produced by cells at a distance from the target cells and carried through the blood or. lymphatic fluid to