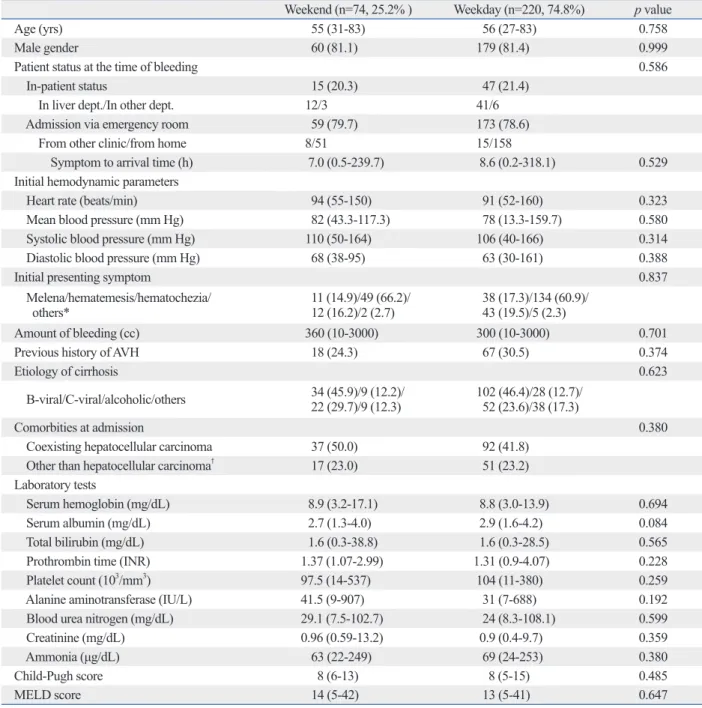
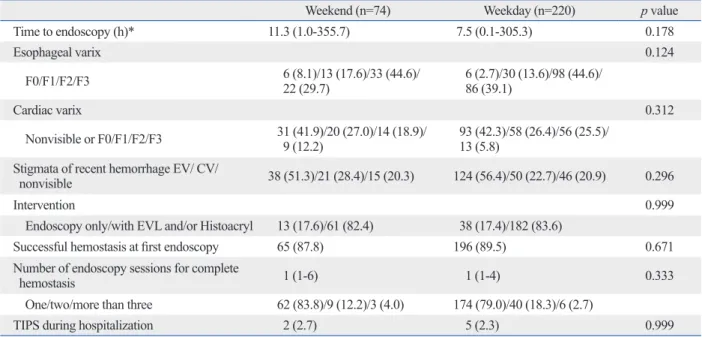
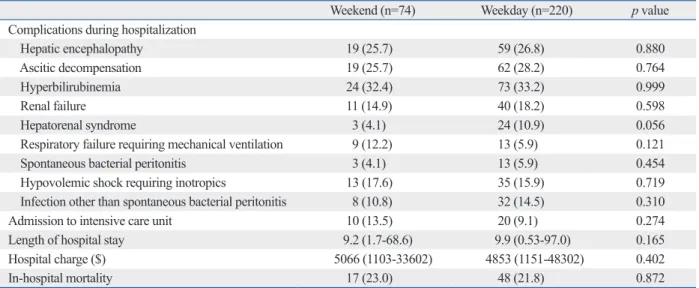
Acute variceal hemorrhage in patients with liver cirrhosis: weekend versus weekday admissions
전체 글
수치

관련 문서
Lee, H.S., et al., Therapeutic efficacy of transcatheter arterial chemoembolization as compared with hepatic resection in hepatocellular carcinoma patients with compensated
Long-term outcome after an early invasive versus selective invasive treatment strategy in patients with non.ST-elevation acute coronary syndrome and elevated
Through this result, it was confirmed that brittle fracture did not occur in high Mn steel and ductile fracture occurred in spite of cryogenic
(2002) Blinded, randomized, multicenter study to evaluate single administration pegfilgrastim once per cycle versus daily filgrastim as an adjunct to chemotherapy in
The hospital anxiety and depression scale (HADS) and the 9-item patient health questionnaire (PHQ-9) as screening instruments for depression in patients with cancer.. Age
• Low dose aspirin is recommended for all patients with ET except high risk for bleeding. • Cytoreductive therapy is recommended for high- risk ET patients with
–The AABB suggests adhering to a restrictive strategy in hospitalized patients with preexisting cardiovascular disease and considering transfusion for patients with symptoms or
In a prospective 2-year study by Kaandorp et al with 154 patients (adults and children), 21% of cases resulted in poor patient outcome (death or severe functional deterioration),